Appendix 4
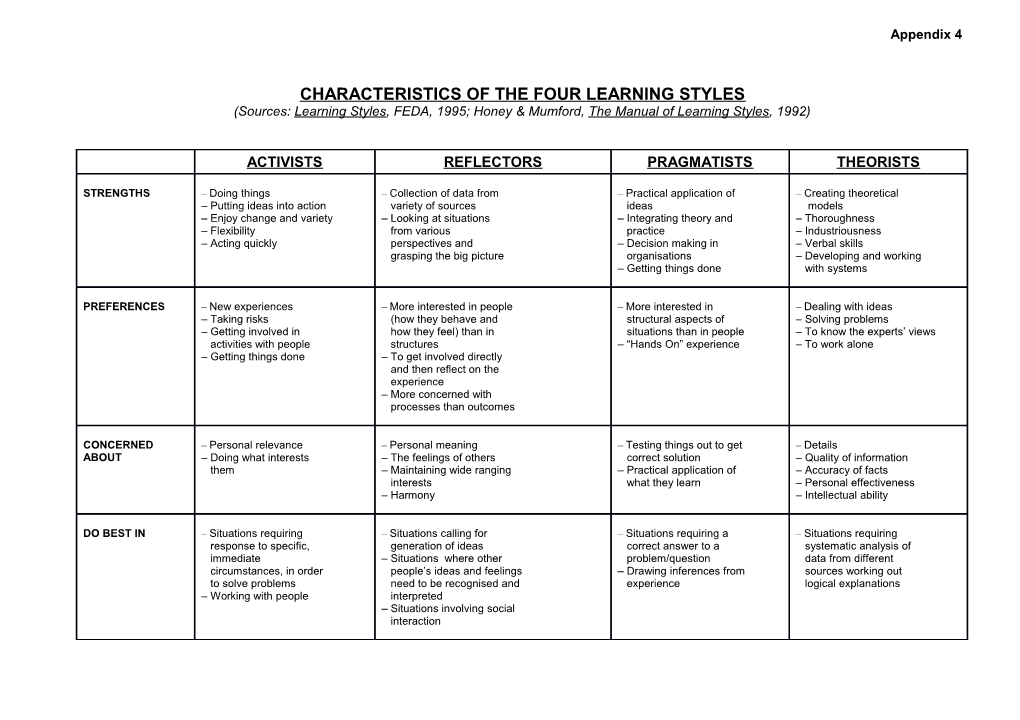
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE FOUR LEARNING STYLES (Sources: Learning Styles, FEDA, 1995; Honey & Mumford, The Manual of Learning Styles, 1992)
ACTIVISTS REFLECTORS PRAGMATISTS THEORISTS
STRENGTHS – Doing things – Collection of data from – Practical application of – Creating theoretical – Putting ideas into action variety of sources ideas models – Enjoy change and variety – Looking at situations – Integrating theory and – Thoroughness – Flexibility from various practice – Industriousness – Acting quickly perspectives and – Decision making in – Verbal skills grasping the big picture organisations – Developing and working – Getting things done with systems
PREFERENCES – New experiences – More interested in people – More interested in – Dealing with ideas – Taking risks (how they behave and structural aspects of – Solving problems – Getting involved in how they feel) than in situations than in people – To know the experts’ views activities with people structures – “Hands On” experience – To work alone – Getting things done – To get involved directly and then reflect on the experience – More concerned with processes than outcomes
CONCERNED – Personal relevance – Personal meaning – Testing things out to get – Details ABOUT – Doing what interests – The feelings of others correct solution – Quality of information them – Maintaining wide ranging – Practical application of – Accuracy of facts interests what they learn – Personal effectiveness – Harmony – Intellectual ability
DO BEST IN – Situations requiring – Situations calling for – Situations requiring a – Situations requiring response to specific, generation of ideas correct answer to a systematic analysis of immediate – Situations where other problem/question data from different circumstances, in order people’s ideas and feelings – Drawing inferences from sources working out to solve problems need to be recognised and experience logical explanations – Working with people interpreted – Situations involving social interaction Appendix 4
PREFERRED WAYS – Self-discovery, trial and error – Learning by listening and – Strong need to work on – Enjoy being taught in a didactic OF LEARNING AND learning sharing ideas with others practical, relevant problems way WORKING – Learning by doing – Groupwork and discussions – To use skills and tinker with – Prefer to work individually – Flexible approaches to – Looking for meaning things rather than in groups learning – Researching and – Test theories and apply – Like to have access to a lot of – Not worried about getting it reviewing common sense information/resources wrong – Thinking before doing – Looking at information in – Collecting data – Can work well with others – Bringing unity to a logical way, and then – Enjoy reading – Like attention, chairing diversity acting on it immediately – To specialise meetings, leading – Standing back from events and – Workshop and laboratory – Planning organising work discussions, etc observe what is happening teaching methods – Thinking things through – More concerned with – To solve problems – Reworking notes/essays doing than feeling and – To reason deductively when to achieve best results thinking focusing on specific problems – Make links between ideas – Like to get “stuck in” – Making instinctive – Examining information carefully without wasting time judgements based on – Critically evaluating information practicality – Thinking sequentially – Clear goals and adequate – Deductive reasoning rewards
DISLIKED WAYS OF – Highly structured – Have difficulty working to – Have difficulty working “out – Unhappy if there is no stated LEARNING AND approaches to learning deadlines of context” and making purpose WORKING – Passive forms of learning – Get frustrated with over simplified connections between – Dislike situations that – Solitary approaches to models and quick solutions contexts involve considering feelings learning – Dislike having to take the – Prefer to work on the job and emotions – Working out detailed lead or the limelight – Dislike theoretical learning – Dislike structured activities action plans – Dislike precise instructions and abstract concepts – Dislike working with – Reviewing processes – Dislike having to take immediate – Unhappy if there are no “shallow” issues – Detailed work action and produce results clear guidelines – Analytical work – Dislike having to take – Unhappy if there is no obvious – Repetition short cuts to get results relevance for an activity
DISADVANTAGED – Doing too many things at once – Easily distracted – Lack of patience with – Need a lot of information BY – Lack of planning – Waste too much time before people’s suggestions before starting work – Poor time management, getting started – Wanting to do everything their – Reluctant to try anything leaving things to last minute – Frustrated by action plans way new – Lack of attention to detail – Can be too easy going – Lack of imagination – Like to do things in a set way – Not checking/testing things out – Sometimes indecisive – Poor presentation – Get bogged down in theory – Jumping in too quickly and – Can forget important details – Details can get in the way – Don’t trust feelings but rely on not thinking things through – Tend to work in bursts of – Inability to consider alternatives logic – Being too pushy at times energy – Intolerance to woolly ideas – Overcautious; don’t take risks – Giving insufficient – Inability to act – Only doing what is perceived as – Heavily reliant on expert consideration to alternative spontaneously directly relevant to a given task opinion without considering ways of doing things – Need to be in control and to other views – Inability to stand back and do it alone – Uncomfortable in group work allow others to take action – Not interested in concepts – May have difficulty or theories understanding emotions Appendix 4 and feelings