Male Reproductive System: I Roger Bick, PhD, MMEd
Reading: Gartner and Hiatt, 379-386; Gartner, Hiatt, Strum, pp311-317, 323-325 Learning Objectives: From the material presented in this lecture and in the laboratory session, you should be able to: Describe the investment tunics of the testes. Differentiate the morphology and function of the Sertoli cells and spermatogenic (sperm) cells. Describe the process of spermiogenesis Describe the head and tail regions of the spermatozoan. Understand the relationship among the hypothalamus, pituitary, and interstitial cells of the testes. Key Words: testes, seminiferous tubules, Sertoli cell, spermatogenesis, spermatocytes, spermiogenesis, spermatozoan, and Leydig cell.
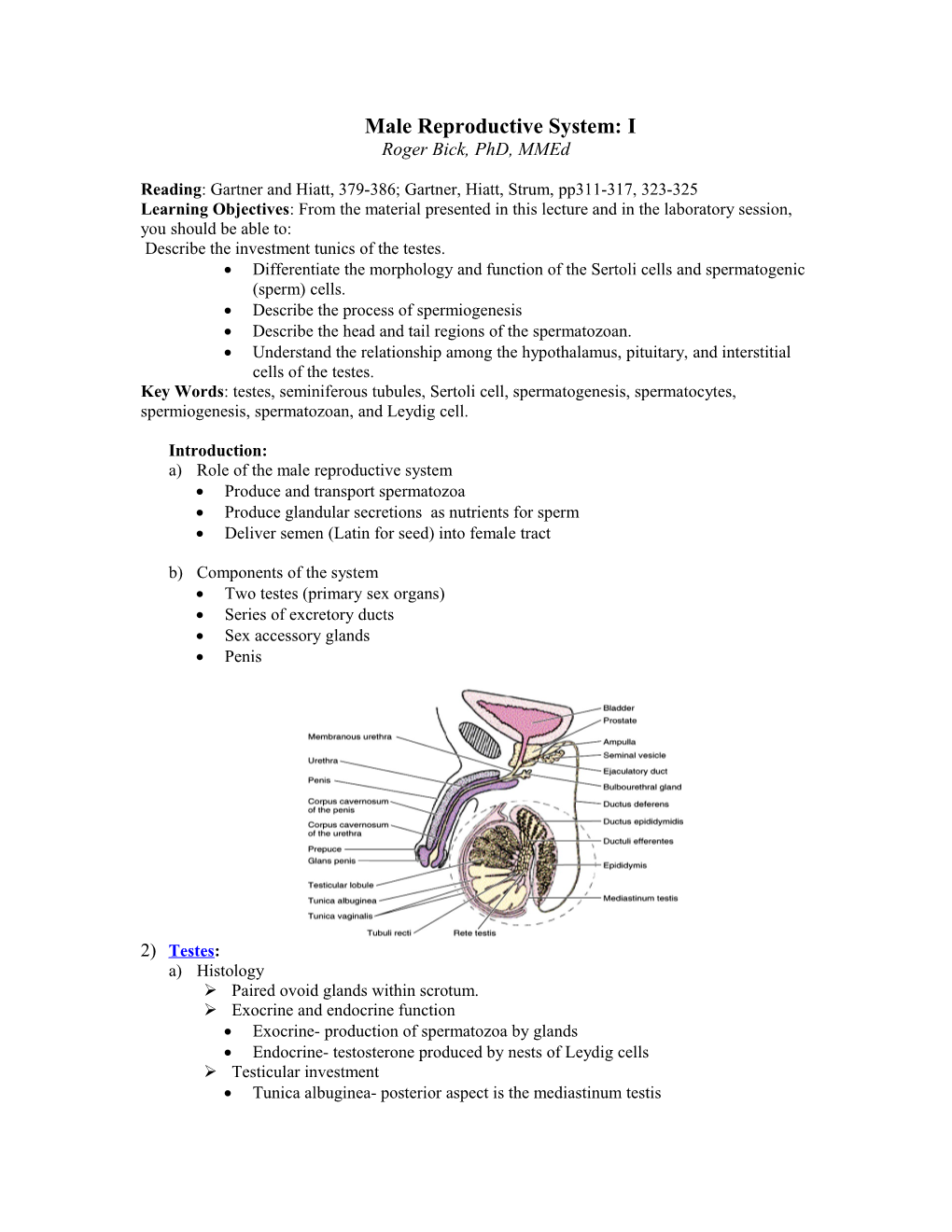
Introduction: a) Role of the male reproductive system Produce and transport spermatozoa Produce glandular secretions as nutrients for sperm Deliver semen (Latin for seed) into female tract
b) Components of the system Two testes (primary sex organs) Series of excretory ducts Sex accessory glands Penis
2) Testes: a) Histology Paired ovoid glands within scrotum. Exocrine and endocrine function Exocrine- production of spermatozoa by glands Endocrine- testosterone produced by nests of Leydig cells Testicular investment Tunica albuginea- posterior aspect is the mediastinum testis Tunica vaginalis- two layers: inner visceral, outer parietal
3) Seminiferous Tubules: a) Highly coiled and branched exocrine glands b) Two major cell types Sertoli (sustentacular) Cells Tall columnar epithelial cells with large oval nucleus and prominent nucleolus Connected together by tight junctions dividing tubule into basal and luminal compartments (Blood-Testis Barrier) Supply mechanical and nutrient support to developing germ cells Phagocytize residual germ cell cytoplasm Regulate release of spermatozoa Secrete androgen-binding proteins (ABP) under the influence of FSH from anterior pituitary
Spermatogenic (germ) cells Lie in lateral recesses of Sertoli cells Mature by series of steps which include: Mitosis, Meiosis, and Metamorphosis
4) Spermatogenesis : formation of spermatozoa from spermatogonia a) Spermatogonium, (Type A and Type B), small cells at basal lamina Type A- Divide by mitosis to maintain supply of stem cells Type B- progenitor cells, mitotic steps and differentiate…..
b) Primary spermatocyte Largest and most abundant Have full complement of DNA (46 diploid chromosomes) also called 4N Enter first meiotic division to form….
c) Secondary spermatocytes Smaller, no generally visualized Half number chromosomes (23 diploid chromosomes) or 2N Rapidly enter second meiotic division to form
d) Spermatids Small cells toward center of tubule with condensed chromatin Have 23 haploid chromosome or 1N (Egg has other half) Undergo metamorphosis to form spermatozoa
5) Spermiogenesis- transition from spermatid to spermatozoa through 3 stages a) Golgi phase- proacrosomal granules b) Acrosome phase- acrosome cap and formation flagellum c) Maturation phase- residual cytoplasm shed and sperm released into tubule lumen with Sertoli cell secretions
6) Structure of mature spermatozoa a) Head- ovoid and flattened, 5 um Acrosomal cap- contain enzymes for egg penetration Nucleus- 1N DNA b) Neck- 2 um, containing paired centrioles c) Flagellum- 53 um Middle piece- 5 um Core of 9 doublet microtubules surrounding central pair of singlets 9 longitudinal dense fibers around core outer rim of mitochondria Principle piece- 43 um NO mitochondria Outer fibrous sheath End piece- 5 um NO sheath Only has core of microtubules (also called axoneme)
d) Influencing factors to Spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis Temperature- 35 C (body core is 37 C) Venous plexus -AKA pampiniform plexus- creates heat-exchange system Sweat evaporation from scrotum e) FSH- acts on Sertoli cells which secrete Androgen-binding protein (binds testosterone) f) LH- acts on interstitial cells (Leydig cells) to secrete testosterone 7) Interstitial (Leydig) cells a) Round to polygonal with central nucleus and “foamy” eosinophilic cytoplasm b) Steroid producer (testosterone) under influence of LH
Male Reproductive System Laboratory I Slide #84, human testis Identify: Tunica albuginea, seminiferous tubules, sertoli cells, spermatogonia, primary spermatocytes, spermatids, spermatozoa, Leydig cells Q: Are the seminiferous tubules exocrine or endocrine? Q: What hormone acts on the Leydig cells? Slide # 85, Immature Monkey Testis Compare this slide to the previous. Note seminiferous tubules have only Sertoli cells and spermatogonia. Q: Are there any Leydig cells? Why not?