Task Assessment Record (Ungradedachievement)
There is no further grading in the assessment of this unit.
Assessor Andrea Beeney Diploma Nursing and Midwifery Subject Study Skills Unit HC7/3/EA/047 Code CBF655 Credits 3 Producing a Written Task Title Task no. for unit 1/2 AC 1.1, 2.1 Assignment
Student A Student This work is my own signature AStudent
Evaluative This task has really helped me in how to plan for further assignments on the course. Comment
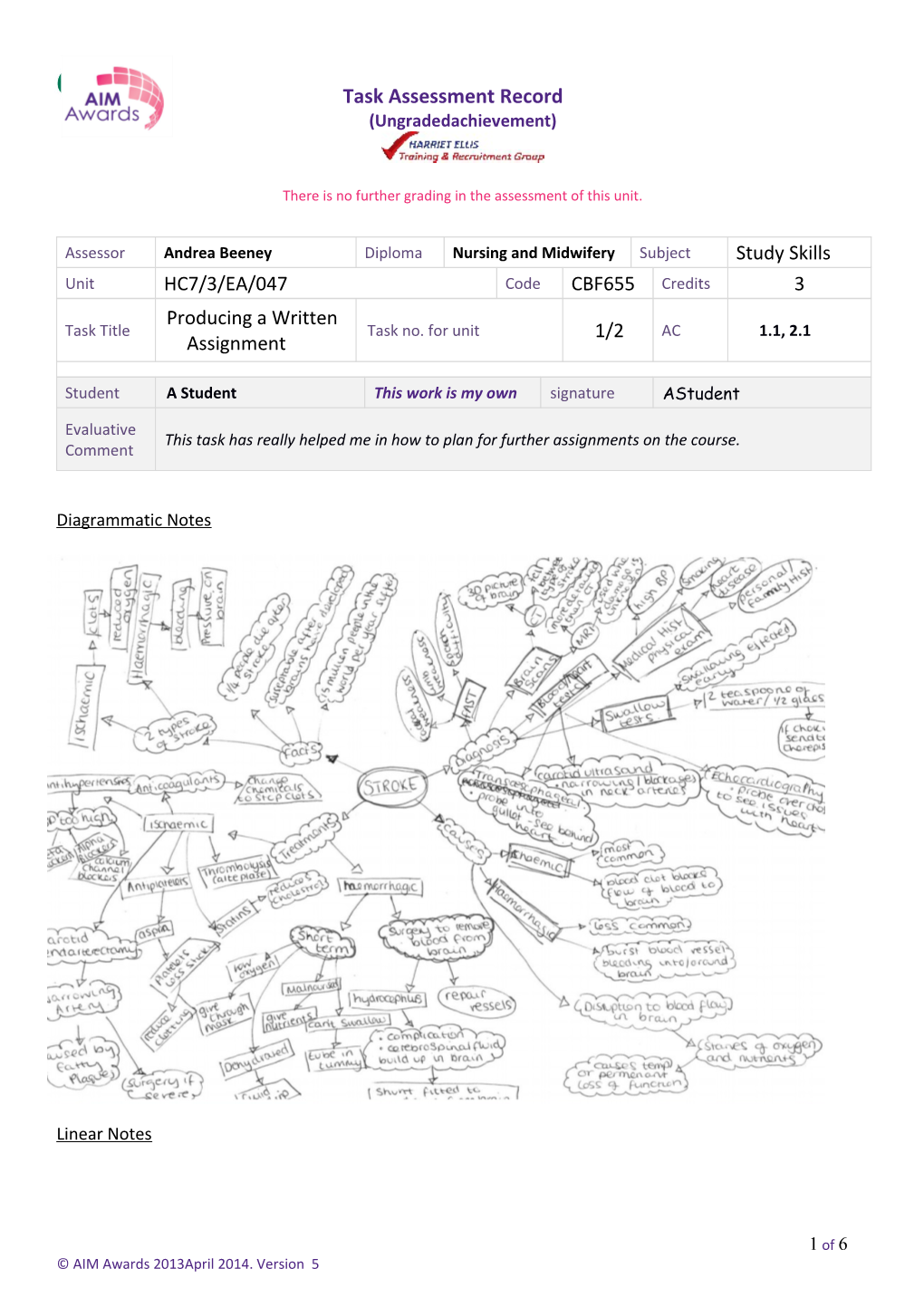
Diagrammatic Notes
Linear Notes
1 of 6 © AIM Awards 2013April 2014. Version 5 Task Assessment Record (Ungradedachievement)
There is no further grading in the assessment of this unit.
2 of 6 © AIM Awards 2013April 2014. Version 5 Task Assessment Record (Ungradedachievement)
There is no further grading in the assessment of this unit.
3 of 6 © AIM Awards 2013April 2014. Version 5 Task Assessment Record (Ungradedachievement)
There is no further grading in the assessment of this unit.
4 of 6 © AIM Awards 2013April 2014. Version 5 Task Assessment Record (Ungradedachievement)
There is no further grading in the assessment of this unit.
Essay Plan Introduction (100 words)
Evolution has caused us to be more likely to suffer from a stroke (direct reference TV)
15 million people worldwide per year have a stoke (direct reference TV)
Around 110,000 people have a stroke every year in England. It is the third leading cause of death after heart disease and cancer (direct reference newspaper)
2 types
Caused by the blood supply to the brain being cut off (direct reference newspaper)
Main Body (800 words)
Diagnosis (300 words)
FAST in first instance- Facial weakness, Arm weakness, Speech problems, Time to call 999 (reference textbook)
Brain scans (first 24 hours)-
o CT – 3d picture of brain, used to tell if ischaemic or haemorrhagic stroke occurred 5 of 6 © AIM Awards 2013April 2014. Version 5 Task Assessment Record (Ungradedachievement)
There is no further grading in the assessment of this unit.
o MRI – detailed picture of body, used when damage/location is unknown
Heart/blood vessel test –
o Carotid ultrasound- shows narrowing/blockages in neck arteries
o Echocardiography- images of heart to check if any abnormalities (ultrasound probe across chest)
o Transoesophageal – ultrasound probe into gullet behind heart- clearer picture
Swallow test- swallowing effect early in stroke, 2 teaspoons of water without choking, then half glass. Send to therapist for detailed assessment if unable to.
Treatment- ischemic (300 words)
Thrombolysis – injections of alteplase, dissolves clots/restores flow. Brain scan to confirm type first as makes hem worse
Antiplatelets- regular aspirin, platelets less sticky, reduce clots.
Anticoagulants- changes chemicals of blood to stop clots
Antihypertensive- BP too high, beta/alpha blockers, calcium channel blockers
Statins- cholesterol too high, reduces in body by blocking enzyme liver produces.
Carotid endarterectomy- narrowing artery by fatty plaque- if severe, surgery offered.
Treatment- Haemorrhagic (200 words)
Surgery- remove blood from brain and repair vessels
Surgery for hydrocephalus- complication – cerebrospinal fluid builds up in brain, headaches, sickness and no balance. Artificial tube into brain to drain fluids.
Short term- Tube in tummy if can’t swallow, Nutritional supplements if malnourished, fluids if dehydrated and oxygen if low. (Internet influenced all above- reference to NHS website)
Conclusion (100 words)
Stoke is medical emergency (direct reference text book)- Doctors diagnose via multiple tests as shown above
Many treatments depending on type of stroke had
6 of 6 © AIM Awards 2013April 2014. Version 5