Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
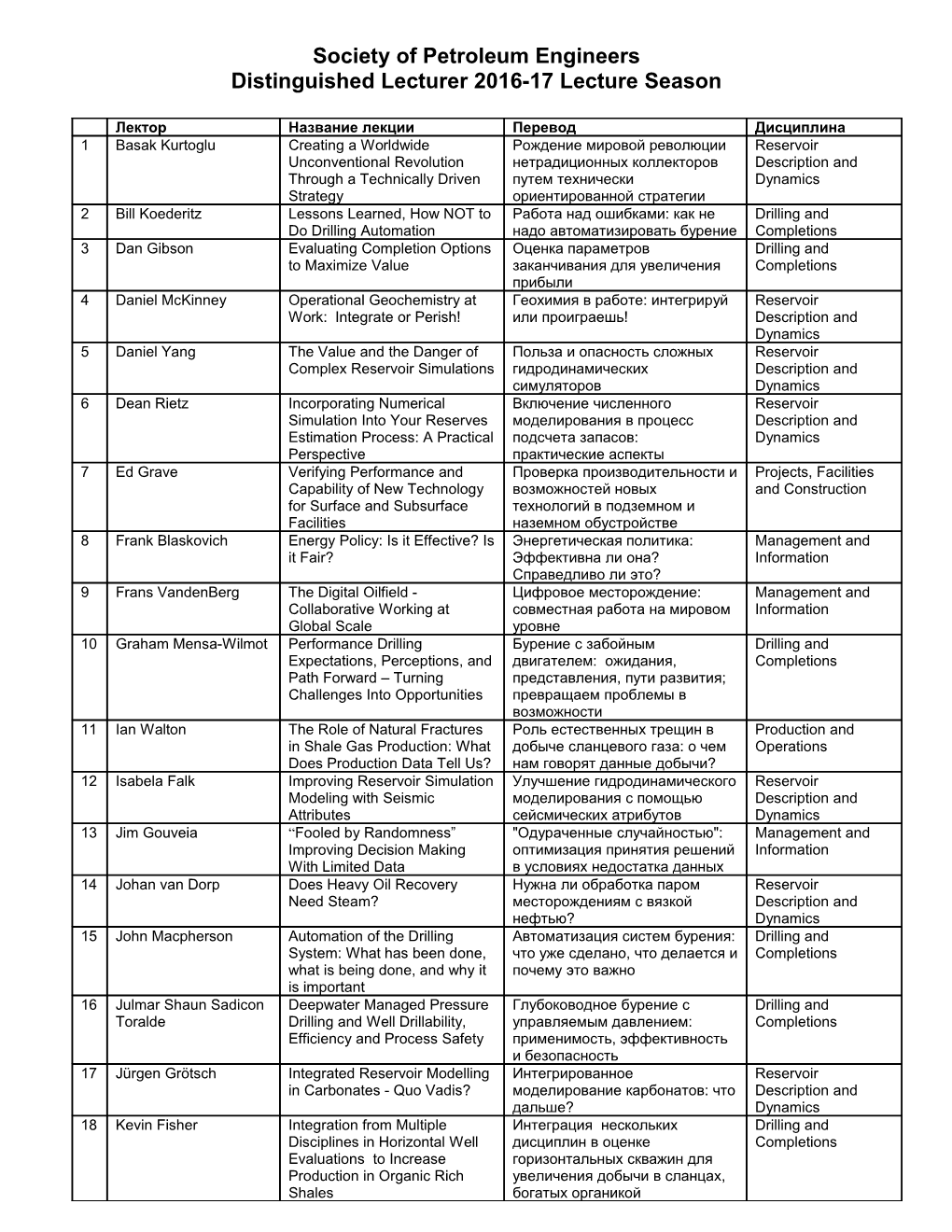
Лектор Название лекции Перевод Дисциплина 1 Basak Kurtoglu Creating a Worldwide Рождение мировой революции Reservoir Unconventional Revolution нетрадиционных коллекторов Description and Through a Technically Driven путем технически Dynamics Strategy ориентированной стратегии 2 Bill Koederitz Lessons Learned, How NOT to Работа над ошибками: как не Drilling and Do Drilling Automation надо автоматизировать бурение Completions 3 Dan Gibson Evaluating Completion Options Оценка параметров Drilling and to Maximize Value заканчивания для увеличения Completions прибыли 4 Daniel McKinney Operational Geochemistry at Геохимия в работе: интегрируй Reservoir Work: Integrate or Perish! или проиграешь! Description and Dynamics 5 Daniel Yang The Value and the Danger of Польза и опасность сложных Reservoir Complex Reservoir Simulations гидродинамических Description and симуляторов Dynamics 6 Dean Rietz Incorporating Numerical Включение численного Reservoir Simulation Into Your Reserves моделирования в процесс Description and Estimation Process: A Practical подсчета запасов: Dynamics Perspective практические аспекты 7 Ed Grave Verifying Performance and Проверка производительности и Projects, Facilities Capability of New Technology возможностей новых and Construction for Surface and Subsurface технологий в подземном и Facilities наземном обустройстве 8 Frank Blaskovich Energy Policy: Is it Effective? Is Энергетическая политика: Management and it Fair? Эффективна ли она? Information Справедливо ли это? 9 Frans VandenBerg The Digital Oilfield - Цифровое месторождение: Management and Collaborative Working at совместная работа на мировом Information Global Scale уровне 10 Graham Mensa-Wilmot Performance Drilling Бурение с забойным Drilling and Expectations, Perceptions, and двигателем: ожидания, Completions Path Forward – Turning представления, пути развития; Challenges Into Opportunities превращаем проблемы в возможности 11 Ian Walton The Role of Natural Fractures Роль естественных трещин в Production and in Shale Gas Production: What добыче сланцевого газа: о чем Operations Does Production Data Tell Us? нам говорят данные добычи? 12 Isabela Falk Improving Reservoir Simulation Улучшение гидродинамического Reservoir Modeling with Seismic моделирования с помощью Description and Attributes сейсмических атрибутов Dynamics 13 Jim Gouveia “Fooled by Randomness” "Одураченные случайностью": Management and Improving Decision Making оптимизация принятия решений Information With Limited Data в условиях недостатка данных 14 Johan van Dorp Does Heavy Oil Recovery Нужна ли обработка паром Reservoir Need Steam? месторождениям с вязкой Description and нефтью? Dynamics 15 John Macpherson Automation of the Drilling Автоматизация систем бурения: Drilling and System: What has been done, что уже сделано, что делается и Completions what is being done, and why it почему это важно is important 16 Julmar Shaun Sadicon Deepwater Managed Pressure Глубоководное бурение с Drilling and Toralde Drilling and Well Drillability, управляемым давлением: Completions Efficiency and Process Safety применимость, эффективность и безопасность 17 Jürgen Grötsch Integrated Reservoir Modelling Интегрированное Reservoir in Carbonates - Quo Vadis? моделирование карбонатов: что Description and дальше? Dynamics 18 Kevin Fisher Integration from Multiple Интеграция нескольких Drilling and Disciplines in Horizontal Well дисциплин в оценке Completions Evaluations to Increase горизонтальных скважин для Production in Organic Rich увеличения добычи в сланцах, Shales богатых органикой 19 Liam Lines Drilling Dynamics – Five Динамика бурения - ответы на Drilling and Fundamental Questions пять фундаментальных Completions Answered вопросов 20 Mack Shippen The Science and Economics of Наука и экономика Production and Multiphase Flow многофазных потоков Operations 21 Mayank Malik How can Microfracturing Как микроГРП улучшает Reservoir Improve Reservoir разработку месторождения? Description and Management ? Dynamics 22 Michael Gillen Applications and Advantages of Применение и преимущества Reservoir Logging-While-Drilling in High каротажа во время бурения в Description and Angle and Horizontal Wells наклонно-направленных и Dynamics горизонтальных скважинах 23 Neal Nagel Stress Shadows: How and Why Зоны ослабления напряжений: Drilling and They Can Affect Hydraulic как и почему они могут повлиять Completions Fracturing in Both Conventional на ГРП в обычных и and Unconventional Shale нетрадиционных сланцевых Plays пластах 24 Pavel Bedrikovetsky Prediction and Management of Прогноз и управление Production and Fines Migration for Enhanced миграцией твердой фазы для Operations Oil & Gas Production интенсификации добычи нефти и газа 25 Randy Freeborn Two Vital Secrets for Building Два важнейших секрета Management and Better Type Wells повышения качества Information строительства скважин 26 Reidar B Bratvold Creating Value from Создание стоимости из Management and Uncertainty and Flexibility неопределенности и гибкости Information 27 Ronald McLeod Human Factors in Barrier Барьерное мышление и Health, Safety, Thinking человеческий фактор Security, Environment and Social Responsibility 28 Segun Jebutu In-situ Wettability Utilizing Low Определение смачиваемости в Reservoir Gradient Magnetic Resonance пластовых условиях с Description and использованием метода Dynamics низкоградиентного магнитного резонанса 29 Shrikant Tiwari Salt Behavior and Drilling Поведение соленосных Drilling and Strategies to Overcome пластов и стратегии бурения Completions Challenges in Pre-Salt для преодоления Exploratory Wells трудностей в подсолевых разведочных скважинах 30 Steve Mackie Dry Hole Analysis: What I Have Анализ сухих скважин: что я Management and Learnt About the Upstream Oil узнал из своих ошибок Information and Gas Industry from My Failures 31 Steve Morice Borehole Seismic Solutions for Применение скважинной Reservoir Integrated Reservoir сейсмики при комплексном Description and Characterization and изучении и мониторинге Dynamics Monitoring залежей 32 Surej Kumar Subbiah Minimize Operational Risk Использование Drilling and Using Shared Geomechanical геомеханической модели Земли Completions Earth Model для минимизации операционных рисков 33 Wally Georgie Your Field is Getting Older: Is Оценка рентабельности Projects, Facilities your Process Engineering Still производственных процессов на and Construction Cost Effective? поздних стадиях разработки Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Creating a Worldwide Unconventional Revolution Through a Technically Driven Strategy
Basak Kurtoglu Citigroup Investment Bank
Abstract:
Unconventional development propelled the United States to produce more oil than it imports for the first time in 20 years. Increased production of domestic oil and gas profoundly impacted economic growth and job creation for the U.S. During this evolution, there was a need to address environmental regulations and infrastructure requirements in order to access the sheer volume of resources. Combined with today’s horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing technology, a strategic development plan can be constructed for any country to create an unconventional energy opportunity. In this lecture, the experience from U.S development is utilized to provide a fully-integrated workflow for developing shale oil and gas reservoirs from exploitation to production.
Starting at the nano-scale, we will zoom into the pore structure to understand the storage and flow paths. Transitioning to the reservoir-scale, well testing and microseismic are utilized to define the flow capacity and estimate the stimulated volume. Learnings from this subsurface characterization is used to guide well completion, flowback, and production operations. The diagnostic methodology specific to each operation can be applied to identify geologically favorable areas and the best completion practice. As development progresses, opportunities to improve recovery can be magnified through optimum well spacing and refracturing. As a final step in the development, determining an appropriate enhanced recovery method is essential to access the remaining resources. Finally, example development scenarios are provided to demonstrate how a technically driven strategy is more effective to maximize value and make the unconventional revolution a global one.
Biography: Basak Kurtoglu is Vice President in the Global Energy Group of Citigroup Investment Bank. Prior to Citi, she was Integrated Project Team Manager at Marathon Oil. She has been instrumental in assimilating multiple disciplines to evaluate and develop unconventional reservoirs. Kurtoglu earned her BS from Middle East Technical University, and her MS and PhD in petroleum engineering from Colorado School of Mines. Her numerous publications range from pore to reservoir scale analyses of unconventional reservoirs with an emphasis on enhancing oil recovery. She serves on the SPE Forum Series Coordinating Committee and the SPE Reservoir Description and Dynamics Advisory Committee. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Lessons Learned, How NOT to Do Drilling Automation
William L. Koederitz GK Plus Innovations LLC
Abstract:
The uses of automation in the drilling process are expanding and are typically resulting in improved drilling performance. However, many of these projects struggle in the initial stages, often trying to overcome a common set of hurdles. Many of these hurdles are not technical challenges, but instead are related to people issues and the methods for implementing the solutions. This presentation covers the basics of drilling automation and describes the problems and solutions that have been found to improve the startup success for drilling automation.
IDEA TO TAKE AWAY - For automation to be successful, the key users, especially the driller, must be involved in every step of design and implementation.
Biography:
Bill Koederitz is Chief Technology Officer at GK Plus Innovations. Previously, Bill spent 20 years building real-time applications and drilling automation systems at National Oilwell Varco. Prior to that, Bill worked as a drilling engineer and as a university researcher. He holds BS, MS and PhD degrees in Petroleum Engineering from Louisiana State University and is a Registered Petroleum Engineer in Texas. He has authored or coauthored 25 technical papers and holds 15 patents. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Evaluating Completion Options to Maximize Value
Dan Gibson Add Energy - Consulting Services
Abstract:
The Completion Engineer integrates the requirements of a number of other disciplines (Reservoir, Drilling, Production, etc) to maximize the value of a hydrocarbon resource. This almost always requires evaluating competing and conflicting factors to determine the 'best' option for a particular problem. This talk will demonstrate a decision making process that allows the stakeholders to compare various options in a fair and roboust way. Two real onshore or offshore examples will be reviewed depending on SPE chapter interest.
Members will take away a new methodology on how to compare competing factors that influence a completion or well design.
Biography:
Mr. Dan Gibson is a Senior Completions & Well Integrity engineer with over 35 years of experience. He has worked his way through the oil and gas production stream from Facilities and Production engineering to Completions in assignments across the USA and around the world (Gabon, Congo, Egypt, Scotland, Russia, and Australia). This breadth of expereince comes across in the presentation and his ability to deal with different audiences with a wide range of challenges.
He has authored or co-authored a number of papers ranging from polymer flood management to ice mechanics and most recently an innovative ICD system. He is one of the most active members of SPE Connect where members can readily contact him with questions. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Operational Geochemistry at Work: Integrate or Perish!
Daniel McKinney Sarawak Shell Berhad
Abstract:
Fluid properties have a profound impact on the exploration and production business; everything from acreage positioning, subsurface evaluation, reservoir performance, top sides design, flow assurance, metallurgy, etc. relies heavily on fluid properties. Yet many times, projects go through decision gates with a general lack of appreciation or awareness of the intricacies and interdependencies that exist within the petroleum system. In addition, one may not even have the proper datasets to realize missed opportunities that could impact significantly on CAPEX and OPEX. Operational Geochemistry is uniquely positioned to bridge the gap between the various disciplines, both subsurface and surface, to make sure that during exploration and appraisal campaigns reliable, complete and consistent datasets are obtained, quality assured and integrated right from the start. It is not a spectator sport where plans are designed only to be handed off to someone else to execute. Involvement from beginning to end is crucial. To do this, the objectives need to be clear and an action plan formulated with sufficient flexibility to react to surprises; and buy-in needs to be sought from all parties far in advance of well delivery. All the while, technologies should be identified and earmarked for deployment where warranted. Last but not least, once data gathering commences, the Operations Geochemist needs to reflect upon the fluid data and properties and identify outliers. In this presentation, a number of case studies are presented illustrating the workflow and describing both the prize and the potential lost opportunities.
Biography:
I graduated in 1992 and 1998 with a B.S. in Chemistry and a Ph.D. in Material Science and Engineering from The Pennsylvania State University. I joined Shell shortly thereafter and have spent 17 years in Houston, New Orleans, and, now, Malaysia providing Geochemistry and formation testing solutions. I am Shell’s Subject Matter Expert (SME) for Operations Geochemistry, and I was one of the founding members of Shell’s Fluid Evaluation and Sampling Technologies (FEAST) team. I have contributed to a number of manuscripts, oral presentations, Special Interest Groups (SIGs), as well as posters at SPE, SPWLA, and Organic Geochemistry Conferences. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
The Value and the Danger of Complex Reservoir Simulations
Daniel Yang Shell Canada Ltd.
Abstract:
The weakness of reservoir simulations is the lack of quantity and quality of the required input; their strength is the ability to vary one parameter at a time. Therefore, reservoir simulations are an appropriate tool to evaluate relative uncertainty but absolute forecasts can be misleading, leading to poor business decisions. As recovery processes increase in complexity, the impact of such decisions may have a major impact on the project viability. A responsible use of reservoir simulations is discussed, addressing both technical users and decision makers. The danger of creating a false confidence in forecasts and the value of simulating complex processes are demonstrated with examples. This is a call for the return of the reservoir engineer who is in control of the simulations and not controlled by them, and the decision maker who appreciates a black & white graph of a forecast with realistic uncertainties over a 3- D hologram in colour.
Biography:
Daniel Yang is Petroleum Advisor at Shell Canada. Holding a PhD in Geophysics from the Technical University of Berlin, Germany, he dedicated 15 years of his oil-industry career to Enhanced Oil Recovery methods, focussing on thermal recovery and originating from 10 years of research in geothermal energy. Daniel worked at Shell International, Canadian Natural Resources Ltd. and Laricina Energy Ltd. He holds two patents, was recognized as Subject Matter Expert in Shell, has over 20 publications, recently received a SPE Best Paper Award, and was a guest lecturer at universities in Germany, U.S.A. and Canada. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Incorporating Numerical Simulation Into Your Reserves Estimation Process: A Practical Perspective
Dean Rietz Ryder Scott Company Petroleum Consultants
Abstract:
Reservoir simulation is a sophisticated technique of forecasting future recoverable volumes and production rates that is becoming commonplace in the management and development of oil and gas reservoirs, small and large. Calculation and estimation of reserves continues to be a necessary process to properly assess the value and manage the development of an oil and gas producer’s assets. These methods of analysis, while generally done for different purposes, require knowledge and expertise by the analyst (typically a reservoir engineer) to arrive at meaningful and reliable results. Increasingly, the simulation tool is being incorporated into the reserves process. However, as with any reservoir engineering technique, certain precautions must be taken when relying on reservoir simulation as the means for estimating reserves. This discussion highlights some of the important facets one should consider when applying numerical simulation methods to use for, or augment, reserves estimates. The main take away will be an appreciation for the areas to focus on to arrive at meaningful and defendable estimates of reserves that are based on reservoir models.
Biography:
Dean C. Rietz, P.E., President and member of the board of directors at Ryder Scott Company, has over 30 years of diverse experience in evaluating oil and gas properties, including more than 25 years applying numerical modeling approaches to these evaluations. Prior to his current position, he managed the Ryder Scott Reservoir Simulation Group for approximately 15 years. Before joining Ryder Scott in 1995, Rietz worked at Chevron, Gruy, and Intera. He received a B.S.P.E. degree from the University of Oklahoma and an M.S.P.E. degree from the University of Houston. His past teaching experience includes in-house material balance schools at Chevron and Eclipse user courses at Intera. Currently, Rietz teaches a two-day SPE simulation course and is an adjunct professor of reservoir simulation at the University of Houston. Rietz has published various papers related to reservoir modeling, including its application to reserves reporting. Rietz is a registered professional engineer in Texas and serves on the Petroleum Engineering Advisory Board for the University of Houston. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Verifying Performance and Capability of New Technology for Surface and Subsurface Facilities
Ed Grave ExxonMobil Upstream Research Company
Abstract:
As we have seen with the advent of the shale oil revolution in the United States, the development of new technology plays an important role in the oil and gas industry. It’s an enabler in reducing capital costs, simplifying production and increasing capacity of new or existing facilities. It can make a marginal project into a profitable development.
Progressing technology, while dealing with significant risk, is a challenge that can be overcome through a technology qualification process. A Technology Qualification Program (TQP) provides a means to identifying the risks and taking the correct steps to mitigate it; not avoid it.
This lecture summarizes the required steps involved in qualifying technology and how to keep track of technology development through the Technology Readiness Level (TRL) ranking system. In addition, some of the pitfalls in executing a TQP program are identified and discussed with emphasis on both component and system testing. Examples are given to illustrate the danger in taking shortcuts when executing the qualification plan.
Data from a recent subsea separation qualification program is presented comparing test results between CFDs, model fluid and actual crude testing at operating conditions. Knowing the limitations of the tools and testing system selected is an important step in closing the gaps identified in the TQP program.
The TRL has evolved at a faster pace and has become more acceptable in the oil and gas industry then the TQP. Nonetheless, continued standardization of both the TQL and TRL is still necessary in order to reduce overall cost of developing technology and allow faster implementation.
Biography:
Ed Grave graduated from New Jersey Institute of Technology with a Master of Science in 1982. Ed started his career at Lummus working on a number of petrochemical projects, in which in gravitated towards mass transfer and separations. He later joined Mobil Research & Development Company in 1990 as a mass transfer specialist. Today Ed is ExxonMobil’s Upstream Senior Technical Advisor for Fractionation & Separation at ExxonMobil Upstream Research Company in Spring, TX. His team is responsible for research, design, and troubleshooting, for all fractionating & separation systems for the entire ExxonMobil Upstream organization.
Ed is recognized for his expertise and as a leader within ExxonMobil in advancing new technology. He also led the effort in designing and qualifying separation system for ultra-deep water, making ExxonMobil ready to meet their future needs.
He initiated and is presently guiding the joint industry Separations Technology Research (STAR) Program on qualifying separation equipment as technical chairman. He also served as vice-chair at SPE’s Separation Technology Technical Section (STTS). Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Energy Policy: Is it Effective? Is it Fair?
Frank Blaskovich Blaskovich Services, Inc.
Abstract:
Developing sound energy policies is difficult under the best circumstances. There is a delicate balance between government's need for revenue, modern society's need for energy and the producer's need for profitability to exploit resources. Many factors can affect the results for all interested parties. Good policies require an appreciation for the interactions among oilfield development and operations, costs and prices, government taxes and regulations and many other factors that are often difficult to define accurately. We live in a complex world that acts like a system with many interconnected components. Humans are ill equipped to understand its behavior. We instinctively focus on short term, local issues and simple cause and effect rather than the bigger picture. This reduces the likelihood that we can design effective policies that will work well over the long term for all stakeholders. There are no easy solutions in complex systems. We developed an approach using system models and regret analysis to find flexible and resilient tax policies, in spite of uncertainties, that would provide all parties with fair, profitable solutions – even though none might achieve their maximum goals. It can also measure the relative benefits of existing energy policies and, potentially, help to improve them. These challenges will only become harder in the future and more important for the energy industry. Now is the time to pursue new ways of thinking to solve these problems.
Biography:
Frank Blaskovich is Vice-President of Blaskovich Services, Inc. in Northern California. He received his B.S. in aerospace engineering from the University of Notre Dame. He has more than 40 years of experience in reservoir engineering and simulation, software development, environmental modeling, and policy analysis. He has worked on energy issues around the world for the largest multi-national energy companies, government agencies and major consulting firms. He has published numerous papers on reservoir simulation and energy policy analysis available in the SPE literature and elsewhere. His work and research activities over the last decade have focused on developing improved energy policies that can benefit all stakeholders fairly. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
The Digital Oilfield - Collaborative Working at Global Scale
Frans van den Berg Shell
Abstract:
Collaborative Working helps assets to operate more efficiently and as one team, resulting in higher production, less cost, lower HSE exposure and higher morale.
Shell has pursued the Digital Oilfield for the last ten years, under the heading of Smart Fields. Collaborative Work Environments (CWEs) were implemented in the majority of assets, live environments now cover over 50% of Shell’s production.
The presentation will provide an overview of current Collaborative Work Environments. It will show examples of CWEs in different types of assets, and of the business value achieved. The large scale implementation was achieved through a structured deployment programme, taking assets and projects through a standard design, implementation and embedding approach.
To embed and sustain the new ways of working, a focus on the people aspects and change management has been critical. Each project included mapping workflows, awareness and training sessions and establishing coaches, support and continuous improvement.
Biography:
Frans van den Berg currently works in the global Smart Fields programme in Shell’s Projects and Technology organisation in the Netherlands. He leads the global implementation of Collaborative Work Environments in Shell. Frans joined Shell after graduation in Physics at Leiden University in The Netherlands. He has held various positions as a petroleum engineer and asset development leader in operational roles and in global technology deployment. He worked ten years in Malaysia and Thailand. He has been involved in the organisation of the SPE Intelligent Energy and Digital Energy Conferences since 2008. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Performance Drilling Expectations, Perceptions, and Path Forward – Turning Challenges Into Opportunities
Graham Mensa-Wilmot Chevron Energy Technology Company
Abstract:
Drilling activities continue to be extended into harsher and more challenging environments. In addition, directional drilling, with its increased activity level, has also become more complex. These conditions have escalating effects on operational costs. Performance drilling is universally accepted as an enabler in operational costs reductions, through improvements in drilling efficiency. However, achievement of these expectations continues to fall short, while also lacking consistency in most instances. These conditions are primarily due to the industry’s different positions on what constitutes performance drilling. In most situations, the use of new technology, sophisticated tools, or expensive drive systems, is classified as performance drilling. Primarily, this lecture will challenge and move away from such positions. Most importantly, it will present new definitions, concepts, and processes that facilitate consistent achievement of performance drilling’s intended objectives and benefits.
In addition to establishing how performance drilling should be executed, a new benchmarking process which focuses on how and why events occur will be discussed. Additionally, clear distinctions between project success and efficiency as they relate to operational costs will also be established. The challenges posed by specific applications, which need performance drilling focus, will be identified and discussed.
Global projects in different applications, where challenges continue to be turned into opportunities, will be presented and supported with the appropriate data and discussions.
Biography:
Graham Mensa-Wilmot is a Sr. Advisor, Drilling Engineer in Chevron's Energy Technology Company. Graham is the MAXDRILL (Performance Drilling) project leader. He has more than 28yrs experience in drilling applications research, downhole tool development, drilling vibrations identification and remediation, drilling mechanics, drilling system design and analysis, and drilling performance improvement. He has authored 42 technical papers and also holds 34 patents on same disciplines.
Graham is a recognized industry leader on performance drilling. He serves on the SPE/IADC Drilling Conference Program Committee, and the SPE Drilling and Completions technical review committee. He previously served for 6 years, on the JPT Editorial committee, as technical editor for the Bits/BHAs and Performance Drilling. Graham also served as a distinguished lecturer on the Petroleum Network Educational Courses series. Graham holds an MS degree in Drilling Engineering from Romanian's University of Petroleum and Gas in Ploiesti. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
The Role of Natural Fractures in Shale Gas Production: What Does Production Data Tell Us?
Ian C. Walton Energy & Geoscience Institute, University of Utah
Abstract:
Natural fractures are very common in shale gas plays. It is often presumed that because the formations are so tight gas can be produced economically only when extensive networks of natural fractures exist. The creation of large fracture surface area in contact with the reservoir is regarded as essential to commercial success. This is facilitated by multi-stage hydraulic fracturing of long horizontal wells using large volumes of low-viscosity (low-cost) fracturing fluid. The fracture systems that are created by this process are indeed large and often complex, due essentially to intersection of the hydraulic fractures with the natural fracture network. However, the efficiency of this process in terms of water usage is now coming under close scrutiny, not least because of growing environmental concerns.
The success of these operations is beyond doubt, but what can be inferred about the accuracy of this conceptual picture in light of many years’ accumulated production data? What does production data tell us about the role of natural fractures, whether initially closed (mineralized) or open, in the production process? This presentation addresses these issues by using a semi-analytic shale gas production model to analyze and interpret production data from many shale gas wells across several different plays. Among the many inferences that can be drawn from the results of this investigation is a fresh appraisal of the role of natural and hydraulic fractures in the production process.
Take-away message: natural fractures may not, after all, be essential for economic shale gas production and may even be detrimental.
Biography:
Ian Walton is a Senior Research Scientist in the Energy & Geoscience Institute at the University of Utah and an Adjunct Professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering. He holds a Ph.D. in Applied Mathematics from the University of Manchester. Dr. Walton has more than 25 years of petroleum industry experience, most recently as a Scientific Advisor for Schlumberger and more than 15 year’s university teaching experience. He has published many technical reports and papers and has been awarded eight patents. He has made many technical presentations at industry conferences, forums and workshops. Current research centers on modeling and forecasting gas and oil production from shales. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Improving Reservoir Simulation Modeling with Seismic Attributes
Isabela Falk Schlumberger
Abstract:
Seismic attributes are being used more and more often in the reservoir characterization and interpretation processes. The new software and computer’s development allows today to generate a large number of surface and volume attributes. They proved to be very useful for the facies and reservoir properties distribution in the geological models, helping to improve their quality in the areas between the wells and areas without wells. The seismic attributes can help to better understand the stratigraphic and structural features, the sedimentation processes, lithology variations, etc. By improving the static geological models, the dynamic models are also improved, helping to better understand the reservoirs’ behavior during exploitation. As a result, the estimation of the recoverable hydrocarbon volumes becomes more reliable and the development strategies will become more successful.
Biography:
Isabela Falk is a Senior Geologist, currently the Subsurface Team Leader in a Schlumberger P&AM project in Romania. Previously she worked as a Project Geoscientist for Fugro-Jason in Germany and Holland. Prior to that, she worked as a Researcher Geologist in the Romanian National Gas Company: Romgaz. Isabela holds a PhD in Geology from the University Babes-Bolyai from Cluj- Napoca, Romania, since 2008. She has 20 years of experience in the Oil& Gas industry, specialized mostly in geological modeling, but is experienced also in seismic inversion. She made several scientific presentations in internal and international conferences and is a member of SPE, SEG and EAGE. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
“Fooled by Randomness” - Improving Decision Making With Limited Data
James Gouveia Rose & Associates LLP
Abstract:
Professionals routinely face the challenge of making informed decisions with limited data sets. Our exploitation of Unconventional resource plays has exacerbated this issue. We commonly refer to these resource plays as “statistical plays”, as large programs have provided repeatable year over year results. Competitive pressures and the desire to get to the right answer as soon as possible has driven the observed decision-making based on limited data sets. In an environment where horizontal well costs can exceed $10 MM and programs hundreds of millions of dollars, decisions based on limited wells have become our industry’s “money pits”. Development decisions are often made without due consideration for the representativeness of the data. Similarly, we frequently test new technologies with limited samples with the expectation that a simple arithmetic comparison of the average results can validate or refute their further application. This talk presents the theory and utilization of aggregation curves as a pragmatic graphical approach to determining the uncertainty in the sampled mean relative to the desired average program outcome. The presentation will conclude with a discussion on the use of sequential aggregation plots as a graphical approach to validating the representativeness of our forecasted results versus based on limited actual results.
Biography:
James Gouveia is a Professional Engineer with a diverse technical, business and operations background. He has worked in a variety of technical and managerial assignments in exploration, reservoir engineering, strategic and business process planning, portfolio and risk management. From 1996 to 1999, Mr. Gouveia was Director of Risk Management for the Amoco Energy Group of North America. In this role he was accountable for assurance of consistent project evaluation of major capital projects. With BP, he was an Assurance champion and Asset manager. Jim has co-authored and presented papers, most recently as a contributing author to the SPEE’s 2011 Monograph 3, and SPE 175527 & 175888 & 121525. Mr. Gouveia is a member of APEGA, SPE, SPEE and AAPG. Mr. Gouveia is a partner in Rose & Associates LLP. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Does Heavy Oil Recovery Need Steam?
Johan van Dorp Shell
Abstract:
Heavy Oil recovery traditionally starts with depletion drive and (natural) waterdrive with very low recoveries as a result. As EOR technique, steam injection has been matured since the 1950s using CSS (cyclic steam stimulation), steam drive or steam flooding, and SAGD (steam assisted gravity drainage). The high energy cost of heating up the oil bearing formation to steam temperature and the associated high CO2 footprint make steam based technology less attractive today and many companies in the industry have been actively trying to find alternatives or improvements. As a result there are now many more energy efficient recovery technologies that can unlock heavy oil resources compared with only a decade ago. This presentation will discuss breakthrough alternatives to steam based recovery as well as incremental improvement options to steam injection techniques. The key message is the importance to consider these techniques because steam injection is costly and has a high CO2 footprint.
Biography:
Johan van Dorp holds an MSc in Experimental Physics from Utrecht University and joined Shell in 1981. He has served on several international assignments, mainly in petroleum and reservoir engineering roles. He recently led the extra heavy-oil research team at the Shell Technology Centre in Calgary, focusing on improved in-situ heavy-oil recovery technologies. Currently, he is senior consultant in the "Nederlandse Aardolie Maatschappij", a JV operated by Shell. Van Dorp is also Shell Group Principal Technical Expert in Thermal EOR and has been involved with most thermal projects in Shell throughout the world, including California, Oman, the Netherlands, and Canada. He (co-)authored 13 SPE papers on diverse subjects. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Automation of the Drilling System: What has been done, what is being done, and why it is important
John Macpherson Baker Hughes
Abstract:
Drilling systems automation is the real-time reliance on digital technology in creating a wellbore. It encompasses downhole tools and systems, surface drilling equipment, remote monitoring and the use of models and simulations while drilling. While its scope is large, its potential benefits are impressive, among them: fewer workers exposed to rig-floor hazards, the ability to realize repeatable performance drilling, and lower drilling risk. While drilling systems automation includes new drilling technology, it is most importantly a collaborative infrastructure for performance drilling.
In 2008, a small group of engineers and scientists attending an SPE conference noted that automation was becoming a key topic in drilling and they formed a technical section to investigate it further. By 2015, the group reached a membership of sixteen hundred as the technology rapidly gaining acceptance. Why so much interest? The benefits and promises of an automated approach to drilling address the safety and fundamental economics of drilling. What will it take? Among the answers are an open collaborative digital environment at the wellsite, an openness of mind to digital technologies, and modified or new business practices. What are the barriers? The primary barrier is a lack of understanding and a fear of automation. When will it happen? It is happening now.
Digital technologies are transforming the infrastructure of the drilling industry. Drilling systems automation uses this infrastructure to deliver safety and performance, and address cost.
Biography:
John Macpherson is a Senior Technical Advisor for Baker Hughes. He holds a BSc (Hons) in Geology from the University of Glasgow. During his 40 years in the oil industry, he has participated in exploratory drilling operations -- primarily in remote areas of South America -- and in various positions in drilling research and development. His focus has been on exploration and drilling: starting with geology, through geomechanics, drilling modeling, to drilling dynamics and drilling systems automation. He has published about 40 papers, and has more than 25 granted patents. He is the Chairman of the SPE Drilling Systems Automation Technical Section (2014 and 2015), and a member of the Drilling Systems Automation Roadmap initiative. He is a member of the JPT editorial committee. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
"Deepwater Managed Pressure Drilling and Well Drillability, Efficiency and Process Safety"
Julmar Shaun Sadicon Toralde Weatherford
Abstract:
Adoption of managed pressure drilling (MPD) technologies of the applied surface backpressure type in deepwater environments have mainly involved a rotating control device (RCD) to create a closed drilling system where flow out of the well is diverted towards and backpressure regulated using an automated MPD choke manifold with a high-resolution mass flow meter that increases sensitivity and reaction time to kicks, losses and other unwanted drilling events.
This integration of MPD equipment into floating drilling rigs to provide it with MPD capabilities, including the capacity to perform pressurized mud cap drilling (PMCD) and riser gas mitigation (RGM), has not only produced improvements in terms of drillability and efficiency, but most importantly, in terms of process safety.
Case histories on how MPD has performed will be presented on the following: • allowed drilling to reach target depth in rank wildcat deepwater wells that have formations prone to severe circulation losses and narrow mud weight windows; • increased drilling efficiency by minimizing non-productive time associated with downhole pressure-related problems and by allowing for the setting of deeper casing seats; • enhanced operational and process safety by allowing for immediate detection of kicks, losses and other critical downhole events. • provided riser gas mitigation capabilities that can detect a gas influx once it enters the drilling fluid stream, and not after it has already broken out above the rig blow-out preventers (BOPs).
Biography:
Julmar Shaun Sadicon Toralde is the Global Champion for Deepwater Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD), Downhole Deployment Valve (DDV) and SteadyState Continuous Flow System technologies, based in Houston, Texas, USA. He helped pioneer deepwater MPD deployment on a dynamically positioned drillship in 2010 and is actively involved in major deepwater MPD rig integration projects globally. Shaun is from the Philippines and holds a Geothermal Engineering degree from Negros Oriental State University, where he taught and conducted research on energy engineering. He previously held various field and office management positions with Weatherford in the Asia Pacific region. He has 50 technical papers / trade articles and various MPD training courses to his name. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Integrated Reservoir Modelling in Carbonates - Quo Vadis?
Jürgen Grötsch Shell Global Solutions International B.V.
Abstract:
Integrated reservoir modelling (IRM) is a best practice in the Upstream industry applied throughout all life cycles stages of oil and gas projects aiming at characterisation of subsurface reservoirs and optimisation of field development phases. In this respect, carbonate and clastic reservoirs are different in a range of aspects which will be highlighted. During the past 25 years, major steps in technology development have proven the importance of IRM as a key subsurface contributor to Upstream projects. A brief history of IRM through time will be provided using carbonate examples from exploration, development up to recent learnings around unconventional hydrocarbon trapping. More importantly, these industry showcases will be used to introduce present-day challenges around IRM in the Upstream business. Despite the significant progress in modelling technologies, root causes for disappointing results of such studies are limitations in software tools and workflows together with the lack of integration. This often causes poor project delivery. Such pitfalls within existing practices in the Upstream industry will be discussed highlighting that tools only are not able to assure success in subsurface reservoir characterisation projects. Finally, an outlook into the future of hydrocarbon development planning and IRM will be provided. Ultimately, end-to-end integration in Upstream project workflows requires focus on associated business decisions, scaling of models and scenario management supported by content and context based data management as well as capabilities around fast iterative feedback loops. Only the combined improvements around tools, processes and people will maximise value for Upstream project delivery.
Biography:
Jürgen is currently Global Learning Advisor Geology at Shell responsible for design and deployment of advanced training programs. In this position, his focus areas are integration and building capabilities around decision based subsurface modelling for muilti-disciplinary teams which he was involved with for the past 25 years in various assignments within Shell Production and Exploration ventures around the world. Jürgen holds a Ph.D. in carbonate sedimentology and has authored and co-authored numerous publications and books. He is known as keynote lecturer from international geoscience conferences and, since 2009, as visiting lecturer at the GeoZentrum of the Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg in Germany. Currently, he is Vice-President of the German Geological Society (DGGV). Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Integration from Multiple Disciplines in Horizontal Well Evaluations to Increase Production in Organic Rich Shales
Kevin Fisher Schlumberger
Abstract:
Drilling horizontal wells is the common mode of operation for field development in permeability- challenged unconventional reservoirs such as an organic shale. Assumptions are made regarding the homogeneity of the reservoir as wells are drilled away from the vertical pilot well. It is assumed that the reservoir characteristics remain uniform and also that the structure is known to remain in a constant orientation based on the dip information at the pilot wellbore. Experience tells us that these assumptions can lead to wells placed out of zone and in rocks with much different reservoir quality and stress magnitude, which can adversely affect the production potential of the well. With the high cost of drilling and completing these wells, it is generally economically beneficial to do some evaluation of the lateral to ensure proper placement of the well and also the optimal placement of completion zones along the lateral. Lateral measurements and petrophysical interpretations can be used to define variations in reservoir quality (RQ) and completion quality (CQ), which can then be used to optimally place perforation clusters in similar rock to increase production when compared to peer geometric wells. The integration and interpretation of pilot and lateral wellbores with a geological structure component is defined as geology quality (GQ). A methodology to integrate data from many sources enables a better understanding of the variability and structural challenges of these complex reservoirs. This integrated methodology has been refined using lessons learned from various case studies showing increased production when compared to geometric completions.
Biography:
Kevin is a Senior Petrophysicist for Schlumberger based in Houston, TX with 25 years of experience in petrophysics and rock physics, after graduating from the University of Tulsa with a degree in Petroleum Engineering. He is currently working in the South Texas Production Technology Integration Center focusing on unconventional resource plays, mainly in the Eagle Ford basin. Additional areas of expertise have been deep water and shelf sturctures in the Gulf of Mexico, tight gas sands in South TX and Rockies, Alaska, Permian Basin, Unconventional Gas & Oil shales, Coal Bed Methane and international (Australia, Brazil, Argentina, United Kingdom, France, Nigeria, Angola, Turkey and Saudi Arabia). Kevin is guest lecturer since 2012 at Rice University for a graduate level petroleum geology class entitled “Economic Geology – Petroleum”. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Drilling Dynamics - Five Fundamental Questions Answered
Liam Lines Weatherford
Abstract:
Understanding downhole dynamics is key to reducing downhole failure and non productive time.
Damage resulting from drilling dynamics costs the industry in excess of $750 million per year in repair and maintenance alone not to mention the additional costs due to reduced drilling efficiency and trips for failure. This presentation answers five fundamental questions relating to drilling dynamics; 1) What it is; 2) How we know it is happening, 3) What the consequences are, 4) How it can be predicted and 5) What can be done to prevent it.
Biography:
Liam Lines is the Global SME for Drilling Mechanics and Vibration for Weatherford Drilling Services. He is charged with advancing the companies understanding of the drilling environment, developing and evaluating new downhole logging-while- drilling and rotary steerable technlogies and defining best practice guidelines for drilling optimization and hazard mitigation. He has a number of patents pending and has presented a series of technical papers at international conferences. Liam has a Masters Degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Bristol and a PgCE in Petroleum Engineering from Harriot Watt University. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
The Science and Economics of Multiphase Flow
Mack Shippen Schlumberger
Abstract:
We are all familiar with the production systems through which reservoir fluids flow to reach our processing facilities. This is a journey characterized by complex multiphase flow phenomena that govern pressure and temperature changes along the way. A monumental amount of research and development work has been invested towards better understanding multiphase flow behavior over the past fifty years. Yet, many challenges remain as we strive to optimize ever more complex production systems fraught with difficult flow assurance issues.
Just how good is the science? And more importantly, how does this impact our bottom line?
This lecture will discuss key concepts of multiphase flow leading to the current “state-of- the-art” models used today. Looking towards the future, the science must be advanced to address areas of greatest uncertainty and align with trends in field development strategies. Recommendations will be presented covering the top 5 areas of research necessary for these purposes. The economic impact of multiphase operations will be illustrated using two examples that provide insight towards maximizing asset value.
Biography:
Mack Shippen is a Principal Engineer with Schlumberger in Houston, where he is responsible for the global business of the PIPESIM multiphase flow simulation software. He has extensive experience in well and network simulation studies, ranging from flow assurance to dynamic coupling of reservoir and surface simulation models. He has served on a number of SPE committees and chaired the SPE Reprint Series on Offshore Multiphase Production Operations. He holds BS and MS degrees in Petroleum Engineering from Texas A&M University, where his research focused on multiphase flow modelling. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
How can Microfracturing Improve Reservoir Management ?
Mayank Malik Chevron
Abstract:
Microfracturing is an excellent method of obtaining direct stress measurements, not only in shales, but in conventional reservoirs as well. Recent advances have shown that microfracturing can help improve reservoir management by guiding well placement, completion design, and perforation strategy.
Microfracturing consists of isolating small test intervals in a well between inflatable packers, increasing the pressure until a small fracture forms and then by conducting a few injection and shut-in cycles, extend the fracture beyond the influence of the wellbore. Results show that direct stress measurements can be successfully acquired at multiple intervals in a few hours and the vertical scale nearly corresponds to electric log resolution. Therefore, microfracture testing (generally performed in a pilot / vertical well) is an appropriate choice for calibrating log derived geomechanical models and obtaining a complete, accurate, and precise vertical stress profile.
This talk describes the microfracturing process and presents several examples that led to increased hydrocarbon recovery by efficient stimulation and/or completion design. Case studies presented range from optimizing hydraulic fracturing in unconventionals, determining safe waterflood injection rates in brownfields, and improving perforation placement in ultra deepwater reservoirs.
Biography:
Mayank Malik is the Global Formation Testing Expert in Chevron's Energy Technology Company and is a champion for advancing research on microfracturing. He holds a B.S. in Mechanical Engineering from Delhi College of Engineering (India), MS in Mechanical Engineering from University of Toronto (Canada), and Ph.D. in Petroleum Engineering from The University of Texas at Austin (USA). Malik has authored numerous papers on petrophysics, formation testing, and microfracturing. He is currently serving on the SPE ATCE Formation Evaluation committee and is also the Chairman for SPWLA Formation Testing Special Interest Group. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Applications and Advantages of Logging-While-Drilling in High-Angle and Horizontal Wells
Michael Gillen Baker Hughes
Abstract:
The drilling industry has undergone a revolution in the past decade, with horizontal drilling becoming the norm for the development of many unconventional and conventional reservoirs. For example, rig count statistics for the US show that since 2004 the percentage of rigs drilling horizontal wells has steadily risen to almost 80% of today’s active drilling rigs. Horizontal drilling, which has enabled the economic development of many reservoirs, will continue to be the prevalent method for drilling in the future.
Horizontal wells pose unique challenges for log interpretation and formation evaluation. Most of the logging technology in use was developed for evaluating vertical wells. The measurement responses observed in horizontal wells are often different from vertical wells in the same reservoir. It is important to understand how standard logging “quad-combo” measurements are affected by the orientation change from vertical to horizontal. Sometimes these changes are misinterpreted or assumed to be tool malfunctions. By understanding the changes in the measurement responses we can take full advantage of the information they provide to understand the formations surrounding the borehole. This talk will address some of these issues and discuss the various applications for real-time LWD measurement to improve drilling efficiency and safety. Case histories are presented to support these points.
The attendees at this talk will leave with an increased understanding of how logging measurements are affected differently in horizontal wells and how to take full advantage of the differences.
Biography:
Michael Gillen is the Global Director for Formation Evaluation Services at Baker Hughes. With 34 years of logging and formation evaluation experience, Mike began his career as a Field Engineer with Dresser Atlas in 1981. He later joined NUMAR Corp. where modern NMR technology was first developed for well logging. He joined Baker Hughes in 2000 and was responsible for several new wireline technology introductions before moving to the Drilling Services group to lead the LWD team. Mike holds a BS in Engineering from the University of Colorado and an MBA from Penn State University. He has published several papers on new wireline and LWD technologies and interpretation techniques and holds two patents in this field. Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Stress Shadows: How and Why They Can Affect Hydraulic Fracturing in Both Conventional and Unconventional Plays
Neal B. Nagel OilField Geomechanics LLC
Abstract:
Much is now made about “Stress Shadows” and their impact on hydraulic fracturing - particularly in multi-stage horizontal laterals commonly used in Unconventionals. Unfortunately, there is no standard definition of Stress Shadows and, as a result, there is much confusion over what they are and aren’t, and, most importantly, why they can have a significant impact on hydraulic fracturing operations. The goal of this presentation will be to address this confusion and more fully explain Stress Shadows and their impact.
The creation of hydraulic fracture width during a stimulation generates a change in the stress field, which alters all three principal stresses as well as tip shear stresses. These stress changes are the Stress Shadows.
As hydraulic fracture propagation is often controlled by the stress field, Stress Shadows may change the propagation path for subsequent hydraulic fractures or, as seen in cluster fracturing, propagation may be impeded completely. The presence of natural fractures and weakness planes can also affect, and be affected by, Stress Shadows. At the hydraulic fracture tip, shear stresses are generated that offer the potential to shear and open closed natural fractures and weak planes – and if opened, it may be possible to stimulate them. Equally important, behind the hydraulic fracture tip Stress Shadows increase the magnitude of all three principal stresses, which tends to close weakness planes making them more difficult to stimulate. Because of these effects and others, understanding and designing for the impact of Stress Shadows is often critical for stimulation optimization.
Biography:
Dr. Neal Nagel is currently Chief Engineer for OilField Geomechanics and has nearly 30 years of industry experience. He is a well-known expert in the geomechanics of Unconventionals and has given many invited SPE, AAPG, HGS, SEG, and SPWLA presentations. Nagel has also authored or coauthored more than 50 technical papers, with 20+ related to Unconventionals, including a keynote presentation at the 2014 SPE HFTC. He is a past SPE Distinguished Lecturer, was chief editor of the 2010 SPE Monograph on Solids Injection, has served on the SPE Drilling and Completions Committee, and also been a local SPE section officer.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Prediction and Management of Fines Migration for Enhanced Oil & Gas Production
Pavel Bedrikovetsky University of Adelaide
Abstract:
Fines migration is the most common formation damage mechanism that challenges the economic viability of petroleum development projects. The phenomenon has been widely reported for production and injection wells, drilling, completion, waterflooding and pressure depletion with water support. It is explained by the lifting of reservoir fines, their migration and pore plugging with consequent permeability decline.
We introduce a maximum retention function for fines that models fines mobilization and allows coreflood interpretation, well impairment history analysis and well behavior prediction. The laboratory and field case studies presented validate the approach. The reservoir study presented shows how to use the coreflood- and well-history data for reliable prediction of productivity decline, its prevention, and mitigation.
The traditional view of fines migration is that it should be avoided because of its detrimental effect on reservoir permeability and hence well productivity. However, the permeability decline effect provides a relatively simple method for water mobility control. We show laboratory and field cases where, compared with “normal” waterflooding, the fines-assisted low salinity waterflood results in a significant increase in reservoir sweep due to fines lifting and permeability decline in the swept zone.
Additionally, in oil and gas reservoirs, the injection of a small fresh water bank into watered out wells, or above the hydrocarbon-water contact, decelerates the invaded water and significantly decreases water production. Huf-n-puf by low-salinity water significantly decreases water production in oil- and gas wells.
Reliable prediction of productivity decline due to fines migration and its effective management to enhance oil and gas production is the key message of this lecture.
This lecture stimulates the petroleum engineer’s thinking into productivity enhancement options and, in particular, that natural or deliberately induced fines migration may often assist in oil and gas production.
Biography:
Pavel is Professor of Petroleum Engineering at the University of Adelaide. He authors a seminal book on reservoir engineering and over 200 papers in international journals and SPE. His research covers formation damage, waterflood and EOR. Pavel holds an MSc in Applied Mathematics, a PhD in Fluid Mechanics and a DSc in Petroleum Engineering from the Russian Gubkin Oil and Gas University. He was a Visiting Professor at Delft University of Technology and at Imperial College of Science and Technology in London. He boasts 35 years of industrial experience in Russia, Europe, Brazil and Australia. Pavel serves as a short course instructor and a Program Committee member at numerous SPE Conferences. He was a 2008-2009 SPE Distinguished Lecturer.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Two Vital Secrets for Building Better Type Wells
Randy Freeborn Energy Navigator
Abstract:
Each year, companies use averaged well production (type wells) to support billion dollar expenditures to buy and develop oil and gas resources. These type wells often have unrepresentative rate-time profiles and recoveries over-stated by as much as 50%. These intolerable errors result from common, but incorrect, assumptions in constructing type well production profiles, and the selection and weighting of analog wells.
Literature related to constructing type wells is sparse and incomplete. This lecture will fill that gap and lead participants to informed decisions for best practices in type well construction. Hind casting examples show that only small errors in recovery result when the type well construction combines historical and predicted production rates. This improvement results from using educated estimates (not intrinsic values) for months with no data to average, and from individual well forecast errors that offset one another. A Monte Carlo method incorporates risk and leads to better well selection and weighting factors, achieving more representative rate- time profiles. The recommended methodology incorporates aggregation and choosing different uncertain parameters. Parameter choice is important because it makes little sense to risk recovery (e.g., P90 for proved reserves) when the application demands a different parameter such as present value. Type well construction methods are common, but they have errors that are difficult to detect. Evaluators are likely using type wells for financial analysis, facility design, cash flow prediction, reserve estimation and debt financing without knowledge of the inaccuracies and options to improve accuracy.
Biography:
Randy Freeborn is a subject matter expert in the field of empirical forecasting, type wells and related technology. Currently, he is Chief Research Engineer at Energy Navigator where he is responsible for identifying and inventing engineering technology for inclusion in the company’s reserve management software. He has been a professional engineer for 44 years and is a member of SPEE and SPE. Freeborn has prepared numerous technical papers for presentation at conferences, workshops and industry meetings. He has given guest lectures at the University of Houston and Texas A&M, and has been called as an expert witness.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Creating Value from Uncertainty and Flexibility
Reidar B. Bratvold University of Stavanger
Abstract:
An increasing number of oil & gas companies use decision analytic methods to deal with complex and uncertain decisions, but still they get consistent under-performance in typical business metrics (cost, production rates, time to start, … ) leading to less value than expected, or, more perniciously, than possible. Uncertainty per se is not the culprit, rather a failure to make the best decisions under uncertainty – which are often non- intuitive. The real value-destroyers are bias and failing to plan for, and exploit, the different ways reality might evolve - if you under-estimate the real uncertainty, you are likely to under-invest in managing its consequences. Making the best decisions requires an accurate assessment of uncertainty (unbiased, neither optimistic nor pessimistic) – and an unbiased approach to managing its consequences – putting as much effort on capturing upside opportunities as mitigating risks. We often make decisions to live up to expectations rather than to live up to possibilities. Despite the ubiquity of options in the oil & gas industry, in practice these embedded options are often overlooked in the formulation and evaluation of investment opportunities, even when uncertainties are explicitly modeled. This talk will illustrate and discuss how to create value from uncertainty and flexibility by applying an option pricing methodology that explicitly focuses on upside possibilities. To properly value flexibility, we must model not only the possible future decisions, but also the information available at the time these decisions are made.
Biography:
Reidar B. Bratvold is Professor of Petroleum Investment and Decision Analysis at the University of Stavanger. His research interests include decision analysis, project valuation, portfolio analysis, real-option valuation, and behavioral challenges in decision-making. Prior to academia, he spent 15 years in the industry in various technical and management roles. He is a co-author of the SPE book Making Good Decisions. Professor Bratvold has previously twice served as an SPE Distinguished Lecturer. He is the 2015 recipient of the North Sea Region SPE Management & Information Award and currently serves as the executive editor for the SPE Economics & Management journal. He is a Fellow of the Society of Decision Professionals and a member of the Norwegian Academy of Technological Sciences. He holds a PhD in petroleum engineering and an MSc in mathematics, both from Stanford University and has studied business and management science at INSEAD and Stanford University.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Human Factors in Barrier Thinking
Ron McLeod Ron McLeod Ltd.
Abstract:
The oil and gas industry places great reliance on layers-of-defenses, or barrier thinking, to protect against process safety incidents. Human performance continues to be the single most widely relied on barrier: whether as a defense in its own right, or in implementing, inspecting, maintaining and supporting engineered defenses. Human error, in its many forms, also continues to be a significant threat to the reliability of engineered and organizational defenses. While approaches to developing and assuring layers of defenses strategies have become increasingly formalized and rigorous in recent years, many organizations struggle to know how to ensure the human defenses they rely on are as robust as they reasonably can be when those strategies are developed and implemented. Drawing on the 2005 explosion and fire at the Buncefield fuel storage site as a case study, the presentation considers issues associated with the independence and effectiveness of human defenses. The key idea SPE members should take away from the lecture is that organizations can improve the strength of their human defenses by being clearer about exactly what it is they expect and intend of human performance to protect against threats. The presentation sets out challenges organizations can use to ensure the human defenses they rely on are as robust and reliable as they reasonably can be.
Biography:
Ron McLeod holds a BSc in Psychology, an MSc in Ergonomics and a Ph.D. in Engineering and Applied Science and is Honorary Professor of Engineering Psychology at Heriot-Watt University. He has more than 30 years experience as a Human Factors specialists and was Shell’s Global Discipline Lead for Human Factors until March 2014. He has been active in organisations including the UK National Advisory Committee on Human Factors, the Process Safety Leadership Group, as well as the IOGP, SPE and CIEHF. He has published in scientific journals and has authored or contributed to numerous technical standards and best- practice guides. His first book, “Designing for Human Reliability: Human Factors Engineering in the Oil, Gas and Process Industries” was published by Elsevier in 2015.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
In-situ Wettability Utilizing Low Gradient Magnetic Resonance
Oluwasegun Jebutu Baker Hughes Inc
Abstract:
Main idea: Evidence has shown that mixed-oil wet reservoirs do exist. How mixed wettability occur is complex, water wet systems can transition to mixed wet, but if we can identify where they occur and know the distribution in the reservoir, we can produce more efficiently.
Hydrocarbon recovery, production mechanisms and field development economics strongly rely on understanding the wetting characteristics of the in-situ reservoir fluids. This paper presents a new approach to estimate wettability, utilizing low-gradient magnetic resonance technology.
Wettability is difficult to measure in-situ, however the interaction of the fluid and rock mineral surfaces have an apparent relaxation time that is influenced by the surface relaxation mechanism of magnetic resonance. Wettability can be measured in the laboratory through contact angle, atomic forces microscope imaging and Ammot index measurements. These are scale-constrained and difficult to replicate original down-hole conditions for these measurements. The new approach enables direct wettability estimation at in-situ reservoir conditions
A spin-lattice function is derived, which is directly related to the interfacial tension and surface wetting fluid properties. A wettability index is then computed from the function using a reference zone below the free water level. The results indicate mixed wetting characteristics in asphaltenes and heavy-to-solid hydrocarbon bearing sections. Several other factors evaluated that may account for the wettability distribution include, asphaltene content of oil, acid number of the oil, rock surface roughness and paleo-diagenetic thermal and pressure history of the reservoir. The early insitu knowledge of the presence of mixed wet systems allows for optimal sweep efficiency planning of future recovery methods.
Biography:
Oluwasegun Jebutu has over 28 years' experience in reservoir characterization supporting Wireline and Logging While Drilling operations. Roles include Strategic Senior Manager, Global integration manager, Reservoir development services, Regional geoscience manager North America, District Petrophysicist, Petrophysical and project consultant, Operations Manager Integrated field studies, worked in USA,United Kingdom, Angola, Nigeria; Baker Hughes, Halliburton, Gearhart. He has a B.SC. Physics and M.SC in Petroleum Engineering, MBA Texas A&M. He has authored patents on NMR technology and co-authored over 40 publications. An SPE Distinguished lecturer in 2011-2012, A member of the SPE and SPWLA, SPE Conference Chairman, SPE Section chairman.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Salt Behavior and Drilling Strategies to Overcome Challenges in Pre-Salt Exploratory Wells
Shrikant Tiwari Saudi Aramco
Abstract:
Swathes of salt in various geometries exist at varying depths in several salt basins in the world with significant accumulation of hydrocarbon beneath. These pre-salt accumulations require drilling through different types of salt structures. The geological uncertainty due to seismic anisotropy and inherently poor imaging below salt layers require sound drilling engineering and solutions-driven drilling practices. Initial salt drilling posed several challenges, for salt behaves very different from other clastic sediments. The challenges vary with the geological conditions and composition of salt body. Several experiments conducted over the years and experience of drilling salt in different basins helped enriching Industry knowledge base to comprehend the salt drilling situation better. Exploratory drilling brings another dimension of challenges with uncertainty of geological conditions. The drilling plan needs to be robust enough to handle these uncertainties and flexible enough to amend drilling strategies based on actual conditions. Devising appropriate well construction and drilling strategy require a sound understanding of salt behavior and its variability with geological conditions. Successful drilling requires aligning drilling solutions with salt behavior under anticipated geological conditions and adopting scenario based approach to handle unexpected situations. This lecture establishes a link between salt characteristics and drilling techniques, enabling technology options and workflows that have been instrumental in successful well construction in frontier areas for pre-salt exploration.
Biography:
Shrikant Tiwari is General Supervisor heading an Offshore Exploration Drilling Engineering Division in Saudi Aramco and is leading exploratory drilling projects in Red Sea and Arabian Gulf. He holds Bachelor of Engineering and MBA degrees. He has over 28 years of experience in the field of drilling and completions for offshore and onshore operations. Shrikant has worked in several International locations in different positions and has authored and co-authored several papers in leading Industry journals. He has successfully led many drilling and completion projects in his career. Drilling project planning and devising drilling strategies for critical well situations are his strengths.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Dry Hole Analysis: What I have Learnt about the Upstream Petroleum Industry from My Failures
Steve Mackie Santos Ltd
Abstract:
Finding and producing oil and gas are the major objectives of any upstream oil and gas company. Both, however, can be highly elusive. Dry hole analysis is an exploration methodology to determine what can be learnt from drilling failures. Using a series of case studies from my own career I look at what we can learn from "failures" - not just those that occur during exploration, appraisal and development but also those that relate to the business as a whole. Having worked for all types of companies - multinationals (both Euopean and USA), local Australian companies and even my own consulting I have been exposed to many and varied management and organisational models. In each case the distilled learnings are universal and applicable at any stage of a carreer. Originally prepared as a Young Petroleum Professionals lecture, the concepts have been expanded to help all professionals see the upstream petroleum industry as a business. As well as uncovering technical findings from failures we can also find out a great deal about the industry that will help working in it become more rewarding and exciting!
Biography:
Steve Mackie has a BSc (geophysics and sedimentology), MBA (strategy) and PhD (decision-making) together with 35+ years’ experience in the upstream petroleum industry functioning in both regional and field specific geoscience and engineering. As well as running his own successful consultancy he has worked with multinationals and local explorers in both technical and managerial roles. He has been forming, managing and developing asset teams, including virtual teams, associated with exploration and development geoscience and engineering for the last 20 years. He currently is Manager – Geophysics at Santos Ltd. He is also an adjunct at the Australian School of Petroleum, University of Adelaide; a member of the Advisory Board to the Australian School of Petroleum; chairman of the Australian Petroleum Production and Exploration Association (APPEA) Technical Program Committee and editor of the APPEA Journal (2009 – 2015). Steve is the Federal President of the Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia (PESA). He is an honorary life member of APPEA and an active member of SPE, AAPG and EAGE.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Borehole Seismic Solutions for Integrated Reservoir Characterization and Monitoring
Steve Morice Shell Todd Oil Services Ltd
Abstract:
Modern oil and gas field management is increasingly reliant on detailed and precise 3D reservoir characterisation, and timely areal monitoring. Borehole seismic techniques bridge the gap between remote surface-seismic observations and downhole reservoir evaluation: Borehole seismic data provide intrinsically higher-resolution, higher-fidelity images than surface-seismic data in the vicinity of the wellbore, and unique access to properties of seismic wavefields to enhance surface-seismic imaging. With the advent of new, operationally-efficient very large wireline receiver arrays; fiber-optic recording using Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS); the crosswell seismic reflection technique, and advanced seismic imaging algorithms such as Reverse Time Migration, a new wave of borehole seismic technologies is revolutionizing 3D seismic reservoir characterization and on-demand reservoir surveillance. New borehole seismic technologies are providing deeper insights into static reservoir architecture and properties, and into dynamic reservoir performance for conventional water-flood production, EOR, and CO2 sequestration – in deepwater, unconventional, full-field, and low-footprint environments. This lecture will begin by illustrating the wide range of borehole seismic solutions for reservoir characterization and monitoring, using a diverse set of current- and recent case study examples – through which the audience will gain an understanding of the appropriate use of borehole seismic techniques for field development and management. The lecture will then focus on DAS, explaining how the technique works; its capability to deliver conventional borehole seismic solutions (with key advantages over geophones); then describing DAS’s dramatic impact on field monitoring applications and business-critical decisions. New and enhanced borehole seismic techniques – especially with DAS time-lapse monitoring – are ready to deliver critical reservoir management solutions for your fields.
Biography:
Steve Morice holds a PhD in Geophysics from Cambridge University, and is a Lead Geophysicist and Shell's global focal-point for well-to-seismic interpretation. With 20 years of experience in the international oil and gas industry, Steve has contributed to the fields of surface- and borehole-seismic survey design, acquisition technologies, processing/imaging techniques, and geophysical interpretation - with particular emphasis on the integration of surface- and borehole data for field development and production optimization. Steve is an author and co-author of numerous technical publications and two patents.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Minimize Operational Risk Using Shared Geomechanical Earth Model
Surej Kumar Subbiah Schlumberger
Abstract:
Stuck drill pipe, lost hole, severe mud losses, unable to hydraulically fracture the formation, well shut down due to sand production, early water breakthrough. Sound familiar? These incidents can cost E&P companies millions of dollars.
Geomechanics combines geology, geophysics, petrophysics and rock mechanics in order to describe state of earth stresses and rock mechanical properties. This can be done along a single wellbore, or in 3D field scale, and the results are presented in what is known as the Shared Geomechanical Earth Model. This model helps in the understanding and managing of the risks associated with rock deformation, which in turn helps minimize operational risks for the life of the field from exploration to abandonment. Examples include wellbore instability, sand production, hydraulic fracturing, injectivity, subsidence, compaction, fractures reactivation, and thermal effects.
This presentation aims to increase awareness as to how one and the same Shared Geomechanical Model can be used by different departments in an E&P company for their operational planning, with focus on drilling and completion activities.
Biography:
Based in Abu Dhabi, Surej Kumar Subbiah is currently the Principal Geomechanics Lead for Schlumberger Middle East. Surej holds BS and MS degrees in petroleum engineering from the University of Technology Malaysia, with specialization in geomechanics. He spent the first five years of his career in an academic environment as a Research Associate and a Lecturer before he joined Schlumberger. With 20 years of experience, Surej has been involved in many applied geomechanics projects from well centric to 3D field scale, and conducted training courses in geomechanics for NeXT as well as SPE Netherlands and SPWLA Abu Dhabi.
Society of Petroleum Engineers Distinguished Lecturer 2016-17 Lecture Season
Your Field is Getting Older: Is your Process Engineering Still Cost Effective?
Wally John Georgie Maxoil Solutions
Abstract:
The lifecycle of developed fields, onshore and offshore will go through different stages of production up to the decline into late field life. Effective reservoir engineering management will lead to prolonging the life of field if a cost effective processing surface facilities strategy is put in place. Factors that lead to the decline in oil production or increase in OPEX may include increased water production, solids handling and the need for relatively higher compression requirements for gas lift. In order to maintain productivity and profitability, an effective holistic engineering approach to optimizing the process surface facilities must be utilized. The challenges of Optimizing Mature Field Production are: 1. Reservoir understanding with potential definition of additional reserves 2. Complete re-appraisal of the operability issues in the production facilities 3. Develop confidence to invest to optimize the process handling capabilities and capacity 4. Low CAPEX simplification of the surface facilities infrastructure to meet challenges 5. An implementation plan that recognizes the ‘Brownfield’ complexities 6. Selection of suitable optimum technology, configuration and training 7. Optimum upgrade plan of the facilities with minimum production losses Successful operation of mature fields and their surface facilities requires successful change management to the new operating strategy. Using a holistic approach can maximize the full potential of mature processing facilities at a manageable CAPEX and OPEX.
Biography:
Dr. Wally Georgie has a B.Sc degree in Chemistry, M.Sc in Polymer Technology, M.Sc in Safety Engineering and PhD in Applied Chemistry with training courses in oil and gas process engineering, production, reservoir and corrosion engineering. He has worked for over 37 years in different areas of oil and gas production facilities, including corrosion control, flow assurance, fluid separation, separator design, gas handling and produced water. He started his career in oil and gas services sector in 1978 based in the UK and working globally with different production issues then joined Statoil as senior staff engineer and later as technical advisor in the Norwegian sector of the North Sea. Working as part of operation team on oil and gas production facilities key focus areas included optimization, operation trouble-shooting, de-bottlenecking, oil water separation, slug handling, process verification, and myriad other fluid and gas handling issues. He then started working in March 1999 as a consultant globally both offshore and onshore, conventional and unconventional in the area of separation trouble shooting, operation assurance, produced water management, gas handling problems, flow assurance, system integrities and production chemistry, with emphasis in dealing with mature facilities worldwide.