Writing -Assessment Foci, Questions, and Sub levels
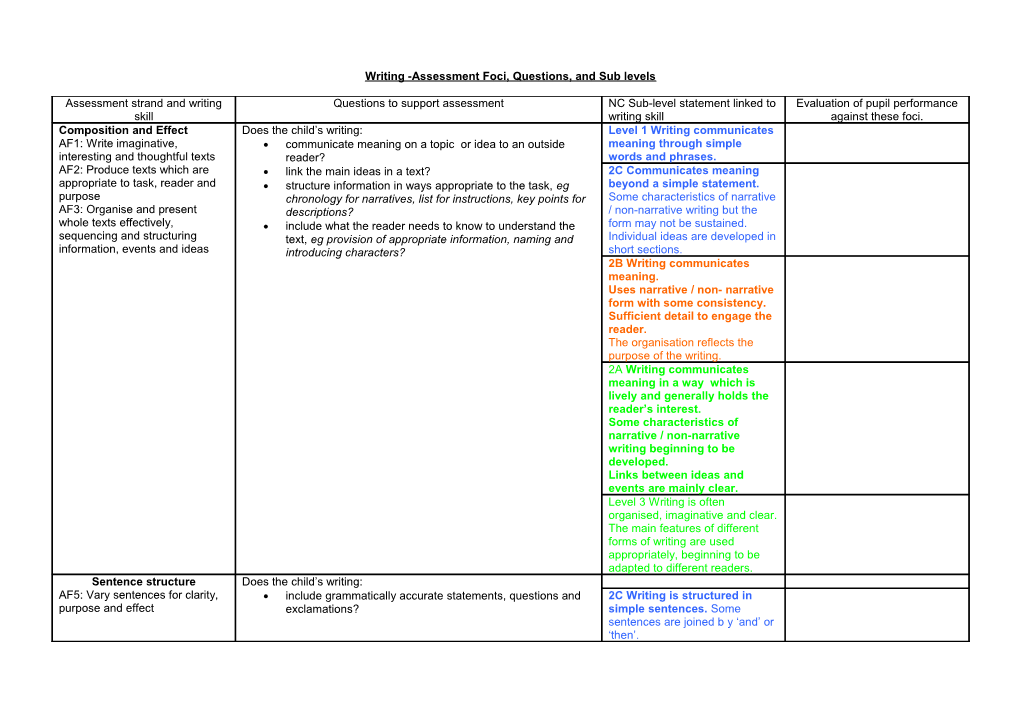
Assessment strand and writing Questions to support assessment NC Sub-level statement linked to Evaluation of pupil performance skill writing skill against these foci. Composition and Effect Does the child’s writing: Level 1 Writing communicates AF1: Write imaginative, communicate meaning on a topic or idea to an outside meaning through simple interesting and thoughtful texts reader? words and phrases. AF2: Produce texts which are link the main ideas in a text? 2C Communicates meaning appropriate to task, reader and structure information in ways appropriate to the task, eg beyond a simple statement. purpose chronology for narratives, list for instructions, key points for Some characteristics of narrative AF3: Organise and present descriptions? / non-narrative writing but the whole texts effectively, include what the reader needs to know to understand the form may not be sustained. sequencing and structuring text, eg provision of appropriate information, naming and Individual ideas are developed in information, events and ideas introducing characters? short sections. 2B Writing communicates meaning. Uses narrative / non- narrative form with some consistency. Sufficient detail to engage the reader. The organisation reflects the purpose of the writing. 2A Writing communicates meaning in a way which is lively and generally holds the reader’s interest. Some characteristics of narrative / non-narrative writing beginning to be developed. Links between ideas and events are mainly clear. Level 3 Writing is often organised, imaginative and clear. The main features of different forms of writing are used appropriately, beginning to be adapted to different readers. Sentence structure Does the child’s writing: AF5: Vary sentences for clarity, include grammatically accurate statements, questions and 2C Writing is structured in purpose and effect exclamations? simple sentences. Some sentences are joined b y ‘and’ or ‘then’. Use simple and compound sentences to make meaning 2B Some sentences linked and clear? extended through connectives Connect ideas together to explain and give more detail, eg other than ‘and’. using because, so, if, when? There is some variation in Expand and adapt elements of sentence structure to gain sentence structure, with more precise meaning, eg lengthening noun phrases, compound and simple varying verbs, developing adverbial phrases? sentences. Variation is evident in word-choices which are sometimes ambitious. 2A Some sentences linked and extended through connectives other than ‘and’. There is some variation in sentence structure, with compound and simple sentences, there may be some subordination within sentences. Descriptive phrases are used to add emphasis. Sequences of sentences extend ideas logically and words are chosen for variety and interest. The basic grammatical structure of sentences is usually correct. Punctuation Does the child’s writing: L1. In their reading or their AF6: Write with technical show understanding of how full stops are used to demarcate writing pupils begin to show accuracy of syntax and units of sense? an awareness of how full punctuation in phrases, clauses include capital letters and full stops to mark beginnings and stops are used. and sentences ends of sentences in different types of tasks? 2CSome evidence of punctuation use question and exclamation marks to demarcate different conventions being used to types of sentences? demarcate units of meaning. use punctuation within the sentence, eg commas in lists? 2B Evidence of some sentence punctuation, (i.e. sentences sometimes demarcated by both a capital letter and a full stop). 2A Growing understanding of the use of punctuation is shown in the use of capital letters and full stops. L3 Punctuation to mark sentences – full stops, capital letters and question marks – is used accurately.
Spelling and Vocabulary Does the child: 2C Some common words from AF8: Use correct spelling draw on knowledge of phonemes and word structure to work the Y 1/ 2 list spelt correctly. AF7: Select appropriate and out how words are spelt? Other words show reliance on effective vocabulary apply knowledge of word structure to spell unfamiliar phonic strategies with some polysyllabic words? recall of visual patterns. use a range of vocabulary to engage interest and convey Vocabulary appropriate to the meaning precisely an imaginatively? subject matter. Some words used effectively. 2B In spelling, phonetically plausible attempts reflect growing knowledge of whole- word structure. Awareness of visual patterns and recall of letter strings. Variation is evident in word-choices which are sometimes ambitious. 2A Spelling of many common monosyllabic words is accurate. Phonetically plausible attempts at polysyllabic words. Variation is evident in word choices which are sometimes ambitious. Descriptive phrases are used to add emphasis. L3 Spelling is usually accurate, including that of common, polysyllabic words. Words are chosen for variety and interest Handwriting L1 Letters are usually clearly shaped and correctly orientated 2C Handwriting is legible despite inconsistencies in orientation, size and use of upper and lower case letters. 2B Handwriting is clear, with ascenders and descenders distinguished, and generally upper and lower case letters are not mixed within the word. 2A Handwriting shows accurate and consistent letter formation. L3 Handwriting is joined and legible.