Density = Mass Volume
Name: Density Canisters
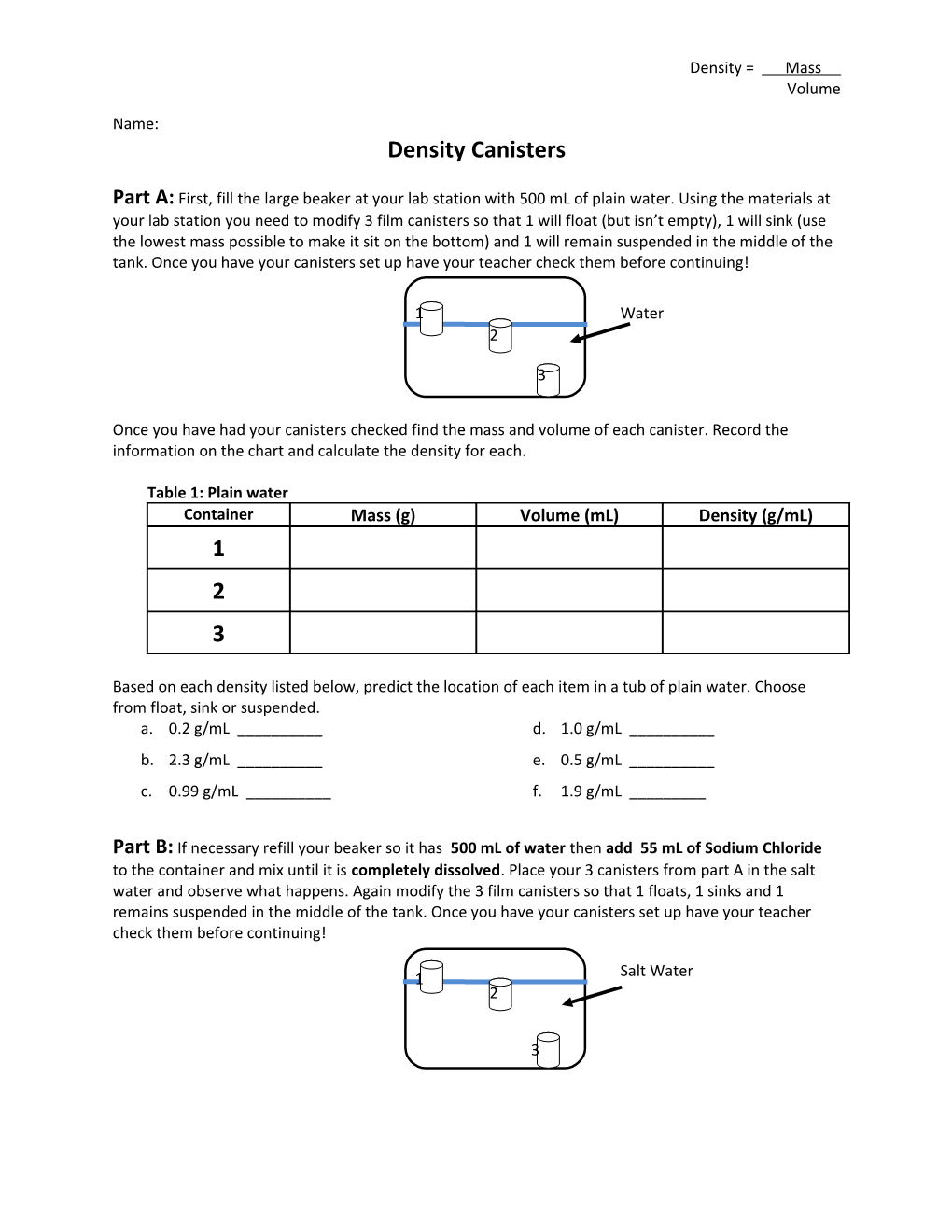
Part A: First, fill the large beaker at your lab station with 500 mL of plain water. Using the materials at your lab station you need to modify 3 film canisters so that 1 will float (but isn’t empty), 1 will sink (use the lowest mass possible to make it sit on the bottom) and 1 will remain suspended in the middle of the tank. Once you have your canisters set up have your teacher check them before continuing!
1 Water 2
3
Once you have had your canisters checked find the mass and volume of each canister. Record the information on the chart and calculate the density for each.
Table 1: Plain water Container Mass (g) Volume (mL) Density (g/mL) 1 2 3
Based on each density listed below, predict the location of each item in a tub of plain water. Choose from float, sink or suspended. a. 0.2 g/mL ______d. 1.0 g/mL ______b. 2.3 g/mL ______e. 0.5 g/mL ______c. 0.99 g/mL ______f. 1.9 g/mL ______
Part B: If necessary refill your beaker so it has 500 mL of water then add 55 mL of Sodium Chloride to the container and mix until it is completely dissolved. Place your 3 canisters from part A in the salt water and observe what happens. Again modify the 3 film canisters so that 1 floats, 1 sinks and 1 remains suspended in the middle of the tank. Once you have your canisters set up have your teacher check them before continuing!
1 Salt Water 2
3 Density = Mass Volume
Once you have had your canisters checked find the mass and volume of each canister. Record the information on the chart (on the next page) and calculate the density for each. Table 2: Salt water Container Mass (g) Volume (mL) Density (g/mL) 1 2 3
Based on each density listed below, predict the location of each item in a tub of salt water. Choose from float, sink or suspended. a. 0.2 g/mL ______d. 1.0 g/mL ______b. 2.3 g/mL ______e. 0.5 g/mL ______c. 0.99 g/mL ______f. 1.9 g/mL ______
Questions: 1.) Explain what happened to the canisters when you put them in salt water instead of plain water.
2.) What did you have to do to the mass of canister 3 to get it to sink in the salt water?
3.) What does the salt water do to the density of each canister?
4.) What conclusion can you make about the difference between plain water and salt water?
5.) The density of the Earth can be calculated by knowing a few different parameters. What are they?
6.) Calculate the density of Earth. Show ALL your work (hint: convert first) Volume of a sphere = (4/3) π r3 Diameter = 12,718 km Mass = 6,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 metric tons
7.) How do you think we estimate how heavy the Earth is? Density = Mass Volume