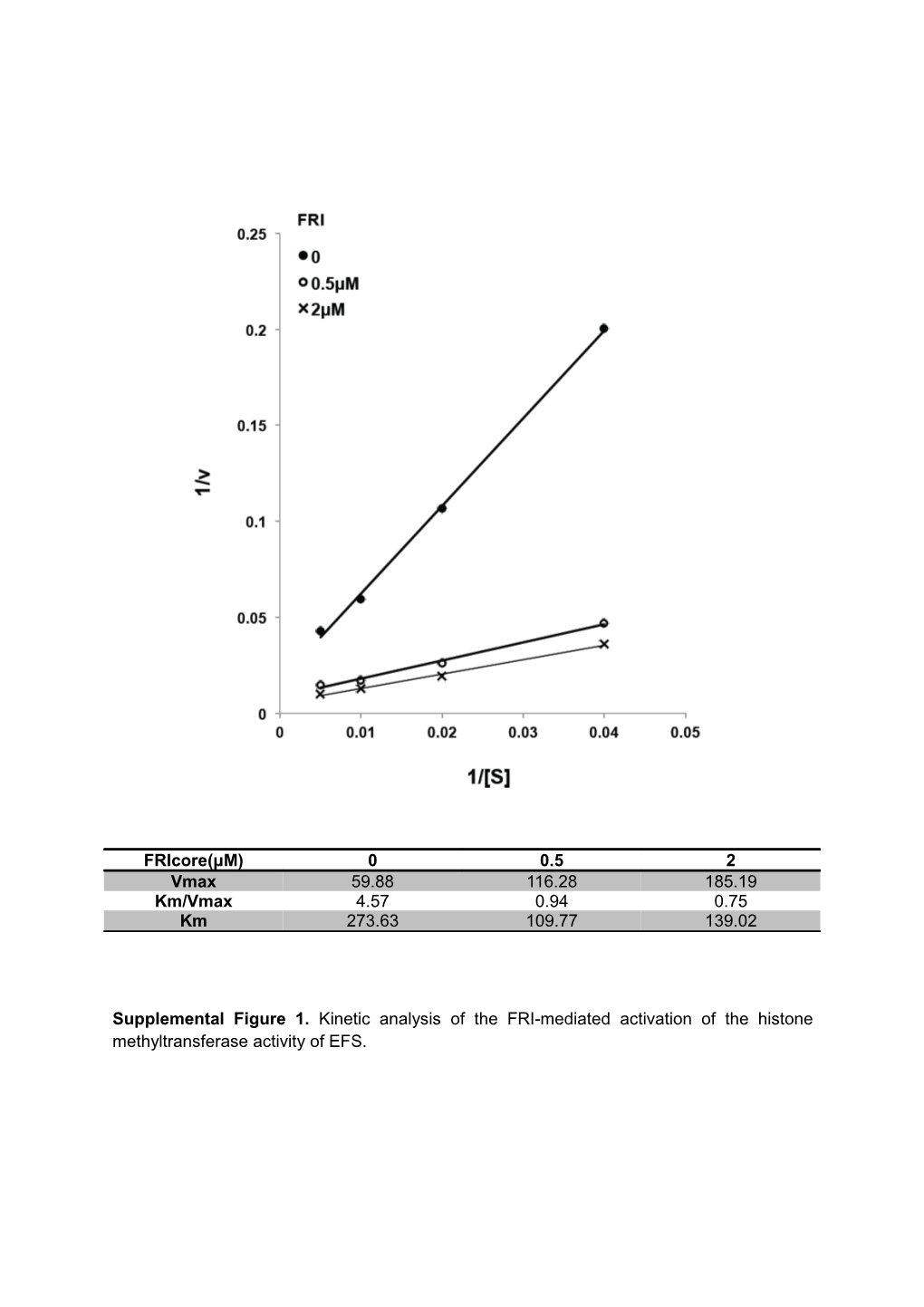
FRIcore(μM) 0 0.5 2 Vmax 59.88 116.28 185.19 Km/Vmax 4.57 0.94 0.75 Km 273.63 109.77 139.02
Supplemental Figure 1. Kinetic analysis of the FRI-mediated activation of the histone methyltransferase activity of EFS. Supplemental Figure 2. FRI specifically stimulates the histone methyltransferase activity of EFS.
A) FRI stimulates EFS, but not the G9a HMTase. FRI weakly stimulates the HMTase activity of ASH1L.
B) FRI, but not BSA, stimulates the histone methyltransferase activity of EFS. Supplemental Figure 3. Sequence alignment of human ASH1L_SET (2069–2288 a.a.) and Arabidopsis EFS_SET (955–1174 a.a.). Supplementary materials and methods
Protein purification – The FRI domain (FRIcore, a.a. 131–432) from Arabidopsis thaliana was cloned into a pET28a vector containing a 6X His tag in its N-terminal region and the Tobacco Etch Virus (TEV) protease cleavage site. The FRI domain was expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) and induced with 1 mM Isopropyl beta-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) for 18 h at 18°C. The cells were lysed in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, and PMSF. Soluble proteins were separated by centrifugation and the N-terminal His-tagged FRI domains were purified by Ni-NTA (Qiagen) affinity chromatography with an elution buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0,
300 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, and 100 mM imidazole. EFS-SET850 (a.a. 850–1166) from Arabidopsis thaliana was cloned into a pGEX4T-1 vector containing a GST tag in its N-terminal region. The protein expression conditions were the same as those used for the FRI domain. EFS-SET850 was then purified by GST affinity chromatography with an elution buffer containing 5% glycerol and 10 mM GSH. EFS-
SET917 (a.a. 917–1263) was cloned into pFastBac HTB, which adds an additional 6X His tag to the N- terminus of the protein, and expressed in an insect cell expression system. EFS-SET917 was purified by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography and the His tag was removed with TEV protease. The protein was further purified via ion exchange (Hitrap Q column, GE healthcare) and size-exclusion chromatography (Superdex 200-26-60, GE healthcare). Then, EFS-SET917 was used for pull-down assays.
In vitro histone methyltransferase assay - EFS_SET850 (100 nM) was incubated in a reaction mixture containing G5E4 nucleosome arrays (12 nucleosomes reconstituted with Xenopus histone octamers on a G5E4 DNA fragment) and 2 μCi of S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H] methionine (3HSAM) (1 mCi, PerkinElmer Life Science, NET 155-3) per 25 μl reaction for 1 hr at room temperature. Reactions were stopped by adding 5X SDS sample buffer and boiling at 95°C. Then, the mixtures were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane by the semi-dry transfer method. The membrane was exposed to an image plate and the image plate was used to expose FLA-7000 (Fuji Film) for autoradiography. Band intensities were measured with Multigauge.
Western blot assay - EFS_SET850 and FRIcore were incubated with substrates in the HMTase assay conditions described above using methyl donor SAM (NEB). Then, the reactants were separated using 15% SDS PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane by the wet transfer method (100 V, 60 min) in transfer buffer containing 25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine, and 20% methanol. The membrane was blocked with 5% skim milk in Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) containing 0.1% Tween 20 for 1 hr in room temperature. Antibodies specific to H3 (9717, Cell Signaling Technology), H3K4me2 (generated by Dr. Daeyoup Lee), H3K4me3 (07-473, Upstate Biotech Millipore), H3K36me2 (9758S, Cell Signaling Technology), or H3K36me3 (9763S, Cell Signaling Technology) were used to detect histone methylations. Bands were scanned with a Chemidoc station (Biorad) and their intensities were compared with Multigauge.
Pull-down assay - 6x HIS-tagged FRIcore and EFS_SET917 were used for the Ni-NTA pull-down assay. FRI was incubated with Ni-NTA resin for 1 hour at 4°C. Then, the beads were washed with a wash buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl, 2 mM DTT for 3 times. The same amounts of beads were aliquoted into each tube along with 10 μg of EFS_SET917. New beads without HIS-tagged
FRIcore were used as a negative control. Then, the samples were incubated for 1 hour at 4°C and washed 3 times with wash buffer. The samples were analyzed via 10% SDS-PAGE with Coomassie staining.
Gel retardation assay – Mono-nucleosomes were prepared for the binding assay with FRIcore and
EFS_SET917. Mono-nucleosomes (0.25 μM) were used for the gel retardation assay and the target proteins were added by increasing their molar ratio with reference to the mono-nucleosomes. The samples were then incubated for 1 hour on ice. After adding 10% sucrose, the samples were separated on a 4% native acrylamide TBE gel (150 V, 60 min). DNA was visualized by Ethidium Bromide (EtBr) staining and proteins were visualized by Coomassie staining.