Alexandra Draughan February 1, 2006 DEVELOPMENTAL DIFFERENCES IN SECOND LANGUAGE LEARNERS
PRE- EMERGENT MIDDLE HIGH LITERATE LITERATE GRADES SCHOOL (grades K-2) (grades 3-5) (grades 6-8) (grades 9-12)
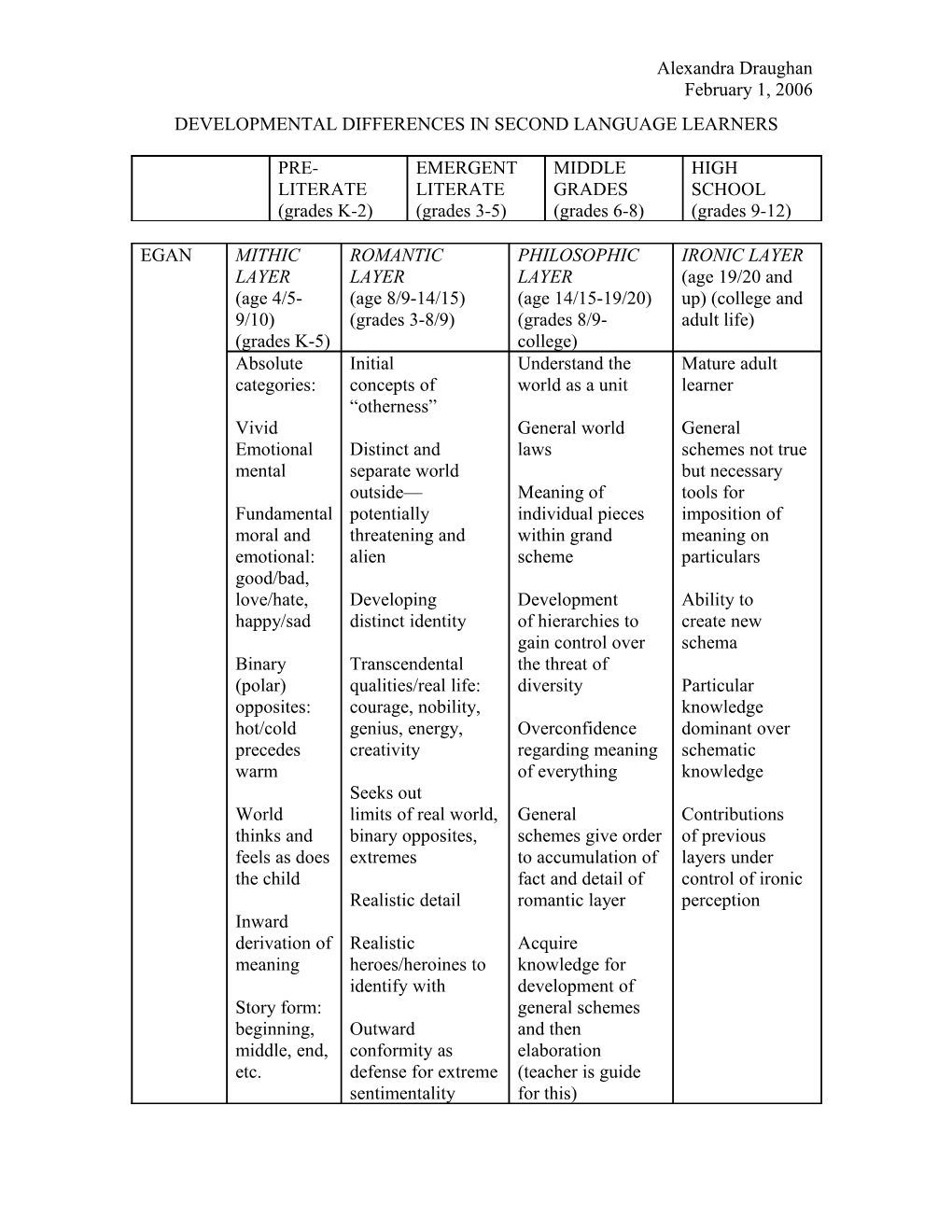
EGAN MITHIC ROMANTIC PHILOSOPHIC IRONIC LAYER LAYER LAYER LAYER (age 19/20 and (age 4/5- (age 8/9-14/15) (age 14/15-19/20) up) (college and 9/10) (grades 3-8/9) (grades 8/9- adult life) (grades K-5) college) Absolute Initial Understand the Mature adult categories: concepts of world as a unit learner “otherness” Vivid General world General Emotional Distinct and laws schemes not true mental separate world but necessary outside— Meaning of tools for Fundamental potentially individual pieces imposition of moral and threatening and within grand meaning on emotional: alien scheme particulars good/bad, love/hate, Developing Development Ability to happy/sad distinct identity of hierarchies to create new gain control over schema Binary Transcendental the threat of (polar) qualities/real life: diversity Particular opposites: courage, nobility, knowledge hot/cold genius, energy, Overconfidence dominant over precedes creativity regarding meaning schematic warm of everything knowledge Seeks out World limits of real world, General Contributions thinks and binary opposites, schemes give order of previous feels as does extremes to accumulation of layers under the child fact and detail of control of ironic Realistic detail romantic layer perception Inward derivation of Realistic Acquire meaning heroes/heroines to knowledge for identify with development of Story form: general schemes beginning, Outward and then middle, end, conformity as elaboration etc. defense for extreme (teacher is guide sentimentality for this) Alexandra Draughan February 1, 2006
DEVELOPMENTAL DIFFERENCES IN SECOND LANGUAGE LEARNERS
PRE- EMERGENT MIDDLE HIGH LITERATE LITERATE GRADES SCHOOL (grades K-2) (grades 3-5) (grades 6-8) (grades 9-12)
PIAGET PREOPERATIONS CONCRETE FORMAL (age 2-7) OPERATIONS OPERATIONS (grades up to 2) (age 7-11) (age 11-15) (grades 2-4/5) (grades 4/5-8/9 up) Preoperational Able to apply Highest thought logical thought to developmental level concrete problems of cognitive Characterized by structures L1 development, Understands other forms of new concepts and Applying or representation, rapid ideas through the beginning to apply conceptual use of hands-on, logical reasoning to development concrete abstract problems experiences without direct Egocentricity experience or More social, less concrete referents Pre and semi egocentric logical reasoning Importance of Single category language use as focus (sorting by informational color, size, etc) exchange Alexandra Draughan February 1, 2006 TEACHER NOTES ON STUDENTS
PRIMARY LEARNERS: IMMEDIATE STUDENTS: EARLY ADOLESCENT PRE-LITERATE EMERGENT LITERATE (TRANSESCENT) (ages 5-7) (ages 8-10) STUDENTS: (grades K-2) (grades 3-5) MIDDLE GRADES (ages 11-14) Can Maximum openness to (grades 6-8) develop good oral skills, diversity pronunciation, and intonation Begin to understand cause Most dramatic developmental with a good model and effect with changes Learn development of cause and Cognitive plateau then new through dramatic and role play effect intellectual tools Tire easily Group work and Changing and often Large systematic approach unpredictable body muscle tasks Concrete experiences Multiplying and rapidly and context shifting interests “Boy and girl germs” Fluid and flexible self-concept Imagination, binary Reworking interpersonal opposites, emotional relationships with adults connections, real hero Turbulent emotions themes with transcendent Extreme idealism qualities overcoming life Asserting independence challenges Powerful peer group Broad exploration of real world limits Heroic character Interested in things unusual and extremes Kindergarten: Grade 3: Grade 6: Follow commands, acceptance, Legends/fairy tales, Extremes, outrageous, or gross, constant movement, 3D geographic facts, food, real stories and real life manipulation, stories, short climates, drama, dress-up, problems, personal and teacher dialogues (names, likes, etc.), gross details, structured tales of challenge and triumph, puppets, talking about selves, dialogues and writing with safety of working and constant comments and choices, incorporate math, presenting with others, expressions making up fairy tales, more television, pop culture, general settled down and academic, teen angst, treated like grown- Grade 1: complicated story-based ups, love and care of animals Crave structure and routine with themes, independent and pets and comparing with some surprises, define personal activities, collections, target culture, lots of structure, space with chairs, turn taking language creations, word unpredictable behaviors, systems, games with hiding banks, partner corrections, everyday ups and downs, objects, mysterious changes, competitive games, humor, wisdom and reflection, silly twist to song or game, riddles, jokes weirdness in own and target pretending, feeling successful, cultures, change activities Alexandra Draughan February 1, 2006 taking home and telling, Grade 4: every ten to fifteen minutes, physical participation in cultural Abstract thought keep on task, same-sex groups, act., reading and writing, short developing, hormones, always give less time for attention span peer pressure, like little activities to keep on task, adult scientists, discovering, role of teacher important not as Grade 2: cooking, making models, peers, teachers must relate and Energy, participation and crafts, performing and understand interests and pretending, TPR adventures, memorizing plays, history, vocabulary, create new things repetitive dialogues, value of facts, legends, written and show them off, content, taken seriously, tasks, enjoy responsibility supplemental language/slang instructions into manageable of homework as a routine, chunks, similar development as computer work with Grade 7: kindergarteners, specific with bookmarked sites, guided Outside classroom interviews, animals, scientific twist to research of topics authentic texts and discussion, lessons accuracy developing, teens Grade 5: their age in target culture, “newness” of foreign mixed partner activities, language wearing off, need information more for creative to be re-ignited with use than for creativity, teacher language and culture by as “instructor,” telephone building on abilities, conversation dialogues, Internet-based activities, shopping and TV prompts, technology, funny, more self-absorbed interesting, multi intelligences, teens in Grade 8: target culture, sitting in Technology and chairs, memorizing lists communication with others, and poems, plays, writing, more realistic situations creating books and (giving and taking direction, projects, performing, asking and denying serious, want to be seen as information), pursue unsure “adults,” pen pals with guidance, abundance of slang, direct answers, informal setting, school and peers in target culture, focus on similarities, change activities every 20 minutes depending on interest, notes, postcards, “reintroduce” fairy tales, teaching others, justice, global awareness, world peace, religion(s), bettering the world, strategies for tasks and independent work, rubrics and teacher expectations, be gentle with feelings Alexandra Draughan February 1, 2006 DEVELOPMENTAL DIFFERENCES IN SECOND LANGUAGE LEARNERS
LEARNER VISUAL, HOLISTIC, ABSTRACT, SEQUENTIAL, DIFFERENCES AUDITORY, LINEAR CONCRETE RANDOM IN LEARNING KINESTHETIC STYLES
LEARNER INTELLIGENCE ACTIVITIES LANGUAGE DIFFERENCES APPLICATION IN Linguistic Reading, writing, telling Almost everything MULTIPLE stories, playing word INTELLIGENCE games, etc. S Logical-Mathematical Experimenting, Surveys, making questioning, figuring out charts and graphs logical puzzles, calculating, etc. Visual-Spatial Designing, drawing, Illustrating a Gouin visualizing, doodling, series; creating a etc. picture of an object by writing the word for the object over and over Bodily-Kinesthetic Dancing, running, TPR activities, jumping, building, adding motions to touching, gesturing, etc. songs and chants Musical Singing, whistling, Using songs, humming, tapping, feet rhythmic chants, and hands, listening, etc. creating melodies for favorite rhymes Interpersonal Leading, organizing, Small group and relating, manipulating, partner work mediating, partying, etc. Intrapersonal Setting goals, meditating, Journaling, portfolio dreaming, being quiet, building planning Naturalist Understanding, Photography, field categorizing, explaining trips, classifying things in the world of nature Alexandra Draughan February 1, 2006 PERSONAL PRE- EMERGENT MIDDLE HIGH OBSERVATIONS LITERATE LITERATE GRADES SCHOOL AND (grades K-2) (grades 3-5) (grades 6-8) (grades 9-12) REFLECTIONS