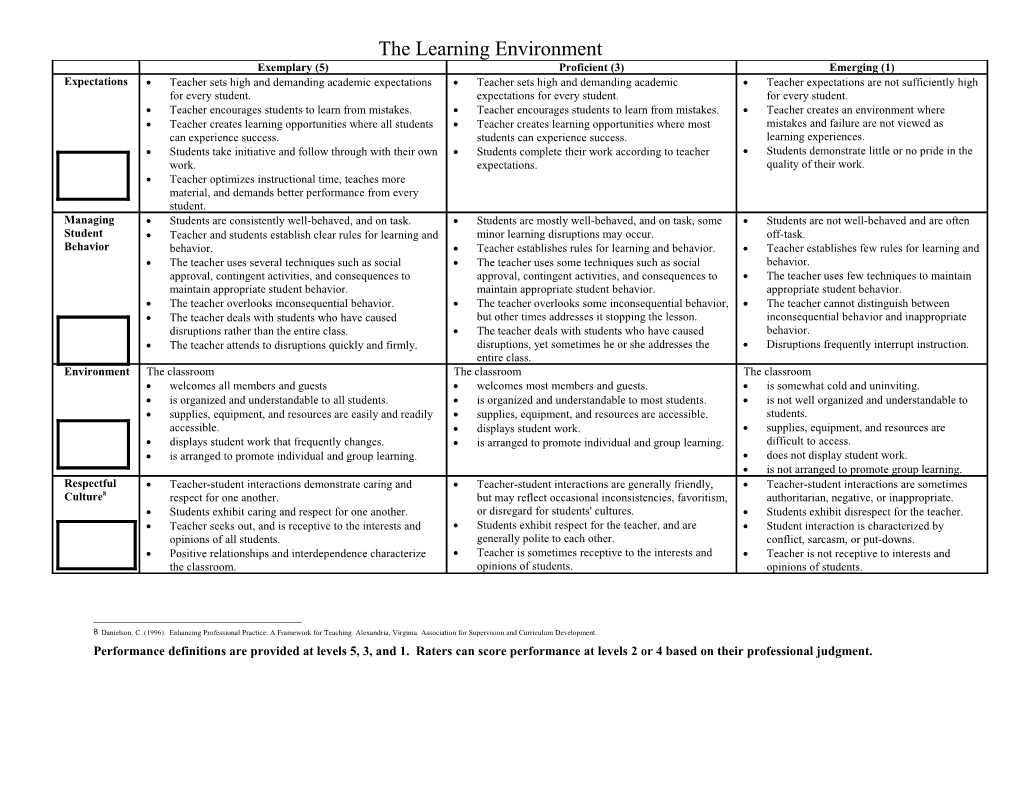
The Learning Environment Exemplary (5) Proficient (3) Emerging (1) Expectations Teacher sets high and demanding academic expectations Teacher sets high and demanding academic Teacher expectations are not sufficiently high for every student. expectations for every student. for every student. Teacher encourages students to learn from mistakes. Teacher encourages students to learn from mistakes. Teacher creates an environment where Teacher creates learning opportunities where all students Teacher creates learning opportunities where most mistakes and failure are not viewed as can experience success. students can experience success. learning experiences. Students take initiative and follow through with their own Students complete their work according to teacher Students demonstrate little or no pride in the work. expectations. quality of their work. Teacher optimizes instructional time, teaches more material, and demands better performance from every student. Managing Students are consistently well-behaved, and on task. Students are mostly well-behaved, and on task, some Students are not well-behaved and are often Student Teacher and students establish clear rules for learning and minor learning disruptions may occur. off-task. Behavior behavior. Teacher establishes rules for learning and behavior. Teacher establishes few rules for learning and The teacher uses several techniques such as social The teacher uses some techniques such as social behavior. approval, contingent activities, and consequences to approval, contingent activities, and consequences to The teacher uses few techniques to maintain maintain appropriate student behavior. maintain appropriate student behavior. appropriate student behavior. The teacher overlooks inconsequential behavior. The teacher overlooks some inconsequential behavior, The teacher cannot distinguish between The teacher deals with students who have caused but other times addresses it stopping the lesson. inconsequential behavior and inappropriate disruptions rather than the entire class. The teacher deals with students who have caused behavior. The teacher attends to disruptions quickly and firmly. disruptions, yet sometimes he or she addresses the Disruptions frequently interrupt instruction. entire class. Environment The classroom The classroom The classroom welcomes all members and guests welcomes most members and guests. is somewhat cold and uninviting. is organized and understandable to all students. is organized and understandable to most students. is not well organized and understandable to supplies, equipment, and resources are easily and readily supplies, equipment, and resources are accessible. students. accessible. displays student work. supplies, equipment, and resources are displays student work that frequently changes. is arranged to promote individual and group learning. difficult to access. is arranged to promote individual and group learning. does not display student work. is not arranged to promote group learning. Respectful Teacher-student interactions demonstrate caring and Teacher-student interactions are generally friendly, Teacher-student interactions are sometimes Culture8 respect for one another. but may reflect occasional inconsistencies, favoritism, authoritarian, negative, or inappropriate. Students exhibit caring and respect for one another. or disregard for students' cultures. Students exhibit disrespect for the teacher. Teacher seeks out, and is receptive to the interests and Students exhibit respect for the teacher, and are Student interaction is characterized by opinions of all students. generally polite to each other. conflict, sarcasm, or put-downs. Positive relationships and interdependence characterize Teacher is sometimes receptive to the interests and Teacher is not receptive to interests and the classroom. opinions of students. opinions of students.
8 Danielson, C. (1996). Enhancing Professional Practice: A Framework for Teaching. Alexandria, Virginia. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development. Performance definitions are provided at levels 5, 3, and 1. Raters can score performance at levels 2 or 4 based on their professional judgment.