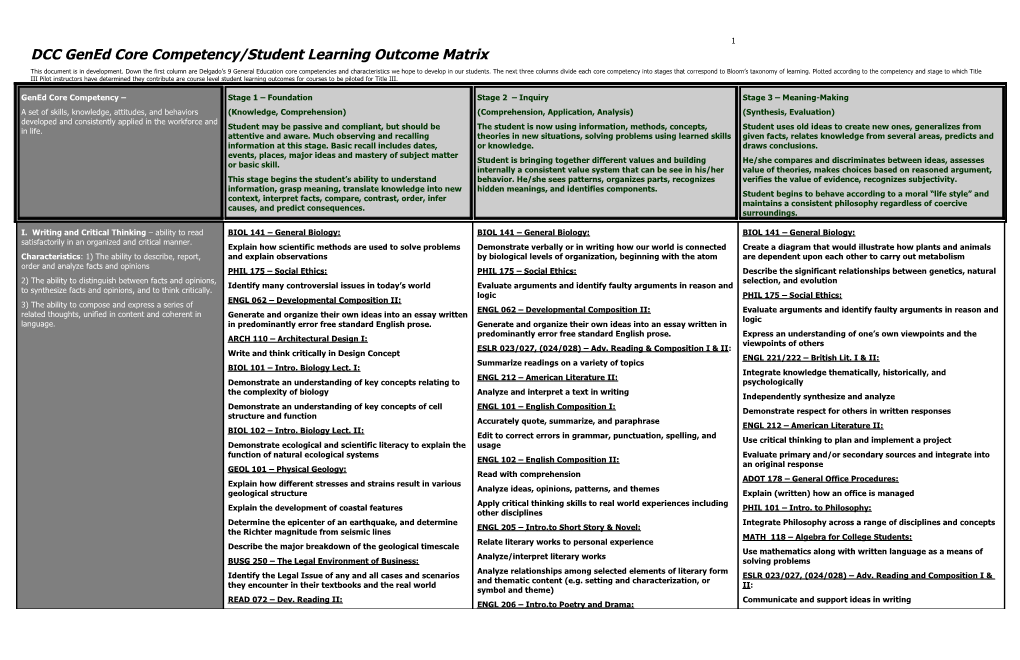
1 DCC GenEd Core Competency/Student Learning Outcome Matrix
This document is in development. Down the first column are Delgado’s 9 General Education core competencies and characteristics we hope to develop in our students. The next three columns divide each core competency into stages that correspond to Bloom’s taxonomy of learning. Plotted according to the competency and stage to which Title III Pilot instructors have determined they contribute are course level student learning outcomes for courses to be piloted for Title III.
GenEd Core Competency – Stage 1 – Foundation Stage 2 – Inquiry Stage 3 – Meaning-Making A set of skills, knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors (Knowledge, Comprehension) (Comprehension, Application, Analysis) (Synthesis, Evaluation) developed and consistently applied in the workforce and Student may be passive and compliant, but should be The student is now using information, methods, concepts, Student uses old ideas to create new ones, generalizes from in life. attentive and aware. Much observing and recalling theories in new situations, solving problems using learned skills given facts, relates knowledge from several areas, predicts and information at this stage. Basic recall includes dates, or knowledge. draws conclusions. events, places, major ideas and mastery of subject matter Student is bringing together different values and building He/she compares and discriminates between ideas, assesses or basic skill. internally a consistent value system that can be see in his/her value of theories, makes choices based on reasoned argument, This stage begins the student’s ability to understand behavior. He/she sees patterns, organizes parts, recognizes verifies the value of evidence, recognizes subjectivity. information, grasp meaning, translate knowledge into new hidden meanings, and identifies components. Student begins to behave according to a moral “life style” and context, interpret facts, compare, contrast, order, infer maintains a consistent philosophy regardless of coercive causes, and predict consequences. surroundings.
I. Writing and Critical Thinking – ability to read BIOL 141 – General Biology: BIOL 141 – General Biology: BIOL 141 – General Biology: satisfactorily in an organized and critical manner. Explain how scientific methods are used to solve problems Demonstrate verbally or in writing how our world is connected Create a diagram that would illustrate how plants and animals Characteristics: 1) The ability to describe, report, and explain observations by biological levels of organization, beginning with the atom are dependent upon each other to carry out metabolism order and analyze facts and opinions PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: Describe the significant relationships between genetics, natural 2) The ability to distinguish between facts and opinions, selection, and evolution Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and to synthesize facts and opinions, and to think critically. logic PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: ENGL 062 – Developmental Composition II: 3) The ability to compose and express a series of ENGL 062 – Developmental Composition II: Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and related thoughts, unified in content and coherent in Generate and organize their own ideas into an essay written logic language. in predominantly error free standard English prose. Generate and organize their own ideas into an essay written in predominantly error free standard English prose. Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the ARCH 110 – Architectural Design I: viewpoints of others ESLR 023/027, (024/028) – Adv. Reading & Composition I & II: Write and think critically in Design Concept ENGL 221/222 – British Lit. I & II: Summarize readings on a variety of topics BIOL 101 – Intro. Biology Lect. I: Integrate knowledge thematically, historically, and ENGL 212 – American Literature II: Demonstrate an understanding of key concepts relating to psychologically the complexity of biology Analyze and interpret a text in writing Independently synthesize and analyze Demonstrate an understanding of key concepts of cell ENGL 101 – English Composition I: Demonstrate respect for others in written responses structure and function Accurately quote, summarize, and paraphrase ENGL 212 – American Literature II: BIOL 102 – Intro. Biology Lect. II: Edit to correct errors in grammar, punctuation, spelling, and Use critical thinking to plan and implement a project Demonstrate ecological and scientific literacy to explain the usage function of natural ecological systems Evaluate primary and/or secondary sources and integrate into ENGL 102 – English Composition II: an original response GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: Read with comprehension ADOT 178 – General Office Procedures: Explain how different stresses and strains result in various Analyze ideas, opinions, patterns, and themes geological structure Explain (written) how an office is managed Apply critical thinking skills to real world experiences including Explain the development of coastal features PHIL 101 – Intro. to Philosophy: other disciplines Determine the epicenter of an earthquake, and determine Integrate Philosophy across a range of disciplines and concepts ENGL 205 – Intro. to Short Story & Novel: the Richter magnitude from seismic lines MATH 118 – Algebra for College Students: Relate literary works to personal experience Describe the major breakdown of the geological timescale Use mathematics along with written language as a means of Analyze/interpret literary works BUSG 250 – The Legal Environment of Business: solving problems Analyze relationships among selected elements of literary form Identify the Legal Issue of any and all cases and scenarios ESLR 023/027, (024/028) – Adv. Reading and Composition I & and thematic content (e.g. setting and characterization, or they encounter in their textbooks and the real world II: symbol and theme) READ 072 – Dev. Reading II: Communicate and support ideas in writing ENGL 206 – Intro. to Poetry and Drama: 2
Use decoding skills in order to read independently at 8-12 Analyze poetry and drama by using interpretative tools Use knowledge of strengths and weaknesses to self-monitor grade level and self-correct writing Write a literary analysis using proper MLA documentation Identify and use context clues to understand the meaning Demonstrate self-awareness of ability as a writer I. Writing and Critical Thinking, (cont.) BIOL 101 – Intro. Biology Lecture I: of unfamiliar vocabulary ENGL 101 – English Composition I: Demonstrate an understanding of key concepts of mechanisms Identify the stated main idea in a paragraph of inheritance and protein synthesis Develop and organize ideas to support and explicit thesis Recognize the supporting details in a paragraph and state statement BIOL 102 – Intro. Biology Lecture II: how they relate to the main idea (pattern of organization) ENGL 102 – English Composition II: Apply a learned strategy to address novel ecological issues/problems Synthesize ideas on a variety of topics GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: ENGL 205 – Intro. to Short Story & Novel: Explain how Plate Tectonics is the universal theory of Geology Analyze others’ literary criticism and apply relevant critical opinions to one’s own analysis and interpretation of literature Explain the differences between metamorphic, igneous, and sedimentary rock and how they are related to the rock cycle Analyze relationships among selected elements of literary form and thematic content MATH 095 – Intro. to Algebra I: GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: Tell the difference between mathematical statement Explain how geological theories relate to modern day life and BUSG 250 – The Legal Environment of Business: modern geological processes, appreciating the planet as a whole Apply these legal issues to come to a conclusion of what would system be a just outcome PSYC 2 40 – Abnormal Psychology: CULA 105 – Theory of Meat, Poultry, & Seafood: Express a tentative personal philosophy regarding the causes Differentiate between all parts of beef, poultry, and game and most effective therapeutic approaches in treating mental disorder Accurately cut and cook meats, poultry, and game Apply the DSM-IV-TR criteria for mental disorder to a character CCSS 107 – College Success Skills: in a major motion picture or work of literature. Analyze what’s required for entering the professional workforce MATH 095 – Intro. to Algebra: MUSC 105 – Music Appreciation: Determine what types of solutions make sense Discuss definitions of Art and Music Write a critical reflection to a piece of music Analyze primary and secondary sources about music including journalism, criticism, and scholarship Explain relationships between music and text ACCT 205 – Financial Accounting: Prepare and interpret basic financial statements for businesses Use accounting information to make investment and other business decisions, and gain competence in business by understanding the language of accounting II. Computation – Ability to understand numerical GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: ARCH 110 – Architectural Design I: GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: data by extracting analyzing and interpreting data, Describe the major breakdown of the Geological timescale Compute and estimate numerical data of their floor plans Explain how geological theories relate to modern day life and apply mathematics in a career setting and use modern geological processes, appreciating the planet as a whole appropriate technology in solving mathematics CULA 105 – Theory of Meat, Poultry, & Seafood: GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: system problems. Accurately identify all weight and measurements required Explain how Plate Tectonics is the universal theory of Geology MATH 095 – Intro. to Algebra: Characteristics: for recipes Explain the differences between metamorphic, igneous, and Calculate the solution using a logical plan 1) The ability to manipulate mathematical language MATH 131 – Trigonometry: sedimentary rock and how they are related to the rock cycle above the basic computational level. MATH 128 – Explorations in College Algebra: Determine how concepts of trigonometry are applied to MATH 131 – Trigonometry 2) The ability to organize information and to recognize solve real world problems in a mathematical setting Question statistics presented in the media rather than blindly Recognize wave patterns in real-world situations and determine patterns among different phenomena. accepting them MATH 091 – Basic Math: what trigonometric functions would be needed to represent 3) An understanding of the importance of logic and self- them mathematically MATH 130 – Pre-Calculus Algebra: 3 discipline in solving problems. Determine the appropriate method to solve basic Arithmetic MATH 095 – Intro. to Algebra: Demonstrate an appreciation for the use of algebraic concepts Problems-specializing in signed numbers in real world occupations Calculate the solution using a logical plan Solving Arithmetic Problems mentally MATH 128 – Explorations in College Algebra: MATH 091 – Basic Math: MATH 130 – Pre-Calculus Algebra: Make better decisions in problem-solving situations by their Use a calculator correctly ability to organize and examine data Articulate the steps involved in solving an algebraic MATH 130 – Pre-Calculus Algebra: equation MATH 118 – Algebra for College Students: Determine the appropriate method to use to solve an algebraic MATH 096 – Intro. Algebra II: Determine the reasonableness of results using mathematical equation knowledge and skills Explain how/when to apply basic algebraic properties MATH 128 – Explorations in College Algebra: II. Computation, (cont.) ACCT 205 – Financial Accounting: Do calculations and make assessments with mathematical Prepare and interpret basic financial statements for businesses information presented in various ways Use accounting information to make investment and other business decisions, and gain competence in business by MATH 118 – Algebra for College Students: understanding the language of accounting Utilize graphs, tables, or charts to organize and interpret various representations of data MATH 096 – Introductory Algebra II: Manipulate mathematical symbols and notation independently to solve problems logically ACCT 205 – Financial Accounting: Record business transactions using accrual method double- entry Generally Accepted Accounting Principles III. Social Issues – Ability to identify significant SOCI 151 – Introduction to Sociology PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: philosophies and lifestyles which societies and Identify emergence of Sociology Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Identify many controversial issues in today’s world individuals have adopted. Identify the three core theories Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and Characteristics: logic logic PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: 1) The ability to analyze a social issue. Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Identify many controversial issues in today’s world 2) The ability to formulate analytical questions about viewpoints of others viewpoints of others behavior. Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason SOCI 151 – Introduction to Sociology SOCI 151 – Introduction to Sociology and logic 3) The ability to locate sources for data. Recognize how individual personal experiences are interrelated Evaluate a social issue Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the 4) An understanding of at least one of the basic to social issues viewpoints of others GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: disciplines in the social sciences and how its principles PSYC 225 – Child Psychology: and theories are applied to an understanding of human Explain how geological theories relate to modern day life and behavior. Examine and discuss critically, any of the principles, issues or modern geological processes, appreciating the planet as a whole conceptual approaches as presented in the course system Connect concepts with real world situations PHIL 101 – Intro. to Philosophy: Apply the concepts to other applied fields of study Demonstrate an appreciation for topics in Philosophy ARCH 110 – Architectural Design I: BIOL 102 – Intro. Biology Lecture II: Identify social issues, theories, and philosophies of Architectural Demonstrate an awareness of how individual choices affect history and styles ecosystems ENGL 102 – English Composition II: Apply critical thinking skills to real world experiences including other disciplines BIOL 101 – Intro. Biology Lecture I: Demonstrate an understanding of key concepts of mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis BIOL 102 – Intro. Biology Lecture II: 4 Explain the complexity of the social, economic, and political dynamics affecting solutions to ecological problems GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: Explain how Plate Tectonics is the universal theory of Geology BUSG 250 – The Legal Environment of Business: Apply these legal issues to come to a conclusion of what would be a just outcome IV. Oral Communication – Ability to conduct public ADOT 178 – General Office Procedures: BIOL 141 – General Biology: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: speaking activities, small group communication skills, Present orally and professionally a research topic Demonstrate verbally or in writing how our world is connected Identify many controversial issues in today’s world and interpersonal communication. individually and in a group. by biological levels of organization, beginning with the atom Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and Characteristics: GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: logic 1) The ability to describe, report, order and analyze Describe the major breakdown of the Geological timescale Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the facts and opinions viewpoints of others PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and 2) The ability to present and express a series of related logic ADOT 178 – General Office Procedures: thoughts, unified in content and coherent in language. Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Explain (orally) how an office is managed. Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason viewpoints of others and logic ENGL 221/222 – British Lit. I & II: GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Debate ideas in a meaningful way. viewpoints of others Explain how Plate Tectonics is the universal theory of Geology Demonstrate respect for others in oral responses BUSG 250 – The Legal Environment of Business: ESLR 023/027, (024/028) – Advanced Reading and Composition Identify the Legal Issue of any and all cases and scenarios they I & II: encounter in their textbooks and the real world Provide meaningful feedback to peers & use feedback from CULA 105 – Theory of Meat, Poultry, & Seafood: others effectively Accurately order and explain the different cuts of meat ARCH 110 – Architectural Design I: CULA 105 – Theory of Meat, Poultry, & Seafood: Demonstrate oral communication skills and public speaking in their projects Accurately follow a recipe both individually and with a group GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: MATH 096 – Intro. Algebra II: Explain how geological theories relate to modern day life and Work constructively in groups to solve problems modern geological processes, appreciating the planet as a whole system V. Leadership – Ability to lead and participate in ADOT 178 – General Office Procedures: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: activities and will develop the capability of self-direction. Increase student’s self-confidence Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Identify many controversial issues in today’s world PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and V. Leadership, (cont.) logic logic Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason viewpoints of others viewpoints of others and logic ENGL 221/222 – British Lit. I & II: ESLR 023/027, (024/028) – Advanced Reading and Composition Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the I & II: viewpoints of others Take self-responsibility for learning Use knowledge of strengths and weaknesses to self-monitor and self-correct writing ADOT 101 – Keyboarding: Demonstrate self-awareness of ability as a writer Demonstrate understanding of proper keyboarding techniques independently CCSS 107 – College Success Skills: Successfully plan their college curriculum Set educational and career goals 5 Apply study skills learned in CCSS to other educational situations Demonstrate self-awareness and self confidence MATH 096 – Intro. Algebra II: Work constructively in groups to solve problems ACCT 205 – Financial Accounting: Have an increased awareness of proper ethical business conduct VI. Citizenry/Respect for Humanity – Ability to PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: recognize individuals’ values, understand and respect Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Identify many controversial issues in today’s world for the values of others and implementation of values in society. Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and and logic logic logic Characteristics: Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the 1) Insight into human experience in other places and at viewpoints of others viewpoints of others viewpoints of others other times. ENGL 206 – Intro. to Poetry and Drama: GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: 2) The ability to reflect on experience, belies, and values Demonstrate a refined appreciation for poetry and drama as art Explain how geological theories relate to modern day life and forms modern geological processes, appreciating the planet as a whole 3) An understanding and appreciation of at least one of system the areas associated with the fine arts – drama, poetry, Connect to the humanities: connect themes in poetry and drama music, historical and imaginative literature, philosophy, to human experience HUMA 105 – Humanities Through the Arts: and rhetoric. ENGL 221/222 – British Lit. I & II: Demonstrate an awareness of how their/other’s biases shape the world Articulate an appreciation for literature as a way of understanding human nature ENGL 212 – American Literature II: Make connections between content and larger world issues BIOL 102 – Intro. Biology Lecture II: Explain the complexity of the social, economic, and political dynamics affecting solutions to ecological problems Demonstrate an awareness of how individual choices affect ecosystems GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: Explain how Plate Tectonics is the universal theory of Geology ACCT 205 – Financial Accounting: Have an increased awareness of proper ethical business conduct BUSG 250 – The Legal Environment of Business: Apply these legal issues to come to a conclusion of what would be a just outcome PHIL 101 – Intro. to Philosophy: Demonstrate an awareness of other’s beliefs HUMA 105 – Humanities Through the Arts: Express the impact of the course content on their life experience Demonstrate an appreciation for topics in Humanities 6 VII. Cultural Expressions – Ability to identify PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: different cultural responses to environment demands, Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Identify many controversial issues in today’s world and recognize cultural diversity. Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and Characteristics: and logic logic logic 1) Insight into human experience in other places and at Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the Express an understanding of one’s own viewpoints and the other times. viewpoints of others viewpoints of others viewpoints of others MUSC 105 – Music Appreciation: ENGL 102 – English Composition II: PSYC 240 – Abnormal Psychology: Accurately use concepts and vocabulary relating to the Analyze ideas, opinions, patterns, and themes Express a tentative personal philosophy regarding the causes elements of music, specifically when listening to a piece of and most effective therapeutic approaches in treating mental BIOL 101 – Intro. Biology Lecture I: music disorder Demonstrate an understanding of key concepts of mechanisms Identify musical genres, styles, and historical periods GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: of inheritance and protein synthesis Explain how geological theories relate to modern day life and BIOL 102 – Intro. Biology Lecture II: modern geological processes, appreciating the planet as a whole Demonstrate an awareness of how individual choices affect system ecosystems GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: Explain how Plate Tectonics is the universal theory of Geology BUSG 250 – The Legal Environment of Business: Identify the Legal Issue of any and all cases and scenarios they encounter in their textbooks and the real world VIII. Technology – Ability to apply basic computer PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: ADOT 101 – Keyboarding: ADOT 101 – Keyboarding: technology when using systematic and critical Identify many controversial issues in today’s world Building speed and accuracy Preparing business documents processes. of one’s own viewpoints and the viewpoints of others ADOT 105 – Survey of Computer Applications: ADOT 105 – Survey of Computer Applications: Characteristics: ADOT 101 – Keyboarding: Develop which Microsoft Office Documents to use in specific Organize and present information orally and in writing with 1) The ability to locate sources for data. circumstances visual aids Utilize proficiently the keyboard ADOT 106 – Word Processing: ADOT 106 – Word Processing: ADOT 105 – Survey of Computer Applications: Load, use and close the Word Program. Use the mouse for input Create a new publication, save the publication, and then reopen Use discipline-related terminology appropriately as well as screen control it and make additions and deletions ADOT 106 – Word Processing: ADOT 178 – General Office Procedures: Use a Word template and Wizard to create standard documents Define Word Processing terms Prepare business documents ADOT 264 – Database Applications: Recognize fonts ADOT 264 – Database Applications: Plan and construct table relationships ADOT 264 – Database Applications Define and construct new database components Plan and construct a full-featured, multi-component, multi- Revise existing database components table, relational database. ADOT 265 – Spreadsheet Applications: ADOT 265 – Spreadsheet Applications: ADOT 265 – Spreadsheet Applications: Utilize functions and create formulas Create, develop, manipulate and enhance spreadsheets Develop and use templates CADD 125 – Drafting I: ARCH 110 – Architectural Design I: Integrate spreadsheets with other Microsoft Office applications Demonstrate mature drafting habits Use technology/basic computer skills (internet) to research CADD 201 – Introduction to Computer-Aided Design ENGL 102 – English Composition II: their design Create standard 2D drawings using CADD tools Integrate current, accurate, and valid information from various CADD 125 – Drafting I: sources, without incident of plagiarism Print CADD technical drawing to industry standards Explain drafting principles & use proper drafting ACCT 218 – Payroll Accounting: CADD 125 – Drafting I: terminology Develop and keep accurate accounts for the company’s payroll Create accurate technical drawings ACCT 218 – Payroll Accounting: transactions ACCT 218 – Payroll Accounting: Create payroll register and employee payroll records. Compute accurate overtime pay for employees paid hourly or at Complete problems that incorporate the entire payroll process, Computation of gross pay and various payroll deductions another rate, such as semi-monthly both manually and computerized 7 BIOL 101 – Intro. Biology Lecture I: GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: Demonstrate an understanding of key concepts relating to the Explain how geological theories relate to modern day life and complexity of biology, the chemical nature of life, and cell modern geological processes, appreciating the planet as a whole structure and function system Demonstrate an understanding of key concepts of mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis
VIII. Technology, (cont.) GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: Explain how Plate Tectonics is the universal theory of Geology MATH 131 – Trigonometry Analyze data to solve triangles and determine areas in real- world situations MATH 130 – Pre-Calculus Algebra: Use technology to enhance the understanding of an algebraic concept MATH 128 – Explorations in College Algebra: Utilize technology to assist in reasoning, decision-making and problem-solving VIX. Logic – Ability to demonstrate the use of PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: PHIL 175 – Social Ethics: applicable scientific techniques, collect observations and Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and Evaluate arguments and identify faulty arguments in reason and evaluate the validity of the conclusion. and logic logic logic Characteristics: BIOL101 – Intro. Biology Lecture: ENGL 102 – English Composition II: ARCH 110 – Architectural Design I: 1) An understanding of at least one branch of the Demonstrate an understanding of key concepts cell Analyze ideas, opinions, patterns, and themes Demonstrate the use of application, scientific and artistic natural sciences. structure and function techniques Apply critical thinking skills to real world experiences including 2) The ability to follow the sequential steps necessary to BIOL 102 – Intro. Biology Lecture II: other disciplines ENGL 102 – English Composition II: analyze and solve a problem. Demonstrate ecological and scientific literacy to explain the BIOL101 – Intro. Biology Lecture I: Integrate current, accurate, and valid information from various 3) The ability to recognize when the absence of data function of natural ecological systems sources, without incident of plagiarism impedes the formation of a sound conclusion. Demonstrate an understanding of key concepts of mechanisms GEOL101 – Physical Geology: of inheritance and protein synthesis PSYC 240 – Abnormal Psychology: Describe the major breakdown of the Geological timescale BIOL 102 – Intro. Biology Lecture II: Differentiate the symptomology of various mental disorders, such as Anxiety Disorders, Depression, Bipolar Disorder, BUSG 250 – The Legal Environment of Business: Apply a learned strategy to address novel ecological Schizophrenia, and personality Disorders issues/problems Demonstrate an understanding of the legal principles of Explain 2-3 approaches (Learning theory, Psychodynamic, business GEOL101 – Physical Geology: cognitive, Humanistic, and Physiological) in treating mental Demonstrate the knowledge of civil, common, and tort law Explain how Plate Tectonics is the universal theory of Geology disorders that apply to those involved in developing and running a Explain the differences between metamorphic, igneous, and GEOL 101 – Physical Geology: business sedimentary rock and how they are related to the rock cycle Explain how geological theories relate to modern day life and Identify the Legal Issue of any and all cases and scenarios MATH 131 – Trigonometry modern geological processes, appreciating the planet as a whole they encounter in their textbooks and the real world system Using identities to sharpen your logical and analytical thought processes MATH 095 – Intro. to Algebra I: MATH 095 – Intro. to Algebra I: Determine what types of solutions make sense Calculate the solution using a logical plan Calculate the solution using a logical plan MATH 118 – Algebra for College Students: MATH 128 – Explorations in College Algebra: Use mathematics along with written language as a means of Make predictions about the future given available information solving problems Math 096 – Intro. to Algebra II: BUSG 250 – The Legal Environment of Business: Apply some of what is learned to everyday life 8 Identify the Legal Issue of any and all cases and scenarios they encounter in their textbooks and the real world MATH 128 – Explorations in College Algebra: Use logical reasoning to solve problems in their lives MUSC 105 – Music Appreciation: Explain relationships between music and text 9 Sample Core Competency Matrix Using LCTCS Discipline Outcomes and Bloom’s Domains This sample matrix model uses adapted outcomes from the LA Dept. of Ed. K-12 Technology Standards (February, 2003), LCTCS guidelines, DCC GenEd Assessment Committee’s Competencies, and Bloom’s domains as a framework for defining levels of competency and the corresponding learning outcomes which would be achieved through GenEd courses and possibly courses in specific majors.
Student Learning Outcomes That Fall Within Each Level of The Competency Categories
GenEd Core Competency Levels Communication Computation/Technology Cultural Sensitivity Citizenry/Social Value Logic/Critical Thinking
Foundation: Use correct syntax, usage, grammar Replicate the competencies gained through Explain the complexities in a global Analyze historical fact and Exhibit ethical behavior. and mechanics to write clear sentences the study of high school algebra and culture. interpretations. Student may be passive and compliant, but Utilize basic scientific and paragraphs. geometry. should be attentive and aware. Much Explain, through personal self- Analyze and communicate the language and processes and observing and recalling information at this Distill a primary purpose into a single, Use mathematics to solve problems and reflection, what it means to live in a values and processes that are be able to distinguish stage. Basic recall includes dates, events, compelling statement. determine if the solutions are reasonable. diverse society. used to formulate theories between scientific and non- places, major ideas and mastery of subject regarding the social context of scientific explanations. Order and develop major points in a Use mathematics to model real world Analyze significant primary texts and matter. individual human behavior. reasonable and convincing manner behaviors and apply mathematical works of art as forms of cultural Analyze, evaluate and test This stage begins the student’s ability to based upon a primary purpose. concepts to solutions for real-world expression. Examine the impact of scientific hypotheses. understand information, grasp meaning, problems. behavioral and social scientific Summarize what someone has said. Explore global cultural diversity and Conduct an experiment, translate knowledge into new context, research on major Use telecommunications to collaborate, cultural similarities. collect and analyze data, and interpret facts, compare, contrast, order, Summarize what someone has written. contemporary issues. publish, and interact with peers, experts interpret results in a infer causes, and predict consequences. Explore the ethical implications of Differentiate between fact and opinion. and other audiences. Examine the impact of laboratory setting. cultural identity and cultural behavioral and social scientific Use a variety of media and formats to integrity. research on individuals. communicate and present information and Analyze the contributions of the past ideas to mult. Audiences. Identify and describe social to the contemporary world. institutions, structures, and Demonstrate an awareness of the ethical, Recognize and articulate the processes. cultural, and societal issues related to diversity of human experience across technology. a range of historical periods and the Practice responsible use of technology complexities of a global culture and systems, information, and software. society.
Student Learning Outcomes That Fall Within Each Level of The Competency Categories
GenEd Core Competency Levels Communication Computation/Technology Cultural Sensitivity Citizenry/Social Value Logic/Critical Thinking
Inquiry: Develop appropriate rhetorical patterns Build upon the competencies gained Explain ways in which human Recognize and articulate the Exhibit ethical behavior. (i.e. narration, exemplification, process, through the study of high school algebra expression expresses the culture and diversity of human experience The student is now using information, Analyze, evaluate and test comparison/contrast, classification, and geometry. values of its time and place. across a range of historical methods, concepts, theories in new scientific hypotheses. cause/effect, definition, and periods and the complexities of situations, solving problems using learned Utilize technology for reasoning and Analyze and describe the impact of argumentation) and other special a global culture. Identify unifying principles skills or knowledge. problem solving. scientific discovery on human functions (i.e. analysis or research) in and patterns in nature, and thought and behavior. Take ethical stands based upon Student is bringing together different values writing or speaking processes. Apply reasoning to analyze data and apply them to problems or appropriate research. and building internally a consistent value graphs. Recognize the ways in which both issues of a scientific nature, Analyze and evaluate oral and/or system that can be see in his/her behavior. change and continuity have affected Explore the relationship recognizing the values of written expression by listening and Make meaningful connections between He/she sees patterns, organizes parts, human history between the individual and nature’s diversity. reading critically for elements that mathematics and other disciplines. recognizes hidden meanings, identifies society as it affects personal reflect an awareness of situation, Analyze and compare geographic, Analyze historical facts and components. Use mathematics to model real world behavior. audience, purpose, and diverse points cultural, and religious institutions interpretations. behaviors and apply mathematical of view. across a range of historical periods. Explain how the relationship concepts to solutions for real-world Practice critical and analytical between individual and society Demonstrate the procedures of problems. methodologies. has affected the family and the planning, organizing, composing, Evaluate the technology selected, the community. Deliberate critically about revising, and editing included in the process, and the final results of a product. how individuals are writing and/or speaking process. influenced by social and Use technology tools to enhance learning, economic institutions and increase productivity, and promote how that belief system may creativity. differ from others. 10
Student Learning Outcomes That Fall Within Each Level of The Competency Categories
GenEd Core Competency Levels Communication Computation/Technology Cultural Sensitivity Citizenry/Social Value Logic/Critical Thinking
Use technology to locate, evaluate, and collect information from a variety of sources. 11
Student Learning Outcomes That Fall Within Each Level of The Competency Categories
GenEd Core Competency Levels Communication Computation/Technology Cultural Sensitivity Citizenry/Social Value Logic/Critical Thinking
Meaning-Making: Manage and coordinate information Use mathematics to model real world Assess the ideas, forces and Exhibit ethical behavior. gathered from multiple sources for the behaviors and apply mathematical values that have created the Student uses old ideas to create new ones, Analyze, evaluate and test purposes of problem solving and concepts to solutions for real-world modern world. generalizes from given facts, relates scientific hypotheses. decision making. problems. knowledge from several areas, predicts and Use appropriate principles, draws conclusions. Demonstrate the use of evidence, Use productivity tools to work methods, and technologies to analysis and persuasive strategies. collaboratively in developing technology- draw conclusions from He/she compares and discriminates rich, authentic, student-centered products. research, and apply those between ideas, assesses value of theories, conclusions to one’s life and makes choices based on reasoned Demonstrate positive attitude toward society. argument, verifies the value of evidence, technology uses that support lifelong recognizes subjectivity. learning, collaboration, personal pursuits, Analyze and compare political, and productivity. economic, and intellectual Student begins to behave according to a institutions across a range of moral “life style” and maintains a consistent Demonstrate a sound understanding of the historical periods. philosophy regardless of coercive nature and operation of technology surroundings. systems. Draw on historical perspective to evaluate contemporary problems and issues. 12 GenEd Core Competency Contribution by Non-GenEd Courses or Programs This table contains examples of how Arizona Western’s Business & Technology Division Contributed to their GenEd competencies. This is a set of examples only and not intended to be exhaustive list. GenEd Core Competency and Stage Business & Technology Contribution Communication - Inquiry The division teaches three courses with a GenEd designation. In BIX 100, ECN 240 and ECN 250, the writing is intensive with several assignments with written requirements in excess of the minimal ‘writing across the curriculum’ requirement. Most courses taught in the division have a writing component. As a result of the emphasis on GenEd outcomes, even the vocational technology area has incorporated a writing component comprised of the welding students developing a small business plan. Critical Thinking – Foundation Students use various levels of analysis in several of the business courses. Economics, accounting, quantitative analysis, legal environment of business all have a strong emphasis on problem solving that includes incorporation of both inductive and deductive reasoning skills. Other courses develop student critical thinking skills in different ways. As an example, in computer programming, abstract and nonlinear reasoning are necessary to envision what the computer will do with the instructions written by the student Quantitative Analysis – Inquiry Quantitative analysis is a core component of accounting, economics, quantitative analysis, as well as the vocational technology courses. Applied Technology – Foundation to Meaning-Making Students learn their technology skills in this division. Instruction starts at the very bottom and works through programming, networking, and web design.