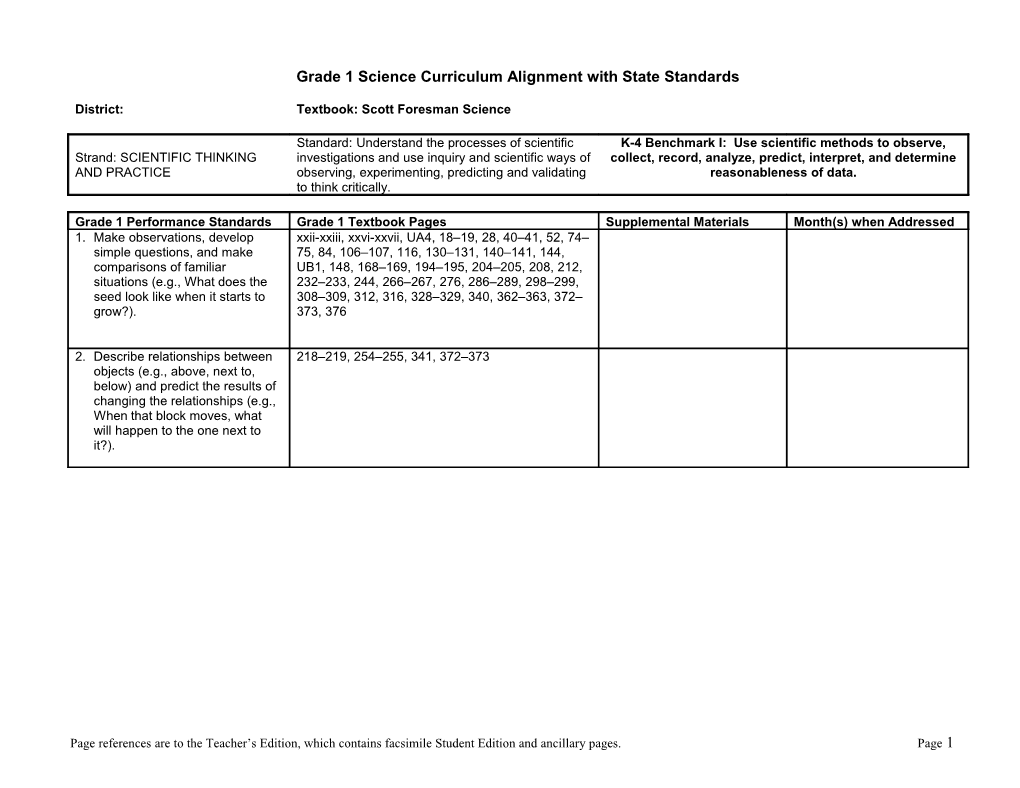
Grade 1 Science Curriculum Alignment with State Standards
District: Textbook: Scott Foresman Science
Standard: Understand the processes of scientific K-4 Benchmark I: Use scientific methods to observe, Strand: SCIENTIFIC THINKING investigations and use inquiry and scientific ways of collect, record, analyze, predict, interpret, and determine AND PRACTICE observing, experimenting, predicting and validating reasonableness of data. to think critically.
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Make observations, develop xxii-xxiii, xxvi-xxvii, UA4, 18–19, 28, 40–41, 52, 74– simple questions, and make 75, 84, 106–107, 116, 130–131, 140–141, 144, comparisons of familiar UB1, 148, 168–169, 194–195, 204–205, 208, 212, situations (e.g., What does the 232–233, 244, 266–267, 276, 286–289, 298–299, seed look like when it starts to 308–309, 312, 316, 328–329, 340, 362–363, 372– grow?). 373, 376
2. Describe relationships between 218–219, 254–255, 341, 372–373 objects (e.g., above, next to, below) and predict the results of changing the relationships (e.g., When that block moves, what will happen to the one next to it?).
Page references are to the Teacher’s Edition, which contains facsimile Student Edition and ancillary pages. Page 1 Grade 1 Science Curriculum Alignment with State Standards
District: Textbook: Scott Foresman Science
Standard I: Understand the processes of scientific K-4 Benchmark II: Use scientific thinking and knowledge Strand: SCIENTIFIC THINKING investigations and use inquiry and scientific ways of and communicate findings. AND PRACTICE observing, experimenting, predicting and validating to think critically.
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Know that simple investigations xxxii, 40–41, 52, 144, 180, 181, 204–205, 208, 212, do not always turn out as planned. 232–233, 244, 245, 298–299, 308–309, 312, 362– 363, 372–373, 376
K-4 Benchmark III: Use mathematical skills and Standard I: Understand the processes of scientific vocabulary to analyze data, understand patterns and Strand: SCIENTIFIC THINKING investigations and use inquiry and scientific ways of relationships, and communicate findings. AND PRACTICE observing, experimenting, predicting and validating to think critically.
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Use numbers and mathematical 108–109, 132–133, 140–141, 170–171, 238–239, language (e.g., “addition” instead of 268–269, 300–301, 316, 330–331, 364–365 “add to,” “subtraction” instead of “take away”) to describe phenomena.
Page references are to the Teacher’s Edition, which contains facsimile Student Edition and ancillary pages. Page 2 Grade 1 Science Curriculum Alignment with State Standards
District: Textbook: Scott Foresman Science
Standard I (Physical Science): Understand the structure and properties of matter, the K-4 Benchmark I: Recognize that matter has different Strand: CONTENT OF SCIENCE characteristics of energy, and the interactions forms and properties. between matter and energy
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Observe that the three states of 150–153, 154–155, 158–159, 168–169, 178–179, matter (i.e., solids, liquids, and 186–187, 188–189, UC2, 210–211, 218–221, 226– gases) have different properties 229 (e.g., water can be liquid, ice, or steam). 2. Describe simple properties of 146–147, 154–157, 158–159, 168–169, 208, 212, matter (e.g., hardness, flexibility, 213, 216–217, 222–225, 228–229, 232–233, 234– transparency). 235, 238–239, 258–259, 286–287, 298–299
Standard I (Physical Science): Understand the structure and properties of matter, the K-4 Benchmark II: Know that energy is needed to get Strand: CONTENT OF SCIENCE characteristics of energy, and the interactions things done and that energy has different forms. between matter and energy
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Observe and describe how UB2, 158–159, 204–205, 222–223, 226–229, 230– energy produces changes (e.g., 231, 240, 272, 274–275, 276, 278–281, 282–283, heat melts ice, gas makes car go 284–285, 290–293, 294–297, 304, 312 uphill, electricity makes TV work).
Page references are to the Teacher’s Edition, which contains facsimile Student Edition and ancillary pages. Page 3 Grade 1 Science Curriculum Alignment with State Standards
District: Textbook: Scott Foresman Science
Standard I (Physical Science): Understand the structure and properties of matter, the K-4 Benchmark III: Identify forces and describe the Strand: CONTENT OF SCIENCE characteristics of energy, and the interactions motion of objects. between matter and energy
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Describe ways to make things UC1, 242–243, 244, 245, 246–249, 250–251, 252– move, what causes them to stop, 253, 256–259, 260–261, 266–267, 272, 308–309, and what causes a change of 310–311, 372–373, 374–375, 376 speed, or change of direction.
2. Observe that gravity makes UC3, UC4, 242–243, 246–249, 254–255 things fall to the ground unless something holds them up.
Page references are to the Teacher’s Edition, which contains facsimile Student Edition and ancillary pages. Page 4 Grade 1 Science Curriculum Alignment with State Standards
District: Textbook: Scott Foresman Science
Standard II (Life Science): Understand the properties, structures, and processes of living K-4 Benchmark I: Know that living things have diverse Strand: CONTENT OF SCIENCE things and the interdependence of living things and forms, structures, functions, and habitats. their environments.
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Know that living organisms (e.g., UA2, 2–3, 4, 6–7, 10–11, 12–13, 18–19, 24, 29, plants, animals) have needs (e.g., 30–33, 34–35, 36–37, 38–39, 40–41, 48, 58–61, water, air, food, sunlight). 68–71, 114–115, 116, 117, 118–121, 122–125, 126–129, 130–131, 136, 140–141, 142–143, 144, 156–157, 188–191, 312, 320–321 2. Know that living organisms (e.g., UA2, 24, 26–27, 28, 29, 30–33, 34–35, 36–37, 38– plants, animals) inhabit various 39, 40–41, 42–43, 46–47, 48, 50–51, 52, 54–55, environments and have various 58–61, 62–67, 68–71, 72–73, 74–75, 76–77, 94– external features to help them 95, 114–115, 118–121, 122–125, 126–129, 130– satisfy their needs (e.g., leaves, 131, 136, 140–141, 142–143, 160–165 legs, claws).
3. Describe the differences and 8–9, 10–11, 12–13, 30–33, 34–35, 36–37, 38–39, similarities among living organisms 40–41, 42–43, 46–47, 53, 56–57, 58–61, 62–67, (e.g., plants, animals). 70–71, 74–75, 90, 93, 94–97, 100–101, 104–105, 106–107, 130–131, 132–133, 140–141, 174–175 4. Observe that living organisms UA3, 18–19, 82–83, 84, 86–91, 92–93, 98–99, (e.g., plants, animals) have 104–105, 106–107, 174–175 predictable but varied life cycles.
Page references are to the Teacher’s Edition, which contains facsimile Student Edition and ancillary pages. Page 5 Grade 1Science Curriculum Alignment with State Standards
District: Textbook: Scott Foresman Science
Standard II (Life Science): Understand the K-4 Benchmark II: Know that living things have properties, structures, and processes of living similarities and differences and that living things change Strand: CONTENT OF SCIENCE things and the interdependence of living things and over time. their environments.
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Identify differences between living 2–3, 4, 5, 14–17, 20–21, 154–155 and nonliving things.
2. Recognize the differences 8–9, 82–83, 84, 85, 86–91, 92–93, 94–97, 98–99, between mature and immature 100–103, 104–105, 108–109 plants and animals (e.g., trees/seedlings, dogs/puppies, cats/kittens).
Standard II (Life Science): Understand the properties, structures, and processes of living K-4 Benchmark III: Know the parts of the human body and Strand: CONTENT OF SCIENCE things and the interdependence of living things and their functions. their environments.
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Describe simple body functions 12–13, 58-61, 80, 88, 160–165, 294–295, 300–301 (e.g., breathing, eating).
2. Describe the basic food 164–165, 294–297, 300–301, 342–345, 346–347, requirements for humans. 348–351, 364–365
3. Describe how some parts of 60–61 human bodies differ from similar This objective can also be developed from: parts of other animals (e.g., hands 8–9, 38, 54–57, 58–61, 62–67, 80 and feet/paws; ears).
Page references are to the Teacher’s Edition, which contains facsimile Student Edition and ancillary pages. Page 6 Grade 1Science Curriculum Alignment with State Standards
District: Textbook: Scott Foresman Science
Standard III (Earth and Space Science): Understand the structure of Earth, the solar system, K-4 Benchmark I: Know the structure of the solar system and the universe, the interconnections among Strand: CONTENT OF SCIENCE and the objects in the universe. them, and the processes and interactions of Earth’s systems.
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Observe the changes that occur UD1, 314–315, 318–321, 322–323, 324–327, 328– in the sky as day changes into night 329 and night into day.
2. Describe the basic patterns of objects as they move through the sky: sun appears in the day 314–315, 317, 318–321, 322–323 moon appears at night but 318–319, 326–327, 328–329 can sometimes be seen during the day sun and moon appear to 289, 314–315, 318–321, 324–327 move across the sky moon appears to change 318, 326–327, 328–329, 330–331 shape over the course of a month.
3. Recognize that the sun, moon, 288–289, 314, 320–321, 322–323, 324–327 and stars all appear to move slowly across the sky.
Page references are to the Teacher’s Edition, which contains facsimile Student Edition and ancillary pages. Page 7 Grade 1 Science Curriculum Alignment with State Standards
District: Textbook: Scott Foresman Science
Standard III (Earth and Space Science): Understand the structure of Earth, the solar system, K-4 Benchmark II: Know the structure and formation of Strand: CONTENT OF SCIENCE and the universe, the interconnections among Earth and its atmosphere and the processes that shape them, and the processes and interactions of Earth’s them. systems.
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Know that simple tools can be xxix, 178–179, 180, 182–185, 194–195, 196–197, used to measure weather conditions 200, 206–207, 208, 209, 276 (e.g., thermometer, wind sock, hand held anemometer, rain gauge) and that measurements can be recorded from day to day and across seasons.
2. Know that there are different 26–27, 30–33, 34–35, 36–37, 38–39, 50–51, 62– climates (e.g., desert, arctic, 63, 70–71, 122–125, 126–129, 130–131, UB3, rainforest). 190–191, 192–193
Page references are to the Teacher’s Edition, which contains facsimile Student Edition and ancillary pages. Page 8 Grade 1 Science Curriculum Alignment with State Standards
District: Textbook: Scott Foresman Science
Standard I: Understand how scientific discoveries, K-4 Benchmark I: Describe how science influences Strand: SCIENCE AND SOCIETY inventions, practices, and knowledge influence, and decisions made by individuals and societies. are influenced by, individuals and societies.
Grade 1 Performance Standards Grade 1 Textbook Pages Supplemental Materials Month(s) when Addressed 1. Know that germs can be xxxii, 75, 145D transmitted by touching, breathing, This objective can also be developed from: and coughing, and that washing 18–19, 84, 148, 168–169, 204–205, 212 hands helps prevent the spread of germs.
2. Describe how science has 160–165, 166–167, 200, 262–263, 290–293, UD4, assisted in creating tools (e.g., 324–325, 334–335, 342–345, 346–347, 348–351, plows, knives, telephones, cell 352–355, 356–359, 360–361, 362–363, 368, 374– phones, computers) to make life 375 easier and more efficient.
3. Describe how tools and machines 160–165, 166–167, 174–175, 262–263, UD4, 324– can be helpful, harmful, or both 325, 334–335, 338–339, 340, 342–345, 346–347, (e.g., bicycles, cars, scissors, 348–351, 352–355, 356–359, 360–361 stoves).
4. Know that men and women of all 24, 48, 80, 112, 136, 176, 200, 272, 304, 336, 368 ethnic and social backgrounds practice science and technology.
Page references are to the Teacher’s Edition, which contains facsimile Student Edition and ancillary pages. Page 9