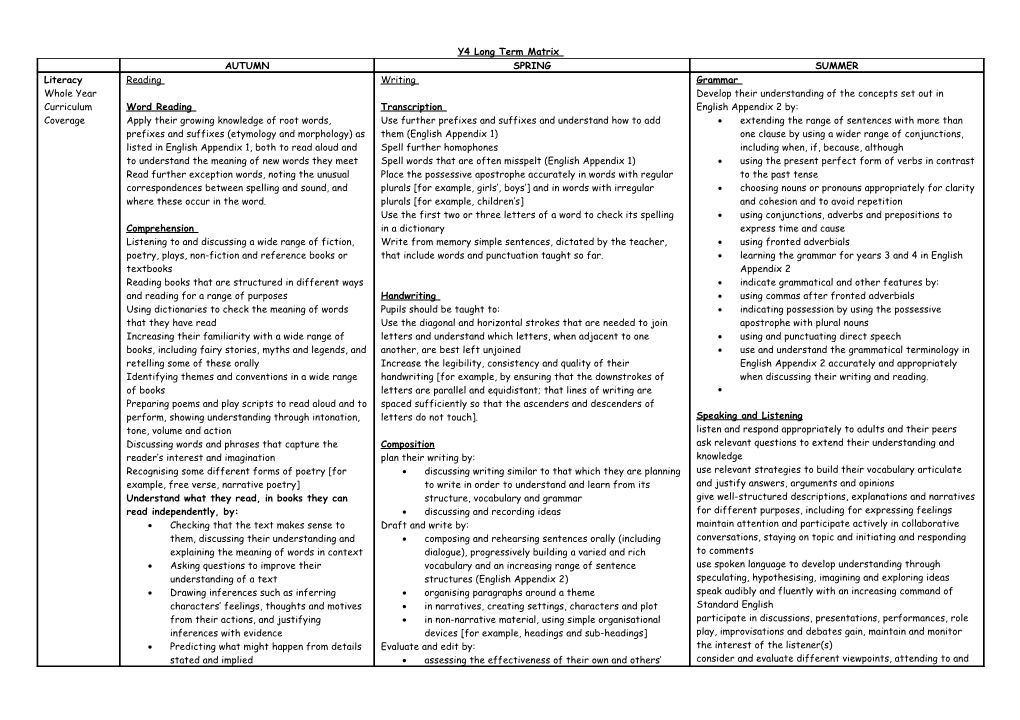
Y4 Long Term Matrix AUTUMN SPRING SUMMER Literacy Reading Writing Grammar Whole Year Develop their understanding of the concepts set out in Curriculum Word Reading Transcription English Appendix 2 by: Coverage Apply their growing knowledge of root words, Use further prefixes and suffixes and understand how to add extending the range of sentences with more than prefixes and suffixes (etymology and morphology) as them (English Appendix 1) one clause by using a wider range of conjunctions, listed in English Appendix 1, both to read aloud and Spell further homophones including when, if, because, although to understand the meaning of new words they meet Spell words that are often misspelt (English Appendix 1) using the present perfect form of verbs in contrast Read further exception words, noting the unusual Place the possessive apostrophe accurately in words with regular to the past tense correspondences between spelling and sound, and plurals [for example, girls’, boys’] and in words with irregular choosing nouns or pronouns appropriately for clarity where these occur in the word. plurals [for example, children’s] and cohesion and to avoid repetition Use the first two or three letters of a word to check its spelling using conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions to Comprehension in a dictionary express time and cause Listening to and discussing a wide range of fiction, Write from memory simple sentences, dictated by the teacher, using fronted adverbials poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or that include words and punctuation taught so far. learning the grammar for years 3 and 4 in English textbooks Appendix 2 Reading books that are structured in different ways indicate grammatical and other features by: and reading for a range of purposes Handwriting using commas after fronted adverbials Using dictionaries to check the meaning of words Pupils should be taught to: indicating possession by using the possessive that they have read Use the diagonal and horizontal strokes that are needed to join apostrophe with plural nouns Increasing their familiarity with a wide range of letters and understand which letters, when adjacent to one using and punctuating direct speech books, including fairy stories, myths and legends, and another, are best left unjoined use and understand the grammatical terminology in retelling some of these orally Increase the legibility, consistency and quality of their English Appendix 2 accurately and appropriately Identifying themes and conventions in a wide range handwriting [for example, by ensuring that the downstrokes of when discussing their writing and reading. of books letters are parallel and equidistant; that lines of writing are Preparing poems and play scripts to read aloud and to spaced sufficiently so that the ascenders and descenders of perform, showing understanding through intonation, letters do not touch]. Speaking and Listening tone, volume and action listen and respond appropriately to adults and their peers Discussing words and phrases that capture the Composition ask relevant questions to extend their understanding and reader’s interest and imagination plan their writing by: knowledge Recognising some different forms of poetry [for discussing writing similar to that which they are planning use relevant strategies to build their vocabulary articulate example, free verse, narrative poetry] to write in order to understand and learn from its and justify answers, arguments and opinions Understand what they read, in books they can structure, vocabulary and grammar give well-structured descriptions, explanations and narratives read independently, by: discussing and recording ideas for different purposes, including for expressing feelings Checking that the text makes sense to Draft and write by: maintain attention and participate actively in collaborative them, discussing their understanding and composing and rehearsing sentences orally (including conversations, staying on topic and initiating and responding explaining the meaning of words in context dialogue), progressively building a varied and rich to comments Asking questions to improve their vocabulary and an increasing range of sentence use spoken language to develop understanding through understanding of a text structures (English Appendix 2) speculating, hypothesising, imagining and exploring ideas Drawing inferences such as inferring organising paragraphs around a theme speak audibly and fluently with an increasing command of characters’ feelings, thoughts and motives in narratives, creating settings, characters and plot Standard English from their actions, and justifying in non-narrative material, using simple organisational participate in discussions, presentations, performances, role inferences with evidence devices [for example, headings and sub-headings] play, improvisations and debates gain, maintain and monitor Predicting what might happen from details Evaluate and edit by: the interest of the listener(s) stated and implied assessing the effectiveness of their own and others’ consider and evaluate different viewpoints, attending to and Identifying main ideas drawn from more writing and suggesting improvements building on the contributions of others than one paragraph and summarising these proposing changes to grammar and vocabulary to improve select and use appropriate registers for effective Identifying how language, structure, and consistency, including the accurate use of pronouns in communication presentation contribute to meaning sentences Retrieve and record information from non- proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors fiction read aloud their own writing, to a group or the whole Participate in discussion about both books class, using appropriate intonation and controlling the that are read to them and those they can tone and volume so that the meaning is clear read for themselves, taking turns and listening to what others say.
Wider reading Kensuke’s Kingdom One man band pixar animation short How to Train a Dragon Where the Wild things are cross information texts about the body/teeth/animal diets Information texts based on famous electrical scientists Information texts based on science topics curricular text information texts about natural disasters Hinduism books based on Diwali Islam information books links atlases Ancient Egypt information books Information texts based on Japan Buddhism information text books Numeracy Number/ Calculation Geometry & Measures Fractions Whole Year count in multiples of 6, 7, 9, 25 and 1000 convert between different units of measure [for example, recognise and show, using diagrams, families of common Curriculum find 1000 more or less than a given number kilometre to metre; hour to minute] equivalent fractions Coverage count backwards through zero to include negative measure and calculate the perimeter of a rectilinear figure count up and down in hundredths; recognise that hundredths numbers (including squares) in centimetres and metres arise when dividing an object by one hundred and dividing recognise the place value of each digit in a four-digit find the area of rectilinear shapes by counting squares tenths by ten number (thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones) estimate, compare and calculate different measures, including solve problems involving increasingly harder fractions to order and compare numbers beyond 1000 money in pounds and pence calculate quantities, and fractions to divide quantities, identify, represent and estimate numbers using compare and classify geometric shapes, including quadrilaterals including non-unit fractions where the answer is a whole different representations and triangles, based on their properties and sizes number round any number to the nearest 10, 100 or 1000 identify acute and obtuse angles and compare and order angles up add and subtract fractions with the same denominator solve number and practical problems that involve all to two right angles by size recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of of the above and with increasingly large positive identify lines of symmetry in 2-D shapes presented in different tenths or hundredths numbers orientations recognise and write decimal equivalents to 1/4, 1/2, 3/4 read Roman numerals to 100 (I to C) and know that complete a simple symmetric figure with respect to a specific line find the effect of dividing a one- or two-digit number by 10 over time, the numeral system changed to include of symmetry and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as the concept of zero and place value describe positions on a 2-D grid as coordinates in the first ones, tenths and hundredths add and subtract numbers with up to 4 digits using quadrant round decimals with one decimal place to the nearest whole the formal written methods of columnar addition and describe movements between positions as translations of a given number subtraction where appropriate unit to the left/right and up/down compare numbers with the same number of decimal places up estimate and use inverse operations to check plot specified points and draw sides to complete a given polygon to two decimal places answers to a calculation solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions solve addition and subtraction two-step problems in Statistics and decimals to two decimal places contexts, deciding which operations and methods to interpret and present discrete and continuous data using use and why appropriate graphical methods, including bar charts and time recall multiplication and division facts for graphs multiplication tables up to 12 Χ 12 solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information use place value, known and derived facts to multiply presented in bar charts, pictograms, tables and other graphs and divide mentally, including: multiplying by 0 and 1; dividing by 1; multiplying together three numbers recognise and use factor pairs and commutativity in mental calculations multiply two-digit and three-digit numbers by a one- digit number using formal written layout solve problems involving multiplying and adding, including using the distributive law to multiply two digit numbers by one digit, integer scaling problems and harder correspondence problems such as n objects are connected to m objects.
Theme or Adventurers and explorers Ancient Egypt Ancient civilizations including the Romans Topic Science Animals including humans Electricity Electricity Living things and their habitats Sounds States of Matter
On-going: September/October November/February November/February March/April April/May June/July seasonal change ICT E - safety Programming Programming/research multimedia presentations skills On-going: use technology safely, respectfully and responsibly; recognise acceptable/unacceptable behaviour; identify a range of ways to report concerns about content and contact understand computer networks including the internet; how they can provide multiple services, such as the world wide web; and the opportunities they offer for communication and collaboration
Article 17 DT Designing and making a hat for different weathers make Egyptian jewellery Design and make a meal from that culture/ healthy snack design and make pyramid with door with a hinge art papier-mâché canopic jar/animal head
On-going: Design, make, evaluate and apply technical knowledge
Articles: 13
Art Hot and cold climates. Look at Egyptian art Learn about great artists, architects and designers in history Create landscape pictures using hot and cold colours Look at Egyptian sculptures – focus on the sphinx – Roman pottery & mosaics Design and create a clay sculpture of the sphinx Improve their mastery of art and design techniques, including drawing, painting and sculptures with a range of materials (pencil, charcoal, paint, clay)
On-going : to create sketch books to record their observations and use them to review and revisit ideas to improve their mastery of art and design techniques, including drawing, painting and sculpture with a range of materials [for example, pencil, charcoal, paint, clay] about great artists, architects and designers in history Articles: 13,
PE Tag Rugby Hockey Gymnastics SAQ Athletics Striking and fielding games Swimming (for select chn) On-going: compare their performances with previous ones and demonstrate improvement to achieve their personal best
Article 13, 31
Music Charanga: Charanga: Charanga: Charanga: Charanga: Charanga: Unit: Mamma Mia – Abba Unit: Five Gold Rings Unit: Glockenspiel Stage Unit: Benjamin Britten - Cuckoo Unit: Lean on Me Unit: Reflect, Rewind and Replay Structure of songs Style: Gospel Style: Western Classical Music linked to literacy. Music 3 Style: Benjamin Britten (Western Topic and cross and your choice from Year 4 and styles of the 70s Style: Learning basic Classical Music), Folk, Big Band Jazz curricular links: Gospel Topic and cross curricular links: and 80s, analysing in its historical context Option to look at all the instrumental skills by Topic and cross curricular links: performance, Sweden as ie from Beethoven to extension activities documents. a country playing tunes in varying Literacy and history, Britten100.org, slavery, Elvis to the Think about the history of music styles www.fridayafternoons.co.uk. The Urban Gospel of Beyonce in context, listen to some and different choirs like Western Classical music and Topic and cross historical context of Jazz and folk the London Community place the music from the units curricular links: music. Gospel Choir. Analysing you have worked through, in their Introduction to the performance. correct time and space. Consolidate the foundations of language of music, the language of music. theory and composition.
Cello and Violin – Egglescliffe Cello and Violin – Egglescliffe Cello and Violin – Egglescliffe On-going: play and perform in solo and ensemble contexts, using their voices and playing musical instruments with increasing accuracy, fluency, control and expression improvise and compose music for a range of purposes using the inter-related dimensions of music listen with attention to detail and recall sounds with increasing aural memory use and understand staff and other musical notations appreciate and understand a wide range of high-quality live and recorded music drawn from different traditions and from great composers and musicians develop an understanding of the history of music Article 31, History Famous explorers and their contributions to society, The achievements of the earliest civilizations – an overview of The Roman empire and its impact on Britain, including: Julius including: Christopher Columbus, Neil Armstrong, where and when the first civilizations appeared and a depth study Caesar’s attempted invasion in 55-54 BC; the Roman Empire Roald Amundsen and Ferdinand Magellan. An indepth of one of the following: Ancient Sumer; The Indus Valley; Ancient by AD 42 and the power of its army; successful invasion by study of the expeditions of Captain Cook (local Egypt; The Shang Dynasty of Ancient China Claudius and conquest, including Hadrian’s Wall; British history link). The difference between explorers and resistance, for example, Boudica; "Romanisation" of Britain: adventurers. The significant turning points in British sites such as Caerwent and the impact of technology, culture history, for example, the discovery of Australia and and beliefs, including early Christianity; Roman withdrawal the colonisation of America. from Britain in c. AD 410 and the fall of the western Roman Empire On-going: Pupils should continue to develop a chronologically secure knowledge and understanding of British, local and world history, establishing clear narratives within and across the periods they study. They should construct informed responses that involve thoughtful selection and organisation of relevant historical information. They should understand how our knowledge of the past is constructed from a range of sources
Geography Describe and understand key aspects of physical Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate Locate the world’s countries using maps to focus on Europe geography, including: climate, zones, biomes and countries and describe features studied (including Russia) and North and South America concentrating vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and Describe and understand key aspects of: physical geography rivers on their environmental regions, key physical and human earthquakes, and the water cycle human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, characteristics, countries and major cities Use maps, atlases and globes to locate countries and economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of Place knowledge understand geographical similarities and describe features studied. natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water differences through the study of human physical geography: Understand geographical similarities and differences types of settlements and land use, economic activity including through the study of human and physical geography trade links, and the distribution of natural resources of a region in a European Country. including energy food, minerals and water Locate the word`s countries using maps to focus on Geographical skills and fieldwork: use maps, atlases, globes Europe, (including the location of Russia) and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and concentrating on their environmental regions describe features studied
On-going:
PSHE Seal: New Beginnings Anti bullying SEAL: Going for gold SEAL SEAL SEAL: Changes BV: identifying and Relationships Getting on and falling out BV: Promoting the value of combating discrimination BV: promotion of tolerance between BV: promoting tolerance democracy in lessons and wider Democracy relating to different cultures school life class / school rules and school council nominations
Article 3, 12, 13, 42 Article 2, 3, 8, 13, 42, Article 3, 12, 13, 42 Article 3, 8, 13, 42 Article 3, 8, 12, 13, 42 Article 3, 12, 13, 42
RE How do Buddhist’s What are the journeys What is Diwali? Why is Why is Easter important to What are the 5 pillars of Islam and why are they important? celebrate special times associated in the it important in Christians? Islam in their lives? Christmas story? Hinduism? Christianity Buddhism Christianity Hinduism
Article 2, 13 Article 2, 13 Article 2, 13 Article 2, 13 Article 2, 13
British Values: promoting tolerance between different cultural traditions by enabling students to acquire an appreciation of their own and other cultures British Values: Understanding the freedom to choose and hold other faiths and beliefs and that this is protected by law