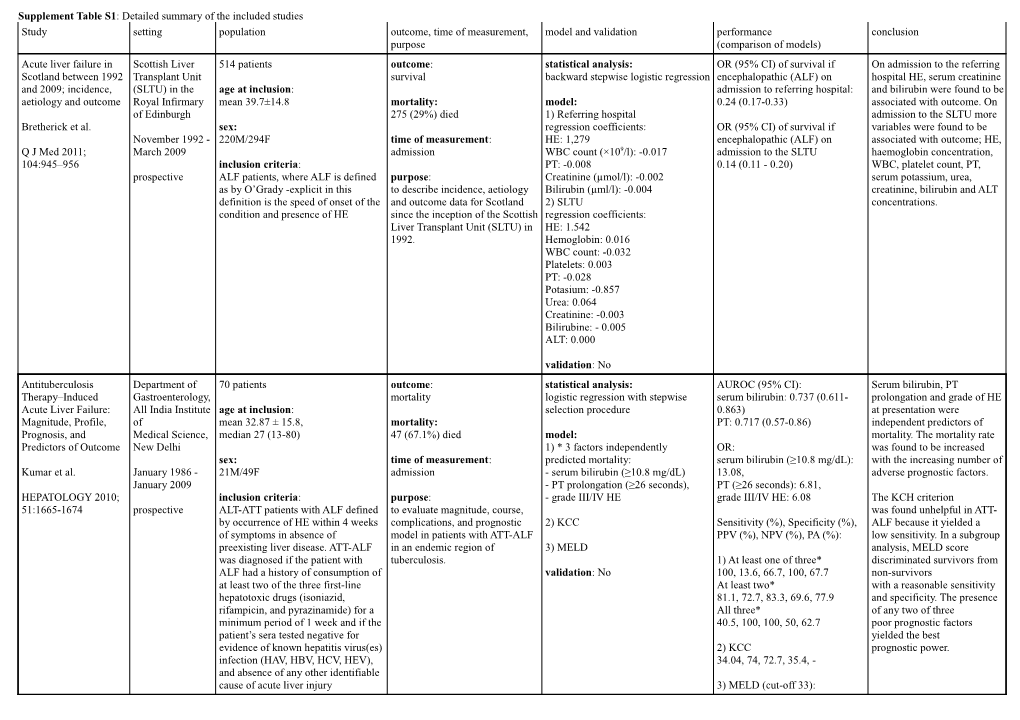
Supplement Table S1: Detailed summary of the included studies Study setting population outcome, time of measurement, model and validation performance conclusion purpose (comparison of models) Acute liver failure in Scottish Liver 514 patients outcome: statistical analysis: OR (95% CI) of survival if On admission to the referring Scotland between 1992 Transplant Unit survival backward stepwise logistic regression encephalopathic (ALF) on hospital HE, serum creatinine and 2009; incidence, (SLTU) in the age at inclusion: admission to referring hospital: and bilirubin were found to be aetiology and outcome Royal Infirmary mean 39.7±14.8 mortality: model: 0.24 (0.17-0.33) associated with outcome. On of Edinburgh 275 (29%) died 1) Referring hospital admission to the SLTU more Bretherick et al. sex: regression coefficients: OR (95% CI) of survival if variables were found to be November 1992 - 220M/294F time of measurement: HE: 1,279 encephalopathic (ALF) on associated with outcome; HE, Q J Med 2011; March 2009 admission WBC count (×109/l): -0.017 admission to the SLTU haemoglobin concentration, 104:945–956 inclusion criteria: PT: -0.008 0.14 (0.11 - 0.20) WBC, platelet count, PT, prospective ALF patients, where ALF is defined purpose: Creatinine (µmol/l): -0.002 serum potassium, urea, as by O’Grady -explicit in this to describe incidence, aetiology Bilirubin (µml/l): -0.004 creatinine, bilirubin and ALT definition is the speed of onset of the and outcome data for Scotland 2) SLTU concentrations. condition and presence of HE since the inception of the Scottish regression coefficients: Liver Transplant Unit (SLTU) in HE: 1.542 1992. Hemoglobin: 0.016 WBC count: -0.032 Platelets: 0.003 PT: -0.028 Potasium: -0.857 Urea: 0.064 Creatinine: -0.003 Bilirubine: - 0.005 ALT: 0.000
validation: No Antituberculosis Department of 70 patients outcome: statistical analysis: AUROC (95% CI): Serum bilirubin, PT Therapy–Induced Gastroenterology, mortality logistic regression with stepwise serum bilirubin: 0.737 (0.611- prolongation and grade of HE Acute Liver Failure: All India Institute age at inclusion: selection procedure 0.863) at presentation were Magnitude, Profile, of mean 32.87 ± 15.8, mortality: PT: 0.717 (0.57-0.86) independent predictors of Prognosis, and Medical Science, median 27 (13-80) 47 (67.1%) died model: mortality. The mortality rate Predictors of Outcome New Delhi 1) * 3 factors independently OR: was found to be increased sex: time of measurement: predicted mortality: serum bilirubin (≥10.8 mg/dL): with the increasing number of Kumar et al. January 1986 - 21M/49F admission - serum bilirubin (≥10.8 mg/dL) 13.08, adverse prognostic factors. January 2009 - PT prolongation (≥26 seconds), PT (≥26 seconds): 6.81, HEPATOLOGY 2010; inclusion criteria: purpose: - grade III/IV HE grade III/IV HE: 6.08 The KCH criterion 51:1665-1674 prospective ALT-ATT patients with ALF defined to evaluate magnitude, course, was found unhelpful in ATT- by occurrence of HE within 4 weeks complications, and prognostic 2) KCC Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), ALF because it yielded a of symptoms in absence of model in patients with ATT-ALF PPV (%), NPV (%), PA (%): low sensitivity. In a subgroup preexisting liver disease. ATT-ALF in an endemic region of 3) MELD analysis, MELD score was diagnosed if the patient with tuberculosis. 1) At least one of three* discriminated survivors from ALF had a history of consumption of validation: No 100, 13.6, 66.7, 100, 67.7 non-survivors at least two of the three first-line At least two* with a reasonable sensitivity hepatotoxic drugs (isoniazid, 81.1, 72.7, 83.3, 69.6, 77.9 and specificity. The presence rifampicin, and pyrazinamide) for a All three* of any two of three minimum period of 1 week and if the 40.5, 100, 100, 50, 62.7 poor prognostic factors patient’s sera tested negative for yielded the best evidence of known hepatitis virus(es) 2) KCC prognostic power. infection (HAV, HBV, HCV, HEV), 34.04, 74, 72.7, 35.4, - and absence of any other identifiable cause of acute liver injury 3) MELD (cut-off 33): 73, 66.6, 86.6, 50, - MELD calculated for 21 patients A new prognostic Keio University 30 patients outcome: statistical analysis: Z<0: estimated poor prognostic The CTLV/SLV ratio is a very formula for adult acute Hospital, Japan need for LT logistic regression stepwise case useful marker for predicting liver failure using age at inclusion: regression model AUROC: 0.87783 the prognosis of adult ALF. computer tomography- January 1999 - 45.7 (19–83) survivors mortality: The prognostic formula derived hepatic May 2007. 46.7 (22–69) death+LT 6 died, model: OR(95%CI): including only the CTLV/SLV volumetric analysis 11 underwent LT 1) Z = -2.3813 - [0.15234 9xTB TB (>17mg/dl): 4.734 (-0.616– ratio and TB is simple and retrospective sex: (mg/dl)] + 2.577) useful and awaits validation in Yamagishi et al. 14M/16F time of measurement: [4.5734 x CTLV/SLV] CTLV/SLV (<0.80): 22.09 a future larger-scale time of diagnosis (0.179–3.453) prospective study. J Gastroenterol 2009; inclusion criteria: 2) KCC 44: 615–623 adult patients with ALF diagnosed purpose: Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), Multiple logistic regression according to the diagnostic criteria of to assess the value of liver 3) MELD PPV (%), NPV (%), PA (%) analysis identified that the the Inuyama Symposium in Japan: volumetry and to generate a new CTLV/SLV ratio was prothrombin time (PT) (%) less than prognostic formula. validation: No 1) 94.1, 76.9, 84.2, 90.9, 80.0 independent predictor and 40% and developed HE greater than KCC not. grade II within 8 weeks after the 2) KCC: onset of symptoms OR(95%CI): 0.7300 (-1.535 – The formula is not inferior to 1.044) MELD and KCC,
3) MELD (cut-off 30): NS Prognostic Implications Hannover 102 patients outcome: statistical analysis: AUROC ± SE (95%CI): The simple, combined BiLE of Lactate, Bilirubin, Medical School, death or need of LT linear regression analysis BiLE 0.87±0.04 (0.80-0.95) score emerged as the best and Etiology in Germany age at inclusion: MELD 0.71±0.05 (0.61-0.82) predictor of poor outcome in German Patients With 38 (16-74) mortality: model: SAPS-III 0.68±0.59 (0.57-0.79) the patient cohort and should Acute Liver Failure. 1996 – 2005 18 (18%) died, 1) BiLE score: be prospectively evaluated in sex: 45 (44%) underwent LT (5 (5%) Bilirubin (µmol/L)/100 Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), other populations. Hadem et al. retrospective 30M/72F died) + lactate (mmol/L) PPV (%), NPV (%): + 4 (in case of indeterminate ALF, AUC values revealed a better Clinical inclusion criteria: 79 survived 8 weeks after Budd-Chiari syndrome, or 1) BiLE (cut-off 6.9): 79, 84, 89, performance of the BiLE Gastroenterology and patients fulfilled the diagnostic admission at ICU (77%) phenprocoumon toxicity) 71 score in comparison with Hepatology 2008; criteria of ALF: HE, acute-onset - 2 (in case of acetaminophen 2) KCC: 58, 82, 83, 55 KCC, MELD score, and the 6:339–345 increase of INR >1.5, and absence of time of measurement: toxicity) 3) MELD (cut-off 32): SAPS III score. signs of chronic liver disease in admission + 0 (in case of any other ALF 65, 69, 77, 55 clinical and ultrasound examination etiology) purpose: to evaluate prognostic parameters 2) KCC in a central European cohort. 3) MELD
4) SAPS III
validation: No Early Indicators of Emergency 144 patients outcome: statistical analysis: c-statistic [95% CI]: MELD and KCH criteria are Prognosis in Fulminant Medical mortality logistic regression analysis with 1) 3 CPI: 0.802 [0.726-0.878] not as useful as a combination Hepatic Failure: An Ward age at inclusion: backward elimination procedure 2) KCC 0.676 [0.588-0.764], of other early CPI in Assessment of the January 1996 - 28.6±12.3 survivors mortality: 3) MELD 0.717 [0.636-0.789] predicting adverse outcome in Model for End-Stage June 1998 33.4±15.8 non-survivors 92 (63.9%) died model: patients with FHF due to acute Liver Disease (MELD) 1) Presence of any 3 of 6 CPI Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), viral hepatitis. and Kings College retrospective sex: time of measurement: age ≥50 yr, JEI >7 days, grade 3 or 4 PPV (%), NPV (%), PA (%): Hospital Criteria. 62M/82F admission HE, presence of cerebral edema, Presence of any 3 CPIs is prothrombin time ≥35 s, and 1) Any 1 factor: superior to MELD and KCH Dhiman et al. inclusion criteria: purpose: creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dL 100.0, 9.6, 66.2, 100.0, 67.4 criteria in predicting the onset of HE occurring within 12 to compare MELD and KCH Any 2 factor: outcome. Liver Transplantation weeks of onset of jaundice and was criteria with other early clinical 2) KCC 97.8, 42.3, 75.0, 91.7, 77.8 2007; 13:814-821 further subclassified into hyperacute prognostic indicators (CPI). Any 3 factor: (interval 0-7 days), acute (interval 8- 3) MELD 73.9, 86.5, 90.7, 65.2, 78.5 28 days), and subacute (interval 29 Any 4 factor: days-12 weeks) liver failure validation: No 30.4, 100.0, 100.0, 44.8, 55.6
2)KCC: 76.1, 67.3, 80.5, 61.4, 72.9
3)MELD (≥ 33): 46.7, 88.5, 87.8, 48.4, 61.9 Utility of the MELD, Department of 58 patients outcome: statistical analysis: OR(95%CI): ALFIHMS has higher KCC and a New In- Gastroenterology, in-hospital mortality logistic regression (Wald step total bilirrubin: 1.2 (1.05 - 1.3 prognostic accuracy, is more Hospital Mortality Instituto Nacional age at inclusion: forward) model APACHE II: 1.3 (1.13- 1.5) specific and more sensitive Score in the Prognosis. de Ciencias FHF: 37 ± 14 mortality: and with higher PPV and NPV Médicas y SFHF 37 ± 18 28 died model: ALFIHMS cut-off point >15 than MELD and KCC in ALF. Pelaez-Luna et al. Nutrición 1) ALFIHM = points is associated with an in- Salvador Zubirán, sex: time of measurement: 0.714 + 0.02 (TB) + 0.03 (APACHE hospital mortality probability Transplantation Mexico City, 17M/41F during admission II score) × 10 >50%. Proceedings 2006; 38, Mexico. 927–929 inclusion criteria: purpose: 2) KCC PPV (%), NPV (%): 1983 – 2004 ALF patients; FHF and SFHF to evaluate and compare a new 1) ALFIHMS (>15): 80, 82 patients, FHF: development of HE ALF in-hospital mortality 3) MELD 2) KCC: 59, 58 retrospective occurring within 2 weeks of the onset prediction score versus KCC and 3) MELD (>25): 71, 73 of jaundice; SFHF: development of MELD score validation: No HE 2 weeks to 3 months after the appearance of jaundice Prognostic implications Department of 101 patients outcome: statistical analysis: Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), Applying the lactate of hyperlactatemia, Hepatology mortality logistic regression analysis PPV (%), NPV (%), PLR (%), modification of the KCH multiple organ failure, at Rigshospitalet, age at inclusion: NLR (%): criteria did improve their and systemic Denmark 49 (12–75) mortality: model: sensitivity, but at the cost of a inflammatory response 48 died, 1) Modified KCC (+lactate) 1) Modified KCC: significantly reduced syndrome in patients January 1999 - sex: 6 underwent LT (1 died, 5 - At the time of onset of grade 3-4 specificity. with June 2004 32M/69F survived) 2) KCC HE: The lactate modification of the acetaminophen-induced 87, 44, 62, 77, 1.57, 0.29 KCC showed no obvious acute liver failure retro/prospective inclusion criteria: time of measurement: 3) SOFA - At any time: advantages over the existing NR severe acetaminophen-induced FHF - admission 91, 40, 61, 82, 1.52, 0.22 selection criteria. Schmidt and Larsen defined as the development of HE - at the time of onset of grade 3-4 validation: No grade 3–4 HE 2) KCC Crit Care Med 2006; - At the time of onset of grade 3-4 Vol. 34, No. 2 purpose: HE: to evaluate arterial lactate as a 53, 81, 75, 64, 2.94, 0.54 prognostic marker in - At any time: acetaminophen-induced 71, 77, 76, 72, 3.03, 0.38 fulminant hepatic failure and to analyze its relationship to known 3) SOFA score >12 causes of hyperlactatemia such as - At the time of onset of grade 3-4 multiple organ failure and HE: inflammation 81, 68, 72, 78, 2.55, 0.28 Fulminant Hepatitis A Acute Liver 29 patients outcome: statistical analysis: AUROC: A prognostic index consisting Virus Infection in the Failure Study death/transplantation forward stepwise (Wald) Cox 1) ALFSG (4 factors): 0.538 of 4 clinical and laboratory United States: Group (ALFSG) age at inclusion: regression modeling ALFSG (≥3 factors): 0.766 features predicted the Incidence, Prognosis, is a multi-center 48±14 mortality: ALFSG (≥2 factors): 0.899 likelihood of transplant/death and Outcomes consortium of 24 4 died, model: ALFSG (≥1 factors): 0.781 significantly better than other sites sex: 9 underwent LT 1) *ALFSG index: 2) KCC: 0.623 published models (KCC, Taylor et al. 18M/14F serum ALT <2,600 IU/L, creatinine 3) MELD (≥35): 0.707 MELD) suggesting that 1/1/1998 - time of measurement: >2.0 mg/dL, intubation, pressors disease specific prognostic HEPATOLOGY 2006; 9/15/2005 inclusion criteria: admission Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), models may be of value in 44:1589-1597 the presence of coagulopathy (i.e., 2) KCC PPV (%), NPV (%): non-acetaminophen ALF. prospective prothrombin time >15 seconds or purpose: 1)ALFSG index (4 factors): international normalized ratio [INR] - to identify the 3) MELD 8, 100, 100, 57 ≥1.5) and HE within 26 weeks of presenting features associated ≥ 3 Factors: 62, 94, 89, 75 symptom onset in the absence of pre- with a poor prognosis (i.e., need validation: No ≥ 2 Factors 92, 88, 86, 93 existing liver disease for liver transplantion, or death) ≥ 1 Factor 100, 56, 65, 100 in HAV patients prospectively enrolled in the serum creatinine (> 2.0 mg/dl): ALFSG observational study. 54, 88, -,- - to develop an HAV specific ALT (<2,600 IU/mL): 77, 75, -, - prognostic model from the ALFSG database 2)KCC: 31, 94, 80, 62 and compare its performance to other published models including 3) MELD (≥35): 54, 88, 78, 70 the King’s College criteria and laboratory MELD scores. A Biochemical Royal Infirmary 1st cohort: 97 patients, outcome: statistical analysis: A value of<16 had an accuracy of Using admission Prognostic Model of of 2nd cohort: 85 patients death/ transplantation stepwise forward logistic regression 93% in predicting death correctly characteristics the model is Outcome in Edinburgh, able to identify patients who Paracetamol-Induced Edinburgh, age at inclusion: mortality: model: Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), die from paracetamol Acute Liver Injury Scotland, United 1st cohort: 36.2±6.8 1st cohort: 1) biochemical criteria: PPV (%), NPV (%): overdose FHF as accurately as Kingdom 2nd cohort: 35.7±6.4 19 died, (400×Pyruvate mmols/L) + 1) 91, 94, 91, 94 KCC, but at a much earlier Dabos et al. (Scottish Liver 6 underwent LT (50×Phenylalanine mmols/L) – stage in their condition. Transplant Unit) sex: 2nd cohort: (4× Hemoglobin g/dL) 2) KCC (on admission): 41, 100, Transplantation 2005; 1st cohort: 50M/47F 26 died, 100, 76 80: 1712–1717 1st cohort: 2nd cohort: 41M/44F 9 underwent LT 2) KCC KCC (at any time): 88, 96, 94, 93 January 1997 - December 1998 inclusion criteria: time of measurement: validation: Yes paracetamol induced acute liver admission 2nd cohort: injury based on guidelines: a January 1999 - progressive coagulopathy where the purpose: December 2000 prothrombin time in seconds was to develop a prognostic model of greater than the time after overdose outcome for patients with retro/prospective in hours or a prothrombin time paracetamol induced acute liver NR greater than 50 seconds at any time, injury based on admission or the presence of metabolic acidosis, parameters hypoglycemia, renal failure or HE. The KCH criteria were applied continuously throughout the patients’ admission. New Prognostic Okayama 1st cohort: 80 patients, outcome: statistical analysis: The score 3 or more predicted This scoring model may be Scoring Model for University 2nd cohort: 26 patients 2-week fatal outcome and need stepwise multiple linear regression prognosis. useful for predicting 2-week Liver Hospital and 11 for transplantation The 2-week survival rate in outcomes and determining the Transplantation in tertiary care age at inclusion: model: patients scoring <2 was more suitable timing for liver Patients with Non- centers with a 1st cohort: 45.5 (16-78) mortality: 1) day 1: 0.028 + 0.205 cause (HBV than 80% in contrast to less than transplantation in patients Acetaminophen- liver 2nd cohort: 61.0 (19-81) cohort1: or indeterminate) + 0.301 SIRS (yes) 30% in patients scoring ≥3. with non-acetaminophen- Related Fulminant transplantation 48 (60.0%) died, + 0.342 ratio of T/D bilirubine (>2.0) related FHF. Hepatic Failure program for sex: 5 underwent LT 11 of 24 patients scoring fulminant hepatic 1st cohort: 33M/47F cohort2: 2) day 4: -0.158 + 0.440 HE (grade <3 on day 1 had a poor 2-week Miyake et al. failure 2nd cohort: 10M/16F 13 (50.0%) died, III or IV) + 0.203 SIRS (yes) + 0.269 prognosis. However, 9 of the 11 4 (15.4%) underwent LT total bilirubin (>15mg/dl) + 0.386 patients scored 3 or more on day Transplantation 2005; 1st cohort: inclusion criteria: ratio of T/D bilirubine (>2.0) 4. The score on day 4 may be 80: 930–936 January 1990 - patients with FHF (criteria included time of measurement: more important in order to March 2001 the development of HE ≥ grade II at the time of diagnosis (day 1), 3) day 8: -0.009 + 0.470 HE (grade determine the suitable timing for 2st cohort: within 8 weeks from the onset of on days 4, 8, and 15 III or IV) + 0.241 SIRS (yes) + 0.268 LT May 2001 - initial symptoms, a prothrombin ratio of T/D bilirubine (>2.0) December activity of less than 40%, and no purpose: Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), 2003 previous chronic or alcoholic liver predicting 2-week outcomes and 4) day 15: -0.047 + 0.524 HE (grade PPV (%), NPV (%): disease) determining the suitable timing III or IV) + 0.388 platelet count 87.5, 90.0, 93.3, 81.8 retrospective for LT in patients with non- (≤10×103/mm3) study; acetaminophen-related FHF prospective validation: Yes validation Biochemical prognostic Royal Infirmary 59 patients outcome: statistical analysis: The result of the equation < 2 Identified biochemical markers of outcome in of mortality stepwise forward logistic regression was able to predict death or LT markers (used in the model) non-paracetamol- Edinburgh, age at inclusion: may be useful in predicting induced fulminant Edinburgh, 41.7±9.3 (underwent LT), 44.1±7.0 mortality: model: Coefficient (95% CI): outcome in patients with non- hepatic failure Scotland, United (died) 43.7±9.3 (survivors) 15 died. 1) 0.5×(albumin [g/L])-2×(lactate Albumin -3.4 (-6.1– -0.9) paracetamol–induced FHF and Kingdom. 19 underwent LT [mmol/L]) -36×(valine [mmol/L]) Lactate 1.3 (0.7–1.9) should be evaluated further in Dabos at al. Scottish Liver sex: -38×(pyruvate[mmol/L]) Pyruvate -1.1 (-2.0– -0.1) a different patient population. Transplant Unit M22/F37 time of measurement: Valine 0.25 (0.08–0.38) Transplantation 2004; admission 2) KCC PT 0.06 (0.1-0.02) Biochemical criteria on No. 2, January 2, Vol. prospective inclusion criteria: Bilirubin 0.03 (0.06-0.002) admission had better positive 77, 200–205, history of acute liver injury with a purpose: validation: No and negative predictive cause other than paracetamol identify early biochemical Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), values, sensitivity, and overdose and fulfillment of at least markers of clinical outcome in PPV (%), NPV (%): specificity than the KCH two of the five KCH criteria of poor patients with non-paracetamol– 1) 94, 86, 91, 86 criteria on admission and prognosis. Patients were also induced FHF overall. admitted if they were HE, that is, had 2) KCC (on admission): developed FHF 45, 88, 83, 43 KCC (overall): 81, 79, 84, 77 MELD Score as a Organ 388 patients outcome: statistical analysis: For an FHF-NA patient with a Liver allocation within the Predictor of Procurement and 30-day survival Cox model MELD score of 35.6, the Status 1 designation may Pretransplant and Transplantation age at inclusion: estimated 30-day survival need to be further stratified Posttransplant Survival Network/ United POD subgroup: mortality: model: probability was 91% if the by diagnosis, and MELD in OPTN/UNOS Status Network for mean 34.4±12.1, median 32 (20-69) 66 died, MELD = 3.78×loge(bilirubin [mg/dL] patient underwent LT score may be useful for
1 Patients Organ Sharing nPOD subgroup: 211 underwent LT + 11.20×loge (INR) + 9.57× immediately upon being listed. prioritizing FHF-NA (OPTN/UNOS) mean 40.3±13.1, median 39 (19-73) loge(creatinine [mg/dL]) + 6.4 The estimated 30-day survival candidates. Kremers et al. time of prediction: probability was 58% for a patient 1 November 1999 sex: NR validation: - awaiting OLT. HEPATOLOGY 2004; - 14 March 2002 POD subgroup: 39:764 –769 15 (19.7%) M purpose: nPOD subgroup: - to evaluate the ability of the prospective 103 (33.0%) M MELD score at listing to predict pretransplant and posttransplant inclusion criteria: survival for patients listed as onset of stage II HE within 8 weeks of UNOS Status 1 the first symptoms of liver disease, - to assess whether the different and asterixis, hyperbilirubinemia, diagnostic groups of patients and marked prolongation of the PT listed as Status 1 differ with (INR) or hypoglycemia respect to pretransplant and posttransplant survival. Aetiology and Liver Unit of 180 patients outcome: statistical analysis: OR (95%CI): ALF caused by HEV had a prognostic factors in Gastroenterology mortality stepwise logistic regression etiolgy (non-E): 20 (2.3–21.4) favourable outcome while acute liver failue in Department at age at inclusion: PT (>30): 9.3 (1.3–50.6) those caused by NANEH India. Sher-I-Kashmir 31.1 ± 14.7 (4–65) mortality: model: age (>40): 4.7 (1.8–344) agent had poor outcome. Institute of 131 died non-E aetiology, HE (grade>2): 7.5 (3.3–61.9) Assessing these variables Khuroo et al. Medical Sciences sex: prothrombin time >30 s, grade of separately showed significant India 69M/111F time of measurement: coma >2, age>40 years and contrasting impact of Journal of Viral admission Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), these two variables on Hepatitis 2003; 10, April 1989–April inclusion criteria: validation: No PPV (%), NPV (%), PA (%): survival of patients. Early 224–231 1996 ALF patients (HE developed purpose: prognostic factors of Any 1 factor: predictors of a poor outcome within 8 weeks of the onset of poor outcome in acute liver 50.9, 76.9, 90.6, 26.3, 55.7 were age >40 years, PTT >30 retro/prospective symptoms of liver disease, in a failure for hepatitis E virus Any 2 factors s, grade of coma >2 and non-E NR patient with no prior known liver 84.9, 76.9, 93.8, 52.6, 82.0 aetiology. disease) Any 3 factors: 90.9, 76.9, 93.0, 83.3, 90.9 All 4 factors: 100, 76.9, 82.4, 100, 88.9 Prognostic Evaluation tertiary care 204 patients population but 186 outcome: statistical analysis: Factors adversely affecting the of Early Indicators in center in patients analyzed mortality logistic regression outcome in FHF patients Fulminant Hepatic northern India complicating viral hepatitis Failure by Multivariate age at inclusion: mortality: model: include presence of overt Analysis study period: in population: 28.5 (1-75) 126 non-survivors reression equation, coefficients: clinical features of raised ICP over 5 years PTT (>100s) 2.41 at the time of hospitalization, Dhiman et al. sex: time of measurement: Raised ICP 2.23 PTT (>100 sec) on admission, retro/prospective 98M/106F (population) admission Age (>50 yr) 1.61 age (> 50 years) , and onset of Digestive Diseases and NR 91M/95F (analysed) Jaundice – HE interval (>7 days) HE seven days after onset of Sciences, 1998; Vol. purpose 1.17 jaundice. 43, No. 6: 1311± 1316 inclusion criteria: to study early prognostic HE (gr 3 or 4) 0.77 patients with ALF defined according factors based on univariate and Bilirubin (≥ 20 mg/dl) 0.24 to the criteria of O’Grady et al, ie, multivariate analysis Constant 1.34 onset of HE occurring within 12 weeks of onset of jaundice and if PTT is > 100 sec, value is 1, further subclassied into hyperacute, otherwise 0; acute and subacute liver failure. if raised ICP is present, value is 1, otherwise 0; if age is > 50 years, value is 1, otherwise 0; if interval between onset of jaundice and onset of HE >7days, value is 1, otherwise 0; if grade of HE is 3 or 4, value is 1, otherwise 0; if total bilirubin leve l is ≥ 20 mg/dl, value is 1, otherwise 0.
final variables: presence of raised ICP, PTT > 100 sec, age (> 50 yr), onset of HE 7 days after onset of jaundice validation: No Early indicators of Liver Unit, 145 patients outcome: statistical analysis: PPV (%), NPV (%), PA (%): For acetaminophen- prognosis in fulminant Queen Elizabeth mortality stepwise logistic regression 1)KCC (at admission): induced FHF patients, KCH hepatic failure: an Hospital, age at inclusion: (POD subgroup): 88, 65, 71 criteria remain the mainstay assessment of the Birmingham, UK median 31 (18-84) mortality: model: (nPOD subgroup): 79, 50, 68 for selecting patients for liver King’s criteria 81 died 1) KCC transplantation. The positive 1990 – 1994 sex: KCC (peak): predictive value of these Anand et al. 60M/85F time of measurement: 2) any of: (POD subgroup): 75, 60, 66 criteria can possibly be retrospective admission, peak Age <20 or >40 years, unfavorable (nPOD subgroup): 68, 25, 61 improved by including white Journal of Hepatology inclusion criteria: etiology, cell count and potassium 1997; 26: 62-68 FHF defined as the development of purpose: jaundice >7 days before HE, PT abnormalities. HE within 8 weeks of the onset of independent indicators of >50s, PT >l00s, Specificity (%), Sensitivity (%), symptoms in a patient without prognosis, risk of death bilirubin >300 µmol/l PA (%): previously known liver disease 2) Any 1 indicator: 0 100 61 3) log [p/l-p] = (2.248× grade of HE) Any 2 indicators: 0 82 50 + (0.0117 × PT in seconds) + (0.0064 Any 3 indicators: 43 82 50 × serum creatinine in µmol/l) + Any 4 indicators: 100 18 50 (0.045 × white cell count as 109/1) + (1.4623 only if serum potassium 3) PPV (%), NPV (%): level > 5.5 mmol/l) - 13.241 WBC>20×109: 82%, 74% Potassium >5.5mmol/l: 85%, validation: No 70% Fulminant hepatitis in a Gastroenterology 423 patients outcome: statistical analysis: Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), The prognostic model tropical population ward of the All mortality Cox’s proportional hazard regression, PPV (%), NPV (%), PA (%): developed in this study was Clinical course cause India Institute of age at inclusion: and multiple stepwise logistic simple, reliable, rapid, and and early predictors of Medical 14-83 mortality: regression Any 1 factor*: relevant to patients in outcome. Sciences, New 288 (66%) died 56.1, 79.7, 86.3, 44.3, 63.3 developing countries for Delhi sex: model: Any 2 factors*: assessment for LT. Acharya et al. 200M/223F time of measurement: 1) logistic reression coefficients: 80.9, 79.7, 87.7, 69.9, 80.4 January 1987 - admission age ( ≥40yr) 1.3 Any 3 factors:* HEPATOLOGY 1996; June 1993 inclusion criteria grade of coma (>2) 0.7 93, 79.7, 86.0, 89.5, 87.3 23:1448-1455 patients with FHF diagnosed by the purpose: cerebral edema 1.3 All 4 factors*: prospective presence of HE within 8 weeks of to identify the demographic infection 1.0 92.3, 79.7, 48, 98.1, 81.8 onset of illness characteristics, causative serum bilirubin (≥15 mg/dL) 1.1 spectrum, clinical features, natural PT (≥25s) 1.2 course, and predictors of outcome among patients with FHF 2) *Cox regression coefficients: cerebral edema 0.87 PT (≥25) 0.43 serum bilirubin (≥15 mg/dL) 0.29 age (≥40 yr) 0.29
validation: No Prognostic factor Veterans General 61 patients outcome: statistical analysis: stepwise logistic Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), The indicators may be useful analysis of FHF SFHF Hospital Taipei non-survival regression PPV (%), PA (%): for selecting patients with in an area endemic for age at inclusion: Any 1 indicator ALF of various etiologies hepatitis January 1982 – 14-83 mortality: model: 100, 67, 95, 100, 95 indicated for OLT and could October 1994 52 non-survivors *age>43years, Any 2 indicators be a useful tool in the area Huo et al. sex: 9 survivors bilirubin >23mg/dL, 69, 100, 100, 36, 74 endemic for HBV infection. A retrospective 52M/9F PTT>19s Any 3 indicators prospective observation is J of Gastroenterology time of measurement: 13, 100, 100, 17, 26 mandatory to justify the and Hepatology 1996; inclusion criteria admission, peak values validation: No validity of these indicators in 11, 560-565 ALF complicated with HE developed the future. in patients without pre-existing liver purpose: disease or cirrhosis within 2 weeks To determined the criteria in (FHF) or 2week to 3 months after selecting candidates for OLT onset of jaundice (SFHF) Early Indicators of Liver Failure 588 patients outcome: statistical analysis: Sensitivity (%), Specificity (%), Criteria for referring patients Prognosis in Fulminant Unit validation: 175 patients transplantation stepwise logistic regression PPV (%), PA (%): with FHF for LT were Hepatic Failure. King’s College 1) established and it is School of age at inclusion: mortality: model: Acetaminophen induced anticipated that these will O'Grady et al. Medicine and NR NR 1) pH<7.3: 49, 99, 95, 81 improve the speed and Dentistry, Acetaminophen induced PT >100s: 79, 67, 72, 71 accuracy of the selection of Gastroentrology 1989; London,UK sex: time of measurement: pH<7.3 serum creatinine>300µmol/L: appropriate candidates. 97:439-45 NR admission, peak or 70, 69, 56, 69 1973-1985 PT>100s + serum inclusion criteria purpose: creatinine>300µmol/L +grade III-IV Nonacidotic patients: validation: 1986- HE developed within 8 wk of the to identify the factors most likely HE: PT>100s: 77, 71, 44, 73 1987 onset of symptoms to indicate a poor prognosis serum creatinine>300µmol/L: tested, leading to the construction Non-acetaminophen induced 77, 58, 35, 63 NR, validation - of models for the selection of Age<10 or>40yr, Unfavorable retrospectively patients for LT etiology, Jaundice>7days before HE, PT>100s + serum creatinine> PTT>50s, Bilirubin>300µmol/L 300µmol/L: 55, 87, 55, 80 PT>100s + serum creatinine> 2) 300µmol/L+grade III-IV HE: *Any of: 45, 94, 67, 83 Age<10 or>40yr, Unfavorable etiology, Jaundice>7days before HE, Non-Acetaminophen related PTT>50s, Bilirubin>300µmol/L Age<10 or>40yr: 50, 90, 96 57 Unfavorable etiology: 80, 60, 90, validation: Yes 76 Jaundice>7days before HE: 82, 90, 97, 83 PTT>50s: 75, 90, 97, 78 PTT>100s: 34, 100, 100, 46 Bilirubin>300µmol/L: 84, 70, 93, 81
2) Patients with PTT<100s Any 2 indicators* 97, 80, 93, 92 Any 3 indicators* 93, 90, 96, 92 Any 4 indicators* 59, 100, 100, 67
Patients not treated by LT: Any 1 indicator* 100, 20, 80, 81 Any 2 indicators 94, 80, 94, 90 Any 3 indicators 91, 90, 97, 90 Any 4 indicators 59, 100, 100, 69 Multivariate analysis of Liver Unit at 115 patients outcome: statistical analysis: - In patients with fulminant prognostic factors in Hopital Beaujon survival 90-days after onset of Cox’s proportional hazard regression hepatitis B the absence of fulminant hepatitis B age at inclusion: jaundice HBsAg in serum has an January 1972 – mean 40 (15-77) model: independent, favourable Bernuau J. et al. December 1981 mortality: factor V level prognostic value. sex: 89 died (77.4%) age HEPATOLOGY 1986; retro/ prospective 43M/72F absence of detectable HBsAg Vol. 6, No. 4: 648-651 NR time of measurement: AFP inclusion criteria: at the data of testing for IgM fulminant hepatitis B diagnosed anti-HBc validation: No based on: histlogically proven acute hepatitis, sever coagulation disorders, purpose: HE within 2 months after the onset of assessment of prognostic factors jaundice, presence of IgManti-HBc in patients with fulminant after onset of HE hepatitis B Prediction of fatality in Intensive Liver 23 patients outcome: statistical analysis: The discriminant power of the It is suggested that the Fulminant Hepatic Unit of mortality discriminative analysis with stepwise estimated discriminant function discriminant score is used to Failure Rigshospitalet, age at inclusion: addition was studied by allocating each select patients with very low Denmark 31.5 (20-72) non-survivors mortality: patient on the basis of all the probability of survival for LT Christensen E. et al. 26 (17-49) survivors 20 died model: other patients (leaving current or liver assistance procedures 1) full score; significant discriminant patient out method). of unknown value. Scand J Gastroenterol Period NR sex: time of measurement: admission function coefficients: 1984; 19:90-96 9M/14/F taurine (24-14C) cholic acid based on Bayes theorem for retro/ prospective conjugation -1.15 discriminant analysis NR inclusion criteria: purpose: sex -0.42 patients with FHF prediction of non-survival pregnancy -0.85 95% CI, Sensitivity (%), carbamide 0.024 Specificity (%) ALP 0.0015 glycolithocholic acid suplhate -0.040 1) 0.41-0.59, 100-95, 100 non-A non-B viral hepatitis -0.74 2) 0.4-0.6, 90-75, 77-92 age 0.012 glycine (24-14C) cholic acid conjugation -0.53 duration of history 0.0044 halothane hepatitis -0.27 grade of HE 0.087 leukocyte count 0.013 constant 0.18
2) reduced score; significant discriminant function coefficients: disulfiram hepatitis 0.83 blood glucose concentration 0.089 duration of history 0.0081 leukocyte count 0.032 age 0.015 prothrombine index -1.28 sex -0.27 viral hepatitis B 0.31 serum potassium 0.12 serum albumin -0.0019 blood type O -0.25 constant -0.45 validation: Yes discriminant score validated by an unbiased method in which each patient is classified on the basis of the other patients’ data ALF, acute liver failure; ATT, antituberculosis therapy ; AUROC = AUC Area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve; CI, confidence interval; F, female; FHF, fulminant hepatic failure; HR, hazard ratio; HE, hepatic encephalopathy; ICP, intracranial pressure; KCC, King’s Collage Criteria; LT, liver transplantation; MELD; Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; NLR, negative likelihood ratio; NPV, negative predictive value; OLT – orthotopic liver transplantation; OR odds ratio; PA, predictive accuracy; PLR, positive likelihood ratio; PPV, positive predictive value; POD – paracetamol overdose group; nPOD – non paracetamol overdose group; PT, prothrombin time; ROC, receiver-operating characteristic