Name Class Date
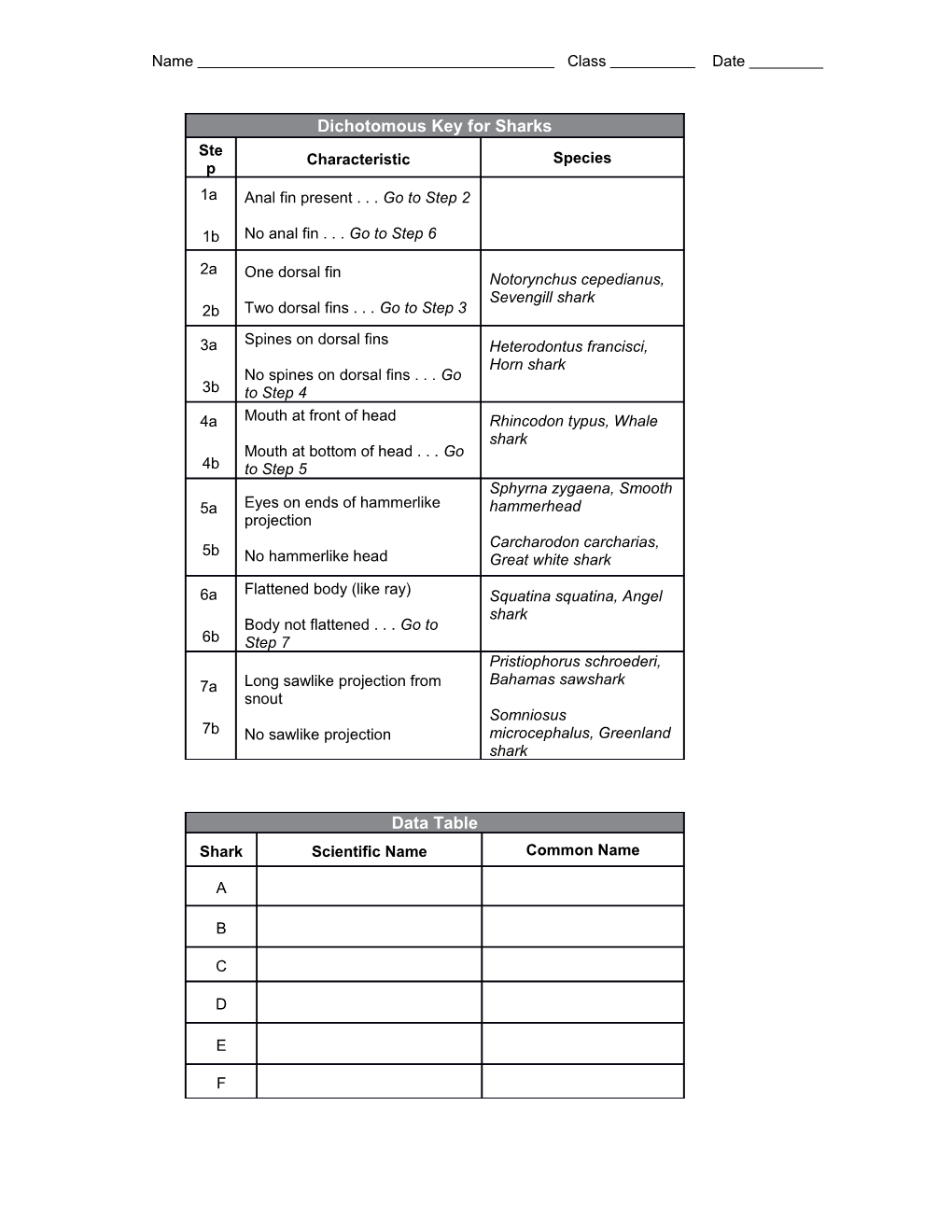
Dichotomous Key for Sharks Ste Characteristic Species p 1a Anal fin present . . . Go to Step 2
1b No anal fin . . . Go to Step 6
2a One dorsal fin Notorynchus cepedianus, Sevengill shark 2b Two dorsal fins . . . Go to Step 3
3a Spines on dorsal fins Heterodontus francisci, Horn shark No spines on dorsal fins . . . Go 3b to Step 4 4a Mouth at front of head Rhincodon typus, Whale shark Mouth at bottom of head . . . Go 4b to Step 5 Sphyrna zygaena, Smooth 5a Eyes on ends of hammerlike hammerhead projection Carcharodon carcharias, 5b No hammerlike head Great white shark
6a Flattened body (like ray) Squatina squatina, Angel shark Body not flattened . . . Go to 6b Step 7 Pristiophorus schroederi, 7a Long sawlike projection from Bahamas sawshark snout Somniosus 7b No sawlike projection microcephalus, Greenland shark
Data Table Shark Scientific Name Common Name
A
B
C
D
E
F 109 Name Class Date
Part B: Construct a Dichotomous Key You will be working with your group to construct a dichotomous for all you working together. 5. Look at your group. Make of list of physical traits that you would use to tell each other apart.
6. Write the names of all of the people in your group. On a separate sheet of paper make a simple drawing of each person with their specific characteristics. Use a letter to label each drawing. A: B: C: D: E: F: G: H: 7. Use the space on page 111 to construct a dichotomous key for your group of organisms, using the key for sharks as a model. 8. Check the usefulness of your key by making a copy of your key and asking another student in a different group to use it to identify your drawings.
110 Name Class Date
Dichotomous Key
Analyze and Conclude 1. Predict How would the dichotomous key for sharks need to change if you wanted to use it to identify ten different sharks?
2. Evaluate What was the most challenging part of making your own dichotomous key?
111 Name Class Date
3. Infer Suppose you had real specimens of your organisms instead of drawings. What other traits could you use to build a dichotomous key?
6. Infer The dichotomous keys in this lab are used to trace organisms to the species level. Could keys be designed which classify unknown organisms to higher levels of the Linnaean system—to a family or order, for example? Why or why not?
112