Little Rock School District Social Studies World History
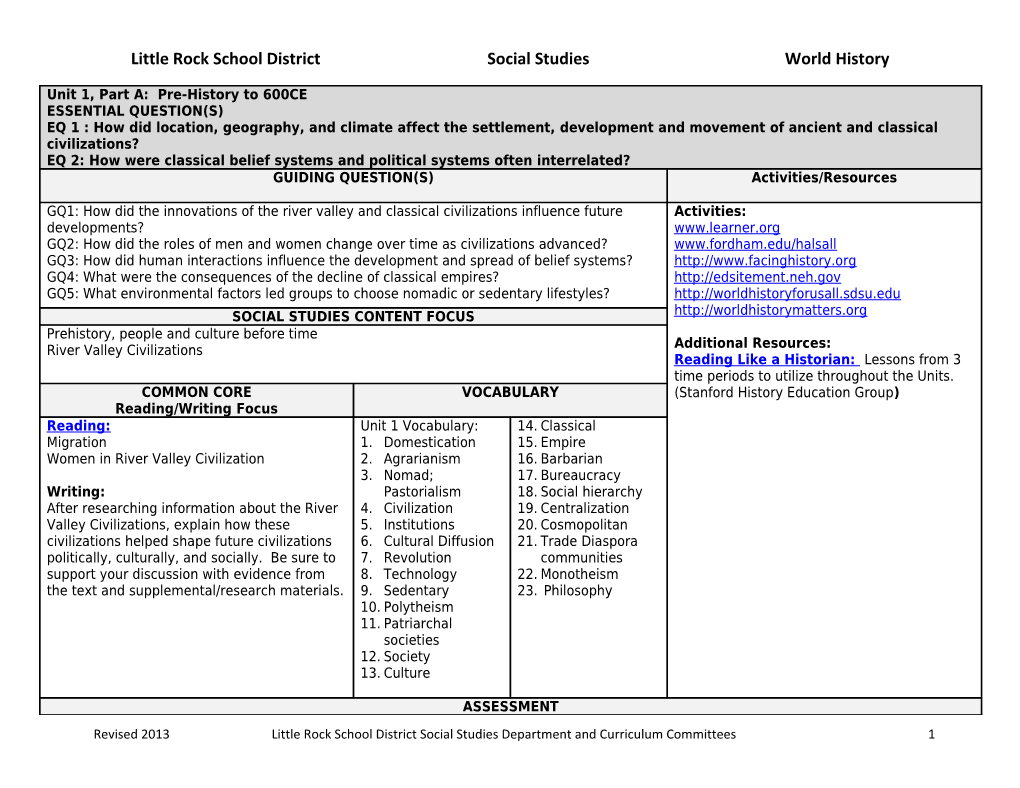
Unit 1, Part A: Pre-History to 600CE ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ 1 : How did location, geography, and climate affect the settlement, development and movement of ancient and classical civilizations? EQ 2: How were classical belief systems and political systems often interrelated? GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
GQ1: How did the innovations of the river valley and classical civilizations influence future Activities: developments? www.learner.org GQ2: How did the roles of men and women change over time as civilizations advanced? www.fordham.edu/halsall GQ3: How did human interactions influence the development and spread of belief systems? http://www.facinghistory.org GQ4: What were the consequences of the decline of classical empires? http://edsitement.neh.gov GQ5: What environmental factors led groups to choose nomadic or sedentary lifestyles? http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS http://worldhistorymatters.org Prehistory, people and culture before time Additional Resources: River Valley Civilizations Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 time periods to utilize throughout the Units. COMMON CORE VOCABULARY (Stanford History Education Group) Reading/Writing Focus Reading: Unit 1 Vocabulary: 14. Classical Migration 1. Domestication 15. Empire Women in River Valley Civilization 2. Agrarianism 16. Barbarian 3. Nomad; 17. Bureaucracy Writing: Pastorialism 18. Social hierarchy After researching information about the River 4. Civilization 19. Centralization Valley Civilizations, explain how these 5. Institutions 20. Cosmopolitan civilizations helped shape future civilizations 6. Cultural Diffusion 21. Trade Diaspora politically, culturally, and socially. Be sure to 7. Revolution communities support your discussion with evidence from 8. Technology 22. Monotheism the text and supplemental/research materials. 9. Sedentary 23. Philosophy 10. Polytheism 11. Patriarchal societies 12. Society 13. Culture
ASSESSMENT Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 1 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings.
STANDARDS ARSLE’S: SMR.1.WH1: Examine the key concepts and historical significance of five major religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.1.WH.2: Examine the key concepts and historical significance of three major Eastern philosophies: Confucianism, Daoism, Legalism SMR.1.WH.3: Explain the contributions of Greek philosophers to Western thought using primary and secondary sources: Socrates – Socratic method, Plato – The Republic, Aristotle SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions SMR.2.WH.2: Investigate the changing roles of women using primary and secondary sources SMR.2.WH.3: Examine the spread of the major religions using historical maps: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism CC.3.WH.1: Explain the causes of the fall of the Roman Empire (e.g., economic, political, military) CC.4.WH.1: Analyze the effect of the Punic Wars on transforming Rome from Republic to Empire CC.4.WH.2: Investigate the effects of the collapse of the Roman Empire on civilization (e.g., barbarian invasions, changing structure of the church, the Byzantine Empire) MS.5.WH.1: Examine the effects of the Neolithic revolution on society (e.g., domestication of plants and animals, increased population, changing technologies) MS.5.WH.2: Describe the causes of mass migration (e.g., famine, disease, war, religious persecution, ethnic cleansing) MS.5.WH.3: Describe the effects of mass migrations on civilization (e.g., Bantu, Great Trek, Irish, Vietnamese) MS.5.WH.4: Discuss the spread of forced labor (e.g., slavery in ancient civilizations, American Indians, Africa) MS.6.WH.1: Illustrate the movement of people over time to different locations using historical maps MS.6.WH.4: Describe the contributions of early Asian civilizations (e.g., Zhou, Qin, Han, Indo-European) ET.7.WH.1: Investigate the significance of the Silk Road using historical maps PG.9.WH.1: Summarize the development of political structures in the cradles of civilization (e.g., Nile River Valley, Indus River Valley, Mesopotamia, China, and South America) PG.9.WH.2: Compare and contrast the political theories found in the Greek city-states of Sparta and Athens PG.9.WH.3: Summarize political power resulting from the following: Mandate of Heaven, divine right, absolutism PG.10.WH.1: Investigate historical law codes using primary and secondary documents (e.g., Hammurabi, Justinian, Magna Carta, Napoleonic) COMMON CORE STANDARDS: Reading: CCSS.10.RH.7: Integrate quantitative or technical analysis (e.g.,charts, research data) with qualitative analysis in print or digital text. CCSS.10.RH.9: Compare and contrast treatments of the same topic in several primary and secondary sources. Writing: CCSS.10.W2: Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. a. Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g.,
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 2 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. b. Develop the topic with well-chosen, relevant, and sufficient facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience’s knowledge of the topic. c. Use varied transitions and sentence structures to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. d. Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to manage the complexity of the topic and convey a style appropriate to the discipline and context as well as to the expertise of likely readers. e. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented (e.g., articulating implications or the significance of the topic). CCSS.10.W4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. Unit 1, Part B: Pre-History to 600 CE ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ 1 : How did location, geography, and climate affect the settlement, development and movement of ancient and classical civilizations? EQ 2: How were classical belief systems and political systems often interrelated? GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
GQ1: How did the innovations of the river valley and classical civilizations influence future Activities: developments? www.learner.org GQ2: How did the roles of men and women change over time as civilizations advanced? www.fordham.edu/halsall GQ3: How did human interactions influence the development and spread of belief systems? http://www.facinghistory.org GQ4: What were the consequences of the decline of classical empires? http://edsitement.neh.gov GQ5: What environmental factors led groups to choose nomadic or sedentary lifestyles? http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS http://worldhistorymatters.org Classical Age: Empires, Religion, Philosophy, Government Fall of Classical Empires
COMMON CORE VOCABULARY Reading/Writing Focus Additional Resources: Reading: Unit 1 Vocabulary: 37. Classical Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Classical Civilization, Silk Roads, Fall of Han 24. Domestication 38. Empire time periods to utilize throughout the Units. 25. Agrarianism 39. Barbarian (Stanford History Education Group) Writing: 26. Nomad; 40. Bureaucracy After researching information about Classical Pastorialism 41. Social hierarchy civilizations, explain how leaders used political 27. Civilization 42. Centralization and religious public works to influence social 28. Institutions 43. Cosmopolitan Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 3 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History development. Be sure to support your 29. Cultural Diffusion 44. Trade Diaspora discussion with evidence from the text or 30. Revolution communities research materials. 31. Technology 45. Monotheism 32. Sedentary 46. Philosophy After researching the spread of Hinduism and 33. Polytheism Christianity, write an essay that argues which 34. Patriarchal group was more successful in binding together societies large numbers of people from different 35. Society traditions into a unified religion. Be sure to 36. Culture examine competing views and support your position with evidence from your research materials. ASSESSMENT Unit 1 DBQ Summative Assessment “The Fall of Rome” Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings. STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.1.WH1: Examine the key concepts and historical significance of five major religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.1.WH.2: Examine the key concepts and historical significance of three major Eastern philosophies: Confucianism, Daoism, Legalism SMR.1.WH.3: Explain the contributions of Greek philosophers to Western thought using primary and secondary sources: Socrates – Socratic method, Plato – The Republic, Aristotle SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions SMR.2.WH.2: Investigate the changing roles of women using primary and secondary sources SMR.2.WH.3: Examine the spread of the major religions using historical maps: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism CC.3.WH.1: Explain the causes of the fall of the Roman Empire (e.g., economic, political, military) CC.4.WH.1: Analyze the effect of the Punic Wars on transforming Rome from Republic to Empire CC.4.WH.2: Investigate the effects of the collapse of the Roman Empire on civilization (e.g., barbarian invasions, changing structure of the church, the Byzantine Empire) MS.5.WH.1: Examine the effects of the Neolithic revolution on society (e.g., domestication of plants and animals, increased population, changing technologies) MS.5.WH.2: Describe the causes of mass migration (e.g., famine, disease, war, religious persecution, ethnic cleansing) MS.5.WH.3: Describe the effects of mass migrations on civilization (e.g., Bantu, Great Trek, Irish, Vietnamese) MS.5.WH.4: Discuss the spread of forced labor (e.g., slavery in ancient civilizations, American Indians, Africa) MS.6.WH.1: Illustrate the movement of people over time to different locations using historical maps MS.6.WH.4: Describe the contributions of early Asian civilizations (e.g., Zhou, Qin, Han, Indo-European) ET.7.WH.1: Investigate the significance of the Silk Road using historical maps PG.9.WH.1: Summarize the development of political structures in the cradles of civilization (e.g., Nile River Valley, Indus River Valley, Mesopotamia, China, and South America) Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 4 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History PG.9.WH.2: Compare and contrast the political theories found in the Greek city-states of Sparta and Athens PG.9.WH.3: Summarize political power resulting from the following: Mandate of Heaven, divine right, absolutism PG.10.WH.1: Investigate historical law codes using primary and secondary documents (e.g., Hammurabi, Justinian, Magna Carta, Napoleonic)
COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.2: Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text. CCSS.10.RH.6: Compare the point of view of two or more authors for how they treat the same or similar topics, including which details they include and emphasize in their respective accounts. Writing: CCSS.10.W1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. a. Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among the claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. b. Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying data and evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both claim(s) and counterclaims in a discipline-appropriate form and in a manner that anticipates the audience’s knowledge level and concerns. c. Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the elationships between claim(s) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. d. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from or supports the argument presented. CCSS.10.W4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. CCSS.10.W5: Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. CCSS.10.W7: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
Unit 2, Part A: Birth of Islam to Renaissance 600-1450 ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: How does the development and spread of new ideas demonstrate cultural exchange?
GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
GQ1: How did the role of Islamic women change as the religion spread? Activities: GQ2: What exchanges in knowledge occurred between Muslims and other religious groups? www.learner.org GQ3: How did the Feudal system create class conflict? How did this change as a result of the www.fordham.edu/halsall plague? http://www.facinghistory.org GQ4: What factors led the Mongols to migrate throughout Europe? http://edsitement.neh.gov GQ5: How did innovation and technology differ between early American civilizations? http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu http://worldhistorymatters.org SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 5 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History Spread of Islam Crusades Africa: Mali, Songhai, Ghana Cultural Exchange Additional Resources: COMMON CORE VOCABULARY Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Reading/Writing Focus time periods to utilize throughout the Units. Reading: Unit 2 Vocabulary: 15. Manor (Stanford History Education Group) Spread of Islam 1. Mysticism 16. Serf 2. Caliph 17. Estates 3. Sultan 18. Crusades Writing: 4. Jihad 19. Papacy After researching information about the role of 5. Dar es Islam 20. Schism women in Islam, write an essay that evaluates 6. Dhimmis 21. Heresy whether the role of women in Islam has 7. Tribute payment 22. Chivalry progressed over time. Be sure to support your 8. Neoconfucianism 23. Sinification position with evidence from the text. Give 9. Feudalism 24. Shogun examples from past or current events or 10. Vassal 25. Daimyo issues to illustrate or clarify your position. 11. Fiefs 26. Samurai 12. Lords 27. Bushido 13. knights 14. Manorialism
ASSESSMENT Unit 2 DBQ Summative Assessment: “The Black Death” Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings. STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.1.WH1: Examine the key concepts and historical significance of five major religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions SMR.2.WH.3: Examine the spread of the major religions using historical maps: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.2.WH.4: Research the effects of the Black Death on Medieval and early Renaissance society (e.g., population, economics, religion) CC.3.WH.2: Investigate the causes of the Crusades (e.g., religious, economic, military, political) CC.4.WH.2: Investigate the effects of the collapse of the Roman Empire on civilization (e.g., barbarian invasions, changing structure of the church, the Byzantine Empire) MS.5.WH.3: Describe the effects of mass migrations on civilization (e.g., Bantu, Great Trek, Irish, Vietnamese) Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 6 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History MS.5.WH.4: Discuss the spread of forced labor (e.g., slavery in ancient civilizations, American Indians, Africa) MS.6.WH.1: Illustrate the movement of people over time to different locations using historical maps MS.6.WH2: Investigate the cultures that developed in the Americas prior to European exploration, Aztec, and North American Indian tribes) MS.6.WH.3: Describe the contributions of early African civilizations (e.g., Ghana, Mali, Songhai) MS.6.WH.4: Describe the contributions of early Asian civilizations (e.g., Zhou, Qin, Han, Indo-European) MS.6.WH.5: Compare and contrast the consequences of the Mongol invasion on India, China, and Russia ET.7.WH.1: Investigate the significance of the Silk Road using historical maps ET.7.WH.4: Analyze the results of slave labor on economic systems ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.1: Summarize the development of political structures in the cradles of civilization (e.g., Nile River Valley, Indus River Valley, Mesopotamia, China, and South America) PG.9.WH.4: Investigate the origin and development of the imperial state: Africa, Asia, Europe, Middle East PG.9.WH.5: Compare and contrast the political structure of European and Japanese feudalism PG.9.WH.7: Discuss theocracy (e.g., John Calvin, Puritans, Islam) PG.9.WH.8: Examine the political theories of socialism, communism, and fascism PG.10.WH.1: Investigate historical law codes using primary and secondary documents (e.g., Hammurabi, Justinian, Magna Carta, Napoleonic) COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.9: Compare and contrast treatments of the same topic in several primary and secondary sources.
Writing: CCSS.10.W8: Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation CCSS.10.W9: Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research
Unit 2, Part B: Birth of Islam to Renaissance 600-1450 ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: How does the development and spread of new ideas demonstrate cultural exchange?
GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 7 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History
GQ1: How did the role of Islamic women change as the religion spread? Activities: GQ2: What exchanges in knowledge occurred between Muslims and other religious groups? www.learner.org GQ3: How did the Feudal system create class conflict? How did this change as a result of the www.fordham.edu/halsall plague? http://www.facinghistory.org GQ4: What factors led the Mongols to migrate throughout Europe? http://edsitement.neh.gov GQ5: How did innovation and technology differ between early American civilizations? http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu http://worldhistorymatters.org SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS Western Europe: Feudalism and Manorialism Bubonic Plague Byzantine Empire, Mongols Post-Classical China Additional Resources: Americas: Olmec, Mayan, Incan, Aztec COMMON CORE VOCABULARY Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Reading/Writing Focus time periods to utilize throughout the Units. Reading: Unit 2 Vocabulary: 15. Manor (Stanford History Education Group) Mongol Migration, Technology in Americas, 1. Mysticism 16. Serf Dark Ages Lesson Feudalism 2. Caliph 17. Estates Dark Ages Documents 3. Sultan 18. Crusades Dark Ages PowerPoint Writing: 4. Jihad 19. Papacy After researching information on the late 5. Dar es Islam 20. Schism Middle Ages, write an essay comparing the 6. Dhimmis 21. Heresy impact of the Plague in Europe on urban 7. Tribute payment 22. Chivalry dwellers versus feudal manors. Be sure to 8. Neoconfucianism 23. Sinification support your discussion with evidence from 9. Feudalism 24. Shogun your textbook and additional resources. 10. Vassal 25. Daimyo 11. Fiefs 26. Samurai 12. Lords 27. Bushido 13. knights 14. Manorialism
ASSESSMENT Unit 2 DBQ Summative Assessment: “The Black Death” Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 8 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings. STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.1.WH1: Examine the key concepts and historical significance of five major religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions SMR.2.WH.3: Examine the spread of the major religions using historical maps: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.2.WH.4: Research the effects of the Black Death on Medieval and early Renaissance society (e.g., population, economics, religion) CC.3.WH.2: Investigate the causes of the Crusades (e.g., religious, economic, military, political) CC.4.WH.2: Investigate the effects of the collapse of the Roman Empire on civilization (e.g., barbarian invasions, changing structure of the church, the Byzantine Empire) MS.5.WH.3: Describe the effects of mass migrations on civilization (e.g., Bantu, Great Trek, Irish, Vietnamese) MS.5.WH.4: Discuss the spread of forced labor (e.g., slavery in ancient civilizations, American Indians, Africa) MS.6.WH.1: Illustrate the movement of people over time to different locations using historical maps MS.6.WH2: Investigate the cultures that developed in the Americas prior to European exploration, Aztec, and North American Indian tribes) MS.6.WH.3: Describe the contributions of early African civilizations (e.g., Ghana, Mali, Songhai) MS.6.WH.4: Describe the contributions of early Asian civilizations (e.g., Zhou, Qin, Han, Indo-European) MS.6.WH.5: Compare and contrast the consequences of the Mongol invasion on India, China, and Russia ET.7.WH.1: Investigate the significance of the Silk Road using historical maps ET.7.WH.4: Analyze the results of slave labor on economic systems ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.1: Summarize the development of political structures in the cradles of civilization (e.g., Nile River Valley, Indus River Valley, Mesopotamia, China, and South America) PG.9.WH.4: Investigate the origin and development of the imperial state: Africa, Asia, Europe, Middle East PG.9.WH.5: Compare and contrast the political structure of European and Japanese feudalism PG.9.WH.7: Discuss theocracy (e.g., John Calvin, Puritans, Islam) PG.9.WH.8: Examine the political theories of socialism, communism, and fascism PG.10.WH.1: Investigate historical law codes using primary and secondary documents (e.g., Hammurabi, Justinian, Magna Carta, Napoleonic) COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.4: Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including vocabulary describing political, social, or economic aspects of history/social studies. CCSS.10.RH.6: Compare the point of view of two or more authors for how they treat the same or similar topics, including which details they include and emphasize in their respective accounts. CCSS.10.RH.7: Integrate quantitative or technical analysis (e.g.,charts, research data) with qualitative analysis in print or digital text. CCSS.10.RH.8: Assess the extent to which the reasoning and evidence in a text support the author’s claims
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 9 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History Writing: CCSS.10.W4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. CCSS.10.W5: Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. Unit 3, Part A: Expansion and Exploration 1450-1750 ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: How did the movements of people (voluntarily or forced) and ideas affect the post-Columbian world? GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
Activities: GQ1: Why did European women contribute less to the Renaissance than their male www.learner.org counterparts? www.fordham.edu/halsall GQ2: How did the “Columbian exchange” affect the new and old worlds? http://www.facinghistory.org GQ3: How did cultural differences create conflict in the Americans after the arrival of http://edsitement.neh.gov Europeans? http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu GQ4: How does the experience of forced migration differ from voluntary movement? http://worldhistorymatters.org GQ5: How did Chinese naval technology compare to contemporary European technology?
SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS Long Distance Trade and Travel Renaissance Additional Resources: Humanism Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Exploration time periods to utilize throughout the Units. COMMON CORE VOCABULARY (Stanford History Education Group) Reading/Writing Focus Reading: Unit 3 Vocabulary: 7. Mercantilism Renaissance, Columbian Exchange 1. Renaissance 8. Colonialism 2. Plantations 9. Middle Passage (Encomienda) 10. Triangular Trade Writing: 3. Mita 11. Mulatto After researching the Renaissance, write an 4. Pandemic 12. Creole essay that discusses the impact the 5. Columbian Renaissance had on government, society, and Exchange art.. Be sure to support your position with 6. Diaspora evidence from your research.
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 10 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History
ASSESSMENT Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings.
STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.1.WH.4: Analyze key elements of the Renaissance: Humanism, revival of interest in ancient Greece and Rome, changing artistic styles (e.g., music, architecture, literature) SMR.1.WH.5: Describe the role of the printing press in the spread of ideas: availability of books, increased literacy, Reformation SMR.2.WH.4: Research the effects of the Black Death on Medieval and early Renaissance society (e.g., population, economics, religion) SMR.2.WH.5: Evaluate the effect of the Renaissance on subsequent events in Europe: Reformation, exploration, Enlightenment, Scientific Revolution CC.4.WH.3: Explain the consequences of the Crusades (e.g., decline in feudalism, increase in trade, shifting political power) MS.5.WH.4: Discuss the spread of forced labor (e.g., slavery in ancient civilizations, American Indians, Africa) MS.6.WH.2: Investigate the cultures that developed in the Americas prior to European exploration (e.g., Maya, Inca, Aztec, and North American Indian tribes) ET.7.WH.2: Research the motivations which drove European exploration (e.g., mercantilism, colonialism, religion) ET.7.WH.3: Analyze the contributions of explorers (e.g., Magellan, Columbus, De Gama, Drake, Zheng He) ET.7.WH.4: Analyze the results of slave labor on economic systems ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.3: Summarize political power resulting from the following: Mandate of Heaven, divine right, absolution PG.9.WH.4: Investigate the origin and development of the imperial state: Africa, Asia, Europe, Middle East
COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.2: Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text. CCSS.10.RH.6: Compare the point of view of two or more authors for how they treat the same or similar topics, including which details they include and emphasize in their respective accounts. CCSS.10.RH.7: Integrate quantitative or technical analysis (e.g.,charts, research data) with qualitative analysis in print or digital text.
Writing: Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 11 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History CCSS.10.W2: Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. a. Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. b. Develop the topic with well-chosen, relevant, and sufficient facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience’s knowledge of the topic. c. Use varied transitions and sentence structures to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. d. Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to manage the complexity of the topic and convey a style appropriate to the discipline and context as well as to the expertise of likely readers. e. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented (e.g., articulating implications or the significance of the topic). CCSS.10.W4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience.
Unit 3, Part B: Expansion and Exploration 1450-1750 ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: How did the movements of people (voluntarily or forced) and ideas affect the post-Columbian world? GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
GQ1: Why did European women contribute less to the Renaissance than their male Activities: counterparts? www.learner.org GQ2: How did the “Columbian exchange” affect the new and old worlds? www.fordham.edu/halsall GQ3: How did cultural differences create conflict in the Americans after the arrival of http://www.facinghistory.org Europeans? http://edsitement.neh.gov GQ4: How does the experience of forced migration differ from voluntary movement? http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu GQ5: How did Chinese naval technology compare to contemporary European technology? http://worldhistorymatters.org
SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS Americas during Exploration Coerced Labor Additional Resources: China and Asian Exploration Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Naval Technologies time periods to utilize throughout the Units. Rise of Ottoman Empire (Stanford History Education Group) COMMON CORE VOCABULARY Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 12 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History Reading/Writing Focus Reading: Unit 3 Vocabulary: 19. Mercantilism Americas after Europeans, Slave Trade, Zheng 13. Renaissance 20. Colonialism He 14. Plantations 21. Middle Passage (Encomienda) 22. Triangular Trade 15. Mita 23. Mulatto Writing: 16. Pandemic 24. Creole After researching the Transatlantic Slave 17. Columbian Trade, write an essay comparing the Exchange experience of forced migration with voluntary 18. Diaspora movement. Support your discussion with evidence from your research.
After researching 15th century naval technology and exploration, write an essay that discusses which society possessed the more sophisticated and innovative maritime technology. Be sure to support your position with evidence from your research. ASSESSMENT
Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings.
STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.1.WH.4: Analyze key elements of the Renaissance: Humanism, revival of interest in ancient Greece and Rome, changing artistic styles (e.g., music, architecture, literature) SMR.1.WH.5: Describe the role of the printing press in the spread of ideas: availability of books, increased literacy, Reformation SMR.2.WH.4: Research the effects of the Black Death on Medieval and early Renaissance society (e.g., population, economics, religion) SMR.2.WH.5: Evaluate the effect of the Renaissance on subsequent events in Europe: Reformation, exploration, Enlightenment, Scientific Revolution CC.4.WH.3: Explain the consequences of the Crusades (e.g., decline in feudalism, increase in trade, shifting political power) MS.5.WH.4: Discuss the spread of forced labor (e.g., slavery in ancient civilizations, American Indians, Africa) MS.6.WH.2: Investigate the cultures that developed in the Americas prior to European exploration (e.g., Maya, Inca, Aztec, and North American Indian tribes) ET.7.WH.2: Research the motivations which drove European exploration (e.g., mercantilism, colonialism, religion) ET.7.WH.3: Analyze the contributions of explorers (e.g., Magellan, Columbus, De Gama, Drake, Zheng He) Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 13 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History ET.7.WH.4: Analyze the results of slave labor on economic systems ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.3: Summarize political power resulting from the following: Mandate of Heaven, divine right, absolution PG.9.WH.4: Investigate the origin and development of the imperial state: Africa, Asia, Europe, Middle East
COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.3: Analyze in detail a series of events described in a text; determine whether earlier events caused later ones or simply preceded them. CCSS.10.RH.7: Integrate quantitative or technical analysis (e.g.,charts, research data) with qualitative analysis in print or digital text. CCSS.10.RH.9: Compare and contrast treatments of the same topic in several primary and secondary sources.
Writing: CCSS.10.W7: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation. CCSS.10.W8: Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation CCSS.10.W9: Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research CCSS.10.W10: Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences.
Unit 4, Part A: European Thought and Impact on the World 1450-1750 ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: How did the individual influence the view of society in post-Renaissance Europe?
GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 14 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History GQ1: How did the end of Feudalism affect women? Activities: GQ2: What were the sources of resistance to the development of new thought? www.learner.org GQ3: How did distance impact the spread of western thought? www.fordham.edu/halsall http://www.facinghistory.org SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS http://edsitement.neh.gov Empire Building http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu Gunpowder Dynasties http://worldhistorymatters.org Transformation of Europe
COMMON CORE VOCABULARY Reading/Writing Focus Additional Resources: Reading: Unit 4 Vocabulary: 7. Counter Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Silver Trade, Exploration 1. Nation-state Reformation time periods to utilize throughout the Units. 2. Absolutism 8. Gunpowder (Stanford History Education Group) Writing: 3. Parliament empires After researching information about 4. Protestant 9. Westernization Feudalism, write an essay that argues Reformation 10. Capitalism whether the concept of honor was stronger for 5. Scientific 11. Commercial Knights or Samurai. Be sure to support your Revolution Revolution position with evidence from your research. 6. European 12. Joint Stock Enlightenment Company
ASSESSMENT
Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings. STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.1.WH1: Examine the key concepts and historical significance of five major religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.1.WH.4: Analyze key elements of the Renaissance: Humanism, revival of interest in ancient Greece and Rome, changing artistic styles Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 15 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History (e.g., music, architecture, literature) SMR.1.WH.5: Describe the role of the printing press in the spread of ideas: availability of books, increased literacy, Reformation SMR.1.WH.6: Explain notable contributions made by individuals during the Scientific Revolution (e.g., Copernicus, Newton, Galileo, Bacon) SMR.1.WH.7: Explain notable contributions made by individuals during the Enlightenment (e.g., Locke, Voltaire, Rousseau, Montesquieu) SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions SMR.2.WH.2: Investigate the changing roles of women using primary and secondary sources SMR.2.WH.3: Examine the spread of the major religions using historical maps: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.2.WH.5: Evaluate the effect of the Renaissance on subsequent events in Europe: Reformation, exploration, Enlightenment, Scientific Revolution CC.3.WH.3: Compare and contrast the Reformation and the Counter-Reformation (e.g., religious, economic, political) MS.5.WH.3: Describe the effects of mass migrations on civilization (e.g., Bantu, Great Trek, Irish, Vietnamese) MS.5.WH.4: Discuss the spread of forced labor (e.g., slavery in ancient civilizations, American Indians, Africa) MS.6.WH.5: Compare and contrast the consequences of the Mongol invasion on India, China, and Russia ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.4: Investigate the origin and development of the imperial state: Africa, Asia, Europe, Middle East PG.9.WH.5: Compare and contrast the political structure of European and Japanese feudalism PG.9.WH.7: Discuss theocracy (e.g., John Calvin, Puritans, Islam)
COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CSS.10.RH.2: Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text. CCSS.10.RH.7: Integrate quantitative or technical analysis (e.g.,charts, research data) with qualitative analysis in print or digital text. CCSS.10.RH.9: Compare and contrast treatments of the same topic in several primary and secondary sources. Writing: CCSS.10.W1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. a. Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among the claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. b. Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying data and evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both claim(s) and counterclaims in a discipline-appropriate form and in a manner that anticipates the audience’s knowledge level and concerns. c. Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the elationships between claim(s) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. d. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from or supports the argument presented.
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 16 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History
Unit 4, Part B: European Thought and Impact on the World 1450-1750 ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: How did the individual influence the view of society in post-Renaissance Europe?
GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
GQ1: How did the end of Feudalism affect women? Activities: GQ2: What were the sources of resistance to the development of new thought? www.learner.org GQ3: How did distance impact the spread of western thought? www.fordham.edu/halsall http://www.facinghistory.org SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS http://edsitement.neh.gov Enlightenment http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu Glorious Revolution http://worldhistorymatters.org Decline of Monarchy Scientific Revolution
COMMON CORE VOCABULARY Additional Resources: Reading/Writing Focus Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Reading: Unit 4 Vocabulary: 18. Counter time periods to utilize throughout the Units. Scientific Revolution, Women and Witchcraft 12. Nation-state Reformation (Stanford History Education Group) 13. Absolutism 19. Gunpowder 14. Parliament empires Writing: 15. Protestant 20. Westernization After researching information about the Reformation 21. Capitalism Enlightenment, identify an individual who 16. Scientific 22. Commercial influenced societal thought and determine the Revolution Revolution modern impact of their ideas and 17. European 12. Joint Stock contributions. Be sure to support your Enlightenment Company discussion with evidence from your research.
ASSESSMENT
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 17 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings.
STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.1.WH1: Examine the key concepts and historical significance of five major religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.1.WH.4: Analyze key elements of the Renaissance: Humanism, revival of interest in ancient Greece and Rome, changing artistic styles (e.g., music, architecture, literature) SMR.1.WH.5: Describe the role of the printing press in the spread of ideas: availability of books, increased literacy, Reformation SMR.1.WH.6: Explain notable contributions made by individuals during the Scientific Revolution (e.g., Copernicus, Newton, Galileo, Bacon) SMR.1.WH.7: Explain notable contributions made by individuals during the Enlightenment (e.g., Locke, Voltaire, Rousseau, Montesquieu) SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions SMR.2.WH.2: Investigate the changing roles of women using primary and secondary sources SMR.2.WH.3: Examine the spread of the major religions using historical maps: Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism SMR.2.WH.5: Evaluate the effect of the Renaissance on subsequent events in Europe: Reformation, exploration, Enlightenment, Scientific Revolution CC.3.WH.3: Compare and contrast the Reformation and the Counter-Reformation (e.g., religious, economic, political) MS.5.WH.3: Describe the effects of mass migrations on civilization (e.g., Bantu, Great Trek, Irish, Vietnamese) MS.5.WH.4: Discuss the spread of forced labor (e.g., slavery in ancient civilizations, American Indians, Africa) MS.6.WH.5: Compare and contrast the consequences of the Mongol invasion on India, China, and Russia ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.4: Investigate the origin and development of the imperial state: Africa, Asia, Europe, Middle East PG.9.WH.5: Compare and contrast the political structure of European and Japanese feudalism PG.9.WH.7: Discuss theocracy (e.g., John Calvin, Puritans, Islam) COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.1: Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources, attending to such features as the date and origin of the information CCSS.10.RH.2: Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text. CCSS.10.RH.6: Compare the point of view of two or more authors for how they treat the same or similar topics, including which details they include and emphasize in their respective accounts. CCSS.10.RH.7: Integrate quantitative or technical analysis (e.g.,charts, research data) with qualitative analysis in print or digital text. Writing: CCSS.9-10.W2: Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes. a. Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. b. Develop the topic with well-chosen, relevant, and sufficient facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience’s knowledge of the topic.
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 18 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History c. Use varied transitions and sentence structures to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. d. Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to manage the complexity of the topic and convey a style appropriate to the discipline and context as well as to the expertise of likely readers. e. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented (e.g., articulating implications or the significance of the topic). CCSS.10.W4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. CCSS.10.W5: Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. CCSS.10.W6: Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology’s capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically Unit 5, Part A: Revolutions 1750-1920 ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: What motivates people to see political, social, and economic change? EQ2: What role do popular ideologies play in change? GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
GQ1: What changes over time led to the development of industry and capitalism? Activities: GQ2: How did the development of new industry impact technological advancement and www.learner.org competition? www.fordham.edu/halsall GQ3: How did the ideas of the Enlightenment influence the revolutionary culture in colonial http://www.facinghistory.org America, Bourbon France, and Spanish Latin America? http://edsitement.neh.gov GQ4: What similar roles did 19th century women (German and Italian) and Sparta women play http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu in the development of a militaristic culture? http://worldhistorymatters.org GQ5: How do large scale migratory patterns impact interactions between foreign groups?
SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS Industrialization Capitalism Additional Resources: Socialism Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Revolutions time periods to utilize throughout the Units. COMMON CORE VOCABULARY (Stanford History Education Group) Reading/Writing Focus Reading: Unit 5 Vocabulary: 6. Mass Leisure Haitian Revolution, Industry and Innovation 1. Nationalism Culture 2. Socialism, 7. Industrialization Writing: Marxism 8. Racism (Social After researching information about the 3. Imperialism Darwinism) Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 19 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History Scientific Revolution, determine to what 4. Militarism 9. Corporation extent new innovation impacted the 5. Mechanization 10. Caudillos development of industry and capitalism. Be 11. Emancipation sure to support your position with evidence from your research.
ASSESSMENT Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings.
STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.1.WH.7: Explain notable contributions made by individuals during the Enlightenment (e.g., Locke, Voltaire, Rousseau, Montesquieu) SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions CC.3.WH.4: Analyze the causes of the 18th and 19th century revolutions (e.g., liberalism, nationalism, imperialism) CC.3.WH.5: Analyze the causes of World War I (e.g., alliances, imperialism, nationalism, militarism) CC.4.WH.4: Analyze the effect of revolution on the creation of independent nation-states (e.g., American Revolution, French Revolution, unification of Germany, unification of Italy, and Latin American independence movements) CC.4.WH.5: Summarize the consequences of the Napoleonic Wars (e.g., the Louisiana Purchase, the Congress of Vienna) CC.4.WH.13: Analyze the responses to imperialism by people under colonial rule at the end of the 19th century (e.g., Boxer Rebellion, Sepoy Rebellion, Opium Wars, Zulu Wars) ET.7.WH.5: Describe the four factors of production necessary to foster an industrial revolution: natural resources, human resources, capital resources, entrepreneurship ET.7.WH.6: Investigate the role 19th century imperialism played in creating spheres of influence and colonization (e.g., partition of Africa, East Asia, India, Latin America) ET.7.WH.7: Compare and contrast the economic elements of capitalism, socialism, and communism ET.8.WH.1: Analyze the development of mass production methods during the late 19th and early 20th centuries: division of labor, assembly line, interchangeable parts ET.8.WH.2: Summarize the Marxist theory of social and political reform (e.g., proletariat, bourgeoisie) ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.4: Investigate the origin and development of the imperial state: Africa, Asia, Europe, Middle East PG.9.WH.6: Describe the political ideologies of the 18th and 19th century revolutions using primary and secondary documents (e.g., American, Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 20 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History French, and Latin American revolutions) PG.9.WH.8: Examine the political theories of socialism, communism, and fascism PG.10.WH.2: Research the formation of alliances in World War I and World War II using available technology (e.g., Triple Alliance, Triple Entente, Axis and Allies)
COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.3: Analyze in detail a series of events described in a text; determine whether earlier events caused later ones or simply preceded them. Writing: CCSS.10.W8: Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation CCSS.10.W9: Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research CCSS.10.W10: Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences.
Unit 5, Part B: Revolutions 1750-1920 ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: What motivates people to see political, social, and economic change? EQ2: What role do popular ideologies play in change? GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
GQ1: What changes over time led to the development of industry and capitalism? Activities: GQ2: How did the development of new industry impact technological advancement and www.learner.org competition? www.fordham.edu/halsall GQ3: How did the ideas of the Enlightenment influence the revolutionary culture in colonial http://www.facinghistory.org America, Bourbon France, and Spanish Latin America? http://edsitement.neh.gov GQ4: What similar roles did 19th century women (German and Italian) and Sparta women play http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu in the development of a militaristic culture? http://worldhistorymatters.org GQ5: How do large scale migratory patterns impact interactions between foreign groups?
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 21 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS New European Order “isms” Additional Resources: Imperialism Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 time periods to utilize throughout the Units. COMMON CORE VOCABULARY (Stanford History Education Group) Reading/Writing Focus Reading: Unit 5 Vocabulary: 17. Mass Leisure Women, Imperialism 12. Nationalism Culture 13. Socialism, 18. Industrialization Marxism 19. Racism (Social Writing: 14. Imperialism Darwinism) After researching 19th century ideologies, 15. Militarism 20. Corporation write an essay that discusses the similar roles 16. Mechanization 21. Caudillos that 19th century women (German and Italian) 22. Emancipation and Spartan women played in the development of a militaristic culture. Be sure to support your discussion with evidence from your research.
ASSESSMENT Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings.
STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.1.WH.7: Explain notable contributions made by individuals during the Enlightenment (e.g., Locke, Voltaire, Rousseau, Montesquieu) SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions CC.3.WH.4: Analyze the causes of the 18th and 19th century revolutions (e.g., liberalism, nationalism, imperialism) CC.3.WH.5: Analyze the causes of World War I (e.g., alliances, imperialism, nationalism, militarism) CC.4.WH.4: Analyze the effect of revolution on the creation of independent nation-states (e.g., American Revolution, French Revolution, unification of Germany, unification of Italy, and Latin American independence movements) CC.4.WH.5: Summarize the consequences of the Napoleonic Wars (e.g., the Louisiana Purchase, the Congress of Vienna) CC.4.WH.13: Analyze the responses to imperialism by people under colonial rule at the end of the 19th century (e.g., Boxer Rebellion, Sepoy Rebellion, Opium Wars, Zulu Wars) ET.7.WH.5: Describe the four factors of production necessary to foster an industrial revolution: natural resources, human resources, capital Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 22 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History resources, entrepreneurship ET.7.WH.6: Investigate the role 19th century imperialism played in creating spheres of influence and colonization (e.g., partition of Africa, East Asia, India, Latin America) ET.7.WH.7: Compare and contrast the economic elements of capitalism, socialism, and communism ET.8.WH.1: Analyze the development of mass production methods during the late 19th and early 20th centuries: division of labor, assembly line, interchangeable parts ET.8.WH.2: Summarize the Marxist theory of social and political reform (e.g., proletariat, bourgeoisie) ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.4: Investigate the origin and development of the imperial state: Africa, Asia, Europe, Middle East PG.9.WH.6: Describe the political ideologies of the 18th and 19th century revolutions using primary and secondary documents (e.g., American, French, and Latin American revolutions) PG.9.WH.8: Examine the political theories of socialism, communism, and fascism PG.10.WH.2: Research the formation of alliances in World War I and World War II using available technology (e.g., Triple Alliance, Triple Entente, Axis and Allies)
COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.6: Compare the point of view of two or more authors for how they treat the same or similar topics, including which details they include and emphasize in their respective accounts. Writing: CCSS.10.W1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. a. Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among the claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. b. Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying data and evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both claim(s) and counterclaims in a discipline-appropriate form and in a manner that anticipates the audience’s knowledge level and concerns. c. Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the elationships between claim(s) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. d. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from or supports the argument presented.
Unit 6, Part A: Century of War 1900-Present ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: How has global interdependence affect the world and its environments?
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 23 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History
GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
GQ1: How does the great depression demonstrate the interdependence of nations? Activities: GQ2: How would the exclusion of women during the war effort have impacted the events of World War I www.learner.org and World War II? www.fordham.edu/halsall GQ3: How has decolonization disrupted/impacted natural borders and identities? http://www.facinghistory.org GQ4: How did new weapon technology impact late 20th century culture? http://edsitement.neh.gov GQ5: How has the fall of Communism disrupted/impacted national borders and identities? http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu GQ6: How has social conflict perpetuated terrorism and genocide in the modern world? http://worldhistorymatters.org SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS World Wars I and II: causes and consequences, women, Holocaust Great Depression COMMON CORE VOCABULARY Additional Resources: Reading/Writing Focus Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Reading: Unit 6 Vocabulary: 15. Decolonization time periods to utilize throughout the Units. WWI Soldiers, Depression 1. Consumerism 16. Neo-colonialism (Stanford History Education Group) 2. Leisure class 17. Globalization 3. Great Depression 18. Green Revolution Writing: 4. Keynesian 19. Religious After researching World War I and II write an Economics Fundamentalism essay that argues how the exclusion of 5. Totalitarianism 20. Terrorism women during the war efforts would have 6. Welfare State 21. Interdependence impacted those conflicts. Be sure to support 7. Internationalism 22. Ecology your position with evidence from your 8. Trench warfare 23. European Union research. 9. Total War 24. Globalization 10. Genocide 25. Mass 11. Technocrat consumption 12. Post-industrial 26. World Trade society Organization 13. Developing 27. Ethnic Cleansing Nation 28. Nuclear 14. Multinational Proliferation Corporations ASSESSMENT Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings. Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 24 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions SMR.2.WH.2: Investigate the changing roles of women using primary and secondary sources CC.3.WH.5: Analyze the causes of World War I (e.g., alliances, imperialism, nationalism, militarism) CC.3.WH.6: Analyze the causes of World War II (e.g., Treaty of Versailles, the Great Depression, rise of dictators) CC.3.WH.7: Research the causes of the Cold War using available technology (e.g., ideological differences between the United States and the U.S.S.R.) CC.3.WH.8: Analyze the role extremist groups have played in creating world instability CC.4.WH.4: Analyze the effect of revolution on the creation of independent nation-states (e.g., American Revolution, French Revolution, unification of Germany, unification of Italy, and Latin American independence movements) CC.4.WH.6: Summarize the consequences of the Russian Revolution (e.g., Russian Civil War, withdrawal from World War I, end of Czarist rule) CC.4.WH.7: Examine the consequences of World War I and the Treaty of Versailles: changing national boundaries, advances in military technology, deterioration of Germany, the Lea. of Nations CC.4.WH.9: Investigate the world-wide effect of genocide in the 20th and 21st centuries using available technology (e.g., Armenia, Holocaust, Cambodia, Bosnia, Rwanda, Kosovo, Sudan) CC.4.WH.10: Investigate the effects of the Cold War on the post-World War II era (e.g., emerging superpowers, containment policies, space race, arms race) CC.4.WH.11: Discuss the post-Cold War era (e.g., Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty, glasnost, perestroika, fall of Berlin Wall) CC.4.WH.12: Investigate the consequences of the Arab - Israeli conflicts from 1948 to the present ET.7.WH.5: Describe the four factors of production necessary to foster an industrial revolution: natural resources, human resources, capital resources, entrepreneurship ET.7.WH.6: Investigate the role 19th century imperialism played in creating spheres of influence and colonization (e.g., partition of Africa, East Asia, India, Latin America) ET.7.WH.7: Compare and contrast the economic elements of capitalism, socialism, and communism ET.8.WH.1: Analyze the development of mass production methods during the late 19th and early 20th centuries: division of labor, assembly line, interchangeable parts ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.8: Examine the political theories of socialism, communism, and fascism PG.10.WH.2: Research the formation of alliances in World War I and World War II using available technology (e.g., Triple Alliance, Triple Entente, Axis and Allies) PG.10.WH.3: Analyze the structure and purpose of the United Nations PG.10.WH.4: Analyze the purpose of post-World War II military alliances [e.g., North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO), Warsaw Pact] COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.1: Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources, attending to such features as the date and origin of the information CCSS.10.RH.2: Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text. CCSS.10.RH.5: Analyze how a text uses structure to emphasize key points or advance an explanation or analysis. Writing: CCSS.10.W1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 25 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History a. Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among the claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. b. Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying data and evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both claim(s) and counterclaims in a discipline-appropriate form and in a manner that anticipates the audience’s knowledge level and concerns. c. Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the elationships between claim(s) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. d. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from or supports the argument presented. CCSS.10.W4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. CCSS.10.W7: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation Unit 6, Part B: Century of War 1900-Present ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S) EQ1: How has global interdependence affect the world and its environments?
GUIDING QUESTION(S) Activities/Resources
GQ1: How does the great depression demonstrate the interdependence of nations? Activities: GQ2: How would the exclusion of women during the war effort have impacted the events of www.learner.org World War I and World War II? www.fordham.edu/halsall GQ3: How has decolonization disrupted/impacted natural borders and identities? http://www.facinghistory.org GQ4: How did new weapon technology impact late 20th century culture? http://edsitement.neh.gov GQ5: How has the fall of Communism disrupted/impacted national borders and identities? http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu GQ6: How has social conflict perpetuated terrorism and genocide in the modern world? http://worldhistorymatters.org SOCIAL STUDIES CONTENT FOCUS Decolonization Cold War Post-Communism World Terrorism/Genocide Additional Resources: COMMON CORE VOCABULARY Reading Like a Historian: Lessons from 3 Reading/Writing Focus time periods to utilize throughout the Units. Reading: Unit 6 Vocabulary: 15. Decolonization (Stanford History Education Group) Decolonization, Atomic Weapons 1. Consumerism 16. Neo-colonialism 2. Leisure class 17. Globalization 3. Great Depression 18. Green Revolution Writing: 4. Keynesian 19. Religious After researching information about the post- Economics Fundamentalism World War II era, identify the impacts 5. Totalitarianism 20. Terrorism decolonization had on modern Nationalism 6. Welfare State 21. Interdependence movements. Be sure to support your 7. Internationalism 22. Ecology Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 26 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History discussion with evidence from your research. 8. Trench warfare 23. European Union 9. Total War 24. Globalization 10. Genocide 25. Mass 11. Technocrat consumption 12. Post-industrial 26. World Trade society Organization 13. Developing 27. Ethnic Cleansing Nation 28. Nuclear 14. Multinational Proliferation Corporations ASSESSMENT Students will complete an ongoing Document Based Assignment formatted to enhance historical analysis, inference, and content. Student work will be checked throughout the assignment for understanding, engagement, and content accuracy. Students will work independently, in small learning groups, as well as in whole class settings. STANDARDS ARSLE’S SMR.2.WH.1: Explain the characteristics of a civilization: calendar, writing, specialization of workers, rise of cities, advanced technology, development of complex institutions SMR.2.WH.2: Investigate the changing roles of women using primary and secondary sources CC.3.WH.5: Analyze the causes of World War I (e.g., alliances, imperialism, nationalism, militarism) CC.3.WH.6: Analyze the causes of World War II (e.g., Treaty of Versailles, the Great Depression, rise of dictators) CC.3.WH.7: Research the causes of the Cold War using available technology (e.g., ideological differences between the United States and the U.S.S.R.) CC.3.WH.8: Analyze the role extremist groups have played in creating world instability CC.4.WH.4: Analyze the effect of revolution on the creation of independent nation-states (e.g., American Revolution, French Revolution, unification of Germany, unification of Italy, and Latin American independence movements) CC.4.WH.6: Summarize the consequences of the Russian Revolution (e.g., Russian Civil War, withdrawal from World War I, end of Czarist rule) CC.4.WH.7: Examine the consequences of World War I and the Treaty of Versailles: changing national boundaries, advances in military technology, deterioration of Germany, the Lea. of Nations CC.4.WH.9: Investigate the world-wide effect of genocide in the 20th and 21st centuries using available technology (e.g., Armenia, Holocaust, Cambodia, Bosnia, Rwanda, Kosovo, Sudan) CC.4.WH.10: Investigate the effects of the Cold War on the post-World War II era (e.g., emerging superpowers, containment policies, space race, arms race) CC.4.WH.11: Discuss the post-Cold War era (e.g., Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty, glasnost, perestroika, fall of Berlin Wall) CC.4.WH.12: Investigate the consequences of the Arab - Israeli conflicts from 1948 to the present ET.7.WH.5: Describe the four factors of production necessary to foster an industrial revolution: natural resources, human resources, capital resources, entrepreneurship ET.7.WH.6: Investigate the role 19th century imperialism played in creating spheres of influence and colonization (e.g., partition of Africa, East Asia, India, Latin America) ET.7.WH.7: Compare and contrast the economic elements of capitalism, socialism, and communism ET.8.WH.1: Analyze the development of mass production methods during the late 19th and early 20th centuries: division of labor, assembly line, interchangeable parts ET.8.WH.3: Describe economic interdependence of nations [e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), World Trade Organization (WTO), General
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 27 Little Rock School District Social Studies World History Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT), European Economic Union (EEU), Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)] PG.9.WH.8: Examine the political theories of socialism, communism, and fascism PG.10.WH.2: Research the formation of alliances in World War I and World War II using available technology (e.g., Triple Alliance, Triple Entente, Axis and Allies) PG.10.WH.3: Analyze the structure and purpose of the United Nations PG.10.WH.4: Analyze the purpose of post-World War II military alliances [e.g., North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO), Warsaw Pact] COMMON CORE STANDARDS Reading: CCSS.10.RH.1: Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources, attending to such features as the date and origin of the information CCSS.10.RH.2: Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text. CCSS.10.RH.5: Analyze how a text uses structure to emphasize key points or advance an explanation or analysis. Writing: CCSS.10.W1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. a. Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among the claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. b. Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying data and evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both claim(s) and counterclaims in a discipline-appropriate form and in a manner that anticipates the audience’s knowledge level and concerns. c. Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the elationships between claim(s) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. d. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from or supports the argument presented. CCSS.10.W4: Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. CCSS.10.W7: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation +
Revised 2013 Little Rock School District Social Studies Department and Curriculum Committees 28