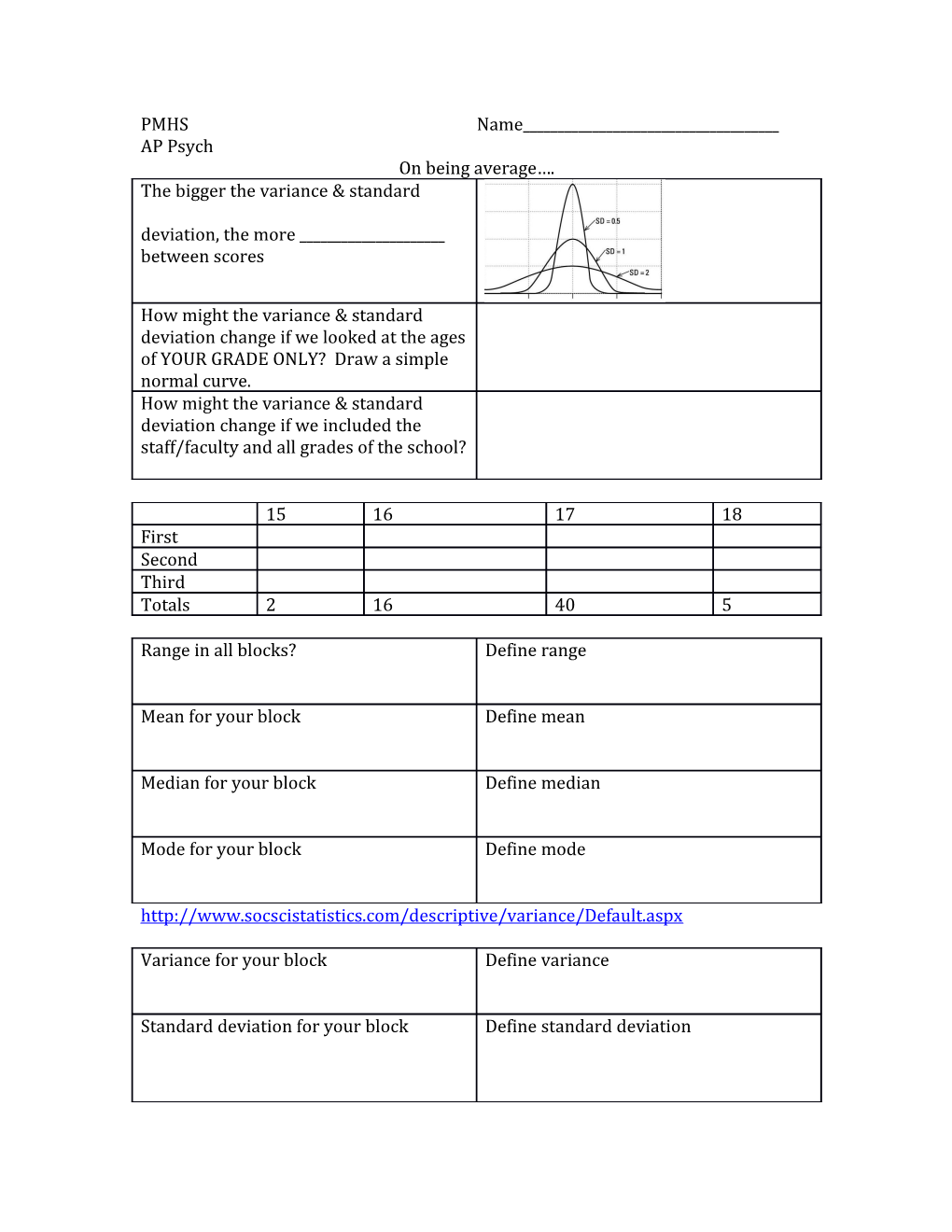
PMHS Name______AP Psych On being average…. The bigger the variance & standard deviation, the more ______between scores
How might the variance & standard deviation change if we looked at the ages of YOUR GRADE ONLY? Draw a simple normal curve. How might the variance & standard deviation change if we included the staff/faculty and all grades of the school?
15 16 17 18 First Second Third Totals 2 16 40 5
Range in all blocks? Define range
Mean for your block Define mean
Median for your block Define median
Mode for your block Define mode http://www.socscistatistics.com/descriptive/variance/Default.aspx
Variance for your block Define variance
Standard deviation for your block Define standard deviation Draw frequency histogram for all blocks (interval or ratio data)
ALL BLOCKS N: 63 M: 16.76 SS: 25.43 (THE SUM OF each score minus the mean then squared) VARIANCE s2 = SS⁄(N - 1) = 25.43⁄(63-1) = 0.41 (calculation above divided by sample–1) STANDARD DEVIATION s = √s2 = √0.41 = 0.64 (square root of variance)
Some practice for the terms we have done so far….
1. Calculate mean, median, and mode for each set of data.
a. IQ’s: 78, 79, 87, 88, 101, 120, 132
b. AP Psych test scores: 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5
2. During the past month, Henri and Sylvia each ate 10 candy bars, while Jerry ate 8, Tricia ate 6, and Tahli ate only 1. The mean number of candy bars eaten by these individuals was: a. 1 b. 5 c. 7 d. 8 e. 10 3. Which is most sensitive to outliers: mean median or mode? (use above example to help)
4. In any distribution of scores, an equal number of scores are both greater than and less than: In a normal distribution, the mean median and mode are roughly the same. THE MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDANCY meet in the middle and the curve is symmetrical. When this does not occur, the data is skewed.
Negative skew Positive skew When the median is higher than the When the median is lower than the mean (that is, the bulk of the data is mean (that is, the bulk of the data is higher than the average) lower than the average) When the mean is pulled down by a When the mean is pulled up by a few few outliers outliers
---- 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 +++
Thanks Michael Britt foot mnemonic https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gzSbAkZE8jw negative positive Penn Manor AP Psychology scores from 2009-2016 National average hovers around 3; PM average around 4.38
Scores (x-axis) Frequency (# of ppl. Relative frequency f/N who had) – (y-axis) * 100 N=376 5 244 54% 4 144 32% 3 52 12% 2 8 1.78% 1 2 .44%
244
204
164
124
84
44
4 Review questions
1. Considering the hypothetical income of your neighborhood, what would a negative skew look like if average income is $50,000? (put hypothetical income on x axis)-Explain what this might mean
2. Considering the hypothetical income of your neighborhood, what would a positive skew look like if average income is $50,000? (put hypothetical income on x-axis)Explain what this implies…
IQ and SAT scores, respectively; add Z-scores
Using the bell curves or normal distributions provided...LABEL z- scores 1. Examine the Weschler Adult Intelligence (top) scale scores. What are the measures of central tendency? 2. What is the standard deviation?______points
Examine the SAT Math scale scores (above). Write in the z-scores. 3.What is the measure of central tendency?
4.What is the standard deviation?______points 5.Which has a higher standard deviation: SAT or IQ test? What does this mean?
6.If your SCORE is 800 on the SAT Math Scale, how many standard deviations (z-scores) are you
from the mean?______7. What is the SCORE one standard deviation above the mean on the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale?______the Z score is:______What is the SCORE one standard deviation below the mean on the SAT Math Scale? _____ The Z score is: A. The Empirical Rule or “68-95-99 Rule” Pretend the mean is a 75% on an AP test. The standard deviation is 5. Draw what the curve might look like. Draw at least two standard deviations away from the mean.
1.What does Z score +1 equal?______What about -2______? (tells us how far away score is from the mean) 2.What does that say about the scores of 68% of the class? They scored between _____ and
______. What about 95% of class? ______and ______
3.What % of class scores 85% and above?______------Pretend the mean inches for a female rat is 300 grams. The standard deviation is 20. Draw what the normal curve might look like. Draw at least three standard deviations away from the mean.
4. What does Z score +1 equal?______What about -2______? (tells us how far away score is from the mean)
5. What do 68% of adult female rats weigh?
6. What do 95% of rats weight?
7. What % of rats weigh below average?
8. What % of rats weigh over 280?
One way to describe data is to show someone as being in a certain percentile. If a person is in the 74th percentile, this means 74% of students performed lower. Describe the percentiles of the following students. a. Mary a.i. 20th percentile Math______
a.ii. 58th percentile English______
a.iii. Which subject can we infer that Mary is better in?______Why?
b. Joe b.i. 85th percentile Math______
b.ii. 45th percentile English______b.iii. Which subject can we infer that Joe is better in? ______Why?
*There is NO 100th percentile.
1. Who is bigger? a) baby is in the 5th percentile for height b) baby is in the 50th percentile for height
2. Variance is 100, standard deviation is ______
3. Variance is 25, standard deviation is ______