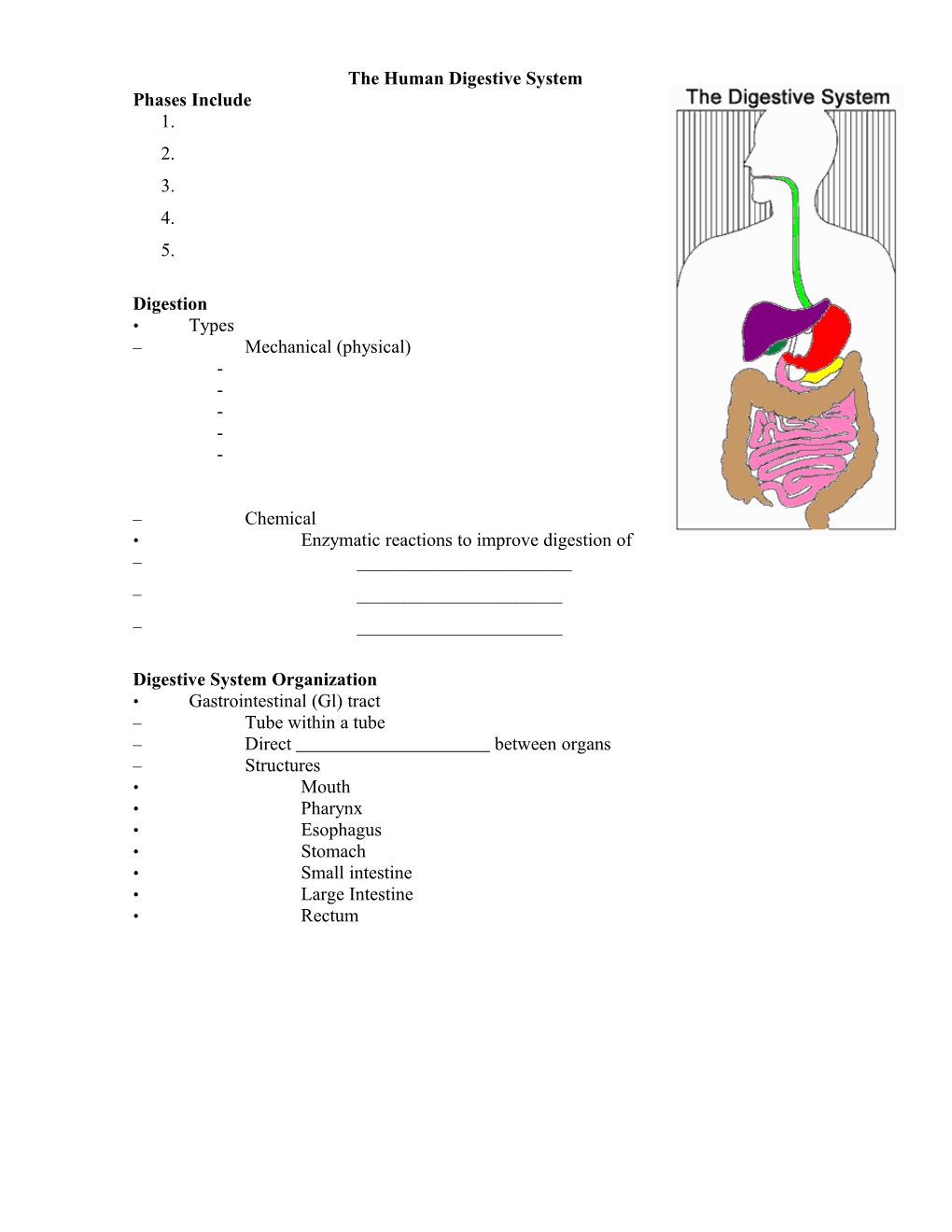
The Human Digestive System Phases Include 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Digestion • Types – Mechanical (physical) - - - - -
– Chemical • Enzymatic reactions to improve digestion of – ______– ______– ______
Digestive System Organization • Gastrointestinal (Gl) tract – Tube within a tube – Direct between organs – Structures • Mouth • Pharynx • Esophagus • Stomach • Small intestine • Large Intestine • Rectum Mouth • Teeth break down food into small pieces. Tongue mixes food with saliva (contains , which helps break down starch). • Epiglottis is a at the back of the throat that closes over the trachea preventing food from entering it.
Esophagus • Approximately 10” long • Functions include: 1. ______2. Moves food from the throat to the stomach using muscle movement called ______• If acid from the stomach gets in here that’s ______
Stomach • muscular bag that stores the food you eat, breaks it down into tiny pieces. • Mixes food with ______that contain enzymes to break down proteins and lipids. • ______in the stomach kills bacteria. • Food found in the stomach is called ______
Small Intestine • Small intestines are roughly meters long • Lining of intestine walls are coated with little ‘fingers’ called to increase surface area. • The villi are covered in , which increases surface area for absorption. • Nutrients from the food pass into the _____through the small intestine walls. • Absorbs: • 80% ingested water • Vitamins • Minerals • Carbonates • Proteins • Lipids
• Secretes ______Large Intestine • About 5 feet long • Accepts what small intestines don’t absorb. • Is also divided into 3 major parts: , receives material from SI which is subdivided into • Ascending • Transverse • Descending (short term storage which holds feces before it is expelled).
Functions 1. digestion 2. digestion – Bacterial digestion including ferment carbohydrates and protein/amino acid breakdown . Absorbs – More water – B and K . Concentrate/eliminate wastes
Accessory Organs Not part of the path of food, but play a . Include:
.
Liver • Directly affects digestion by producing bile – helps digest fat – Processes nutrients in the blood, filters out and waste including and – Activates vitamin D
Gall Bladder • Stores bile from the , releases it into the . • Fatty diets can cause gallstones
Pancreas • Produces digestive enzymes to and proteins • Neutralizes that enter small intestine • Regulates blood sugar by producing .
References and Links
• The Real Deal on the Digestive System, • http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/yrdd/index.htm • Pancreas: Introduction and Index, http://arbl.cvmbs.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/digestion/pancreas/index.html • Your Gross and Cool Body - Digestive System, http://yucky.discovery.com/noflash/body/pg000126.html • http://highered.mcgraw- hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation__organs_of_digestion.ht ml