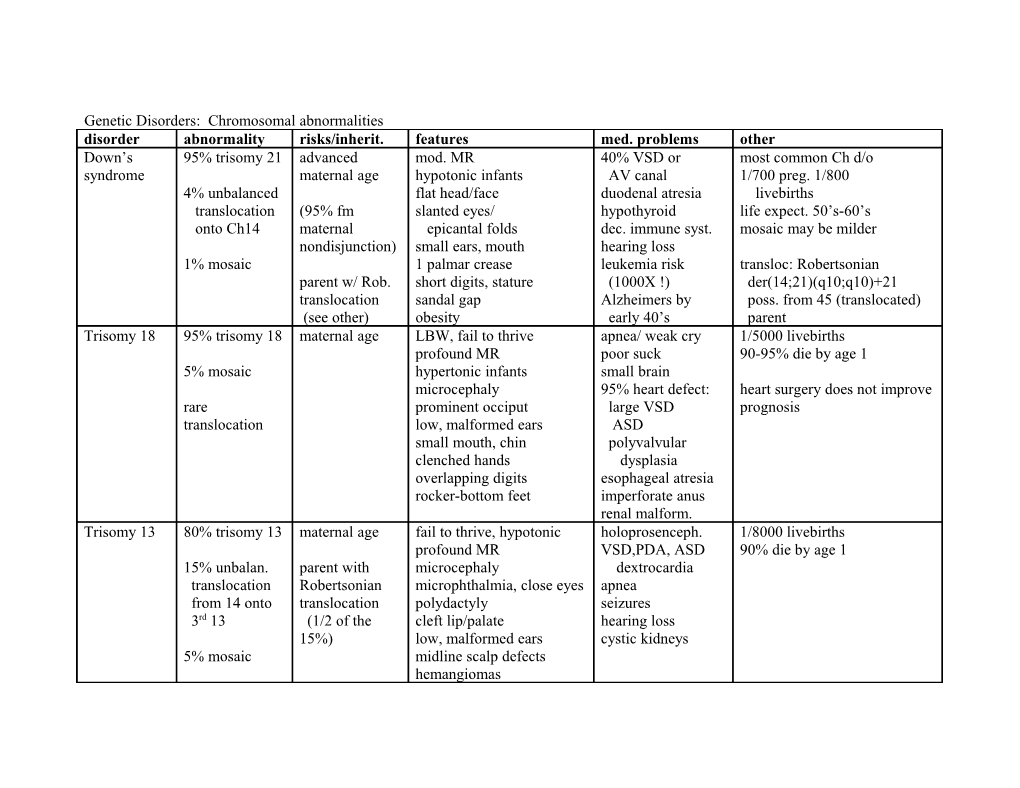
Genetic Disorders: Chromosomal abnormalities disorder abnormality risks/inherit. features med. problems other Down’s 95% trisomy 21 advanced mod. MR 40% VSD or most common Ch d/o syndrome maternal age hypotonic infants AV canal 1/700 preg. 1/800 4% unbalanced flat head/face duodenal atresia livebirths translocation (95% fm slanted eyes/ hypothyroid life expect. 50’s-60’s onto Ch14 maternal epicantal folds dec. immune syst. mosaic may be milder nondisjunction) small ears, mouth hearing loss 1% mosaic 1 palmar crease leukemia risk transloc: Robertsonian parent w/ Rob. short digits, stature (1000X !) der(14;21)(q10;q10)+21 translocation sandal gap Alzheimers by poss. from 45 (translocated) (see other) obesity early 40’s parent Trisomy 18 95% trisomy 18 maternal age LBW, fail to thrive apnea/ weak cry 1/5000 livebirths profound MR poor suck 90-95% die by age 1 5% mosaic hypertonic infants small brain microcephaly 95% heart defect: heart surgery does not improve rare prominent occiput large VSD prognosis translocation low, malformed ears ASD small mouth, chin polyvalvular clenched hands dysplasia overlapping digits esophageal atresia rocker-bottom feet imperforate anus renal malform. Trisomy 13 80% trisomy 13 maternal age fail to thrive, hypotonic holoprosenceph. 1/8000 livebirths profound MR VSD,PDA, ASD 90% die by age 1 15% unbalan. parent with microcephaly dextrocardia translocation Robertsonian microphthalmia, close eyes apnea from 14 onto translocation polydactyly seizures 3rd 13 (1/2 of the cleft lip/palate hearing loss 15%) low, malformed ears cystic kidneys 5% mosaic midline scalp defects hemangiomas Genetic Disorders: Chromosomal abnormalities disorder abnormality risks/inherit. features med. problems other Turner 45X paternal non- short length/stature L cardiac: up to 2% preg. (99% sp abort) syndrome mosaic 45X/ disjunction webbed neck aorta coarctation 1/5000 female livebirths 46XX low posterior hairline bicuspid AV no age assoc. shield-shaped chest aortic stenosis normal intelligence but inc. mosaic 45X/ high palate lymphedema risk of math/spatial LD 46XY* nevi renal malformations *XY risk of gonadoblastoma: 46X, various absent 20 sex cx Htn, DM prophylactic gonadectomy partial X del, streak gonads hypothyroid iso, trans. low E, high FSH/LH amenorrhea tx: GH, E/P cycling after infertility puberty, assist reproduction Triple X 47 XXX nondisjunction normal phenotype LD, behavioral 1/1000 female livebirths syndrome (either parent) tall stature prob. rare 48 (4X) or maternal age IQ lower than siblings (10- normal fertility but inc. risk of 49(5X) 15 pts) MR w/ inc. X’s Chrom. abnor. in offspring Klinefelter 90% 47 XXY nondisjunction normal pre-pubertal pheno. infertility 1/1000 male livebirths syndrome (either parent) tall stature, long legs gynecomastia most common cause of male 10% mosaic maternal age small testes occ. small penis hypogonadism female fat distribution low normal IQ mosaic milder low T, high E2/ FSH speech, motor delay LD, behavioral tx: testosterone, surgery for gynecomastia XYY 47 XYY paternal tall stature occ. LD 1/1000 male livebirths nondisjunction cystic acne antisocial?? normal intelligence large teeth nomal fertility but risk of Chrom. abnor. in offspring Fragile X fra(X)q27.3 X-linked dom. large/prominent: head, moderate MR 1/1500 male livebirths syndrome FMR1 gene w/ forehead, ears, jaw poor coordination 80% full mutation # of repeats: anticipation lax eustacian tubes ADHD 20% premutation (asympt.) 43-200 premut. double-jointed, flat feet ear infections 1/2500 female livebirths >200 full mut. automatisms full mutation: 30% affected macroorchidism (fertile) premutation asympt. Genetic disorders: Monogenic disorder abnormality risks/inherit. features med. problems other NF-1 tumor suppress. AD multiple neurofibromas skeletal lesions 1/3000 von- defect usu. trunk, organs reduced intelligence neurofibromin down-reg. Recklings- 50% new mut. café au lait spots risk of meningioma, p21-Ras oncoprotein hausen 17q11.2: Lisch nodules (iris optic glioma, neurofibromin hamartomas) CML in kids, others variable expressivity but 100% poss. GI bleeds penetrance Marfan’s missense FBN1: AD tall/thin mitral prolapse 1/20,000 syndrome missing or frontal bossing cystic avg. survival 30-40 yrs. defective prom. supraorbital ridges medionecrosis fibrillin-1 scaffold for elastin fibrillin hyperextensive joints aortic dissection abnormal fib. disrupts by 15q21 ectopia lentis dominant negative mech. Familial various AD w/ dosage heterozygotes: 2-3x chol. PVD heterozygotes: 1/500 hyperchol- mutations in homozygotes: 5-6x chol. early MI/stroke esterolemia LDL receptor xanthomas (often by age 20 in over 100 single mutations in 5 gene (Ch19) atherosclerosis homozygotes) classes can cause PKU classic: absent AR normal 1st months eczema 1/12,000 in U.S. phenyl- PAH delayed development hyperactivity high in Scandinavian descent ketonuria malignant: def. poor feeding, vomiting failure to walk, talk blood levels Phe 10X normal BH4 irritability posturing,rocking also in urine and CSF non-PKU severe MR (<60) seizures Phe metabolites in urine (odor) benign: partial low pigmentation def PAH musty odor (phenylacetate newborn screen required in sweat, urine) prenatal/carrier available Galactosemia Gal-1P uridyl AR normal at birth cataracts (galacitol) 1/62000 transferase milk ingestion: vomiting MR (irrev. w/ diet) various genes involved: Duarte deficiency diarrhea, failure to thrive physical retardation variant w/ 25% activity jaundice hypergonadotropic galactokinase hepatomegaly, cirrhosis hypogonadism in newborn screen req. (Beutler) deficiency (no hypoglycemia female (low E2) prenatal : enzy. act in am. fluid MR or hepatic) poor coagulation risk fatal sepsis restrict galactose & lactose Genetic disorders: Monogenic, cont. disorder abnormality risks/inherit. features med. problems other Lysosomal Storage Diseases: sphingolipidoses, glycogen storage, and mucopolysaccharidoses Tay-Sachs hexosaminidase AR GM2 ganglioside accum. death age 2-3 1/30 Ashkenazi Jews carrier -A (- subunit) 4-base insertion motor/mental deterioration deficiency (frameshift or cherry-red macula spot splice) Gaucher glucocerebroside AR Glc.cerebroside accum. early death in most common LSD deficiency I: adults; splenomegaly infants defect in macrophage, monos bone disease assay WBCs or skin fibroblasts II: infants tx: expensive recomb. enzyme III: juvenile; CNS dysfxn BMT seizures, mental decline Metachromatic arylsulfatase A AR sulfatides accum. death in 5-10 yrs assay WBCs or skin fibroblasts leuko- deficiency multiple forms: motor sx: demyelination & name b/c dyes bind excess dystrophy usu child onset gliosis sulfatides on nerve tissue progressive BMT promising Pompe’s -1,4 AR glycogen accum. hypotonia assay skin fibroblasts (Type 2 glucosidase def. massive cardiomegaly cardiorespiratory glycogen hepatomegaly failure in 2yrs storage) Hurler -L-iduronidase AR heparan, dermatan sulfate coronary artery & assay WBCs or skin fibroblasts syndrome deficiency normal at birth valvular lesioins (MPS I) grotesque deformities blind/deaf BMT very successful hepatosplenomegaly joint stiffness progressive MR umbilical hernia corneal clouding death 6-10 yrs untx Hunter ? X-linked R same as above except no corneal clouding and assay WBCs or skin fibroblasts syndrome milder course (MPS II) BMT very successful note: lysosomal storage diseases cx by foamy cells or by “balloon cells” with distended lysosomes mucopolysaccharides = glycosaminoglycans, i.e. dermatan, heparan, keratan, and chondroitin sulfate Genetic diseases: monogenic, cont. disorder abnormality risks/inherit. features med. problems other glycogen storage diseases I. von Gierke’s glucose-6- AR glycogen accum. in liver hypoglycemia total gly storage dis: 1/50,000 phosphatase hepatomegaly hyperlipidemia deficiency renomegaly hyperuricemia II. Pompe’s see lysosomal storage diseases V. McArdle’s muscle glycogen AR muscle cramps after mild total gly storage dis: 1/50,000 phosphorylase exercise deficiency failure to produce lactic acid miscellaneous X-linked disorders ornithine transcarbamylase def. X-linked D ?????? Lesch-Nyhan HGPRT X-linked R severe nerologic problems self-mutilation extract teeth prophylactically deficiency MR gout/renal stones (prevent injury) hyperuricemia DMD/ various mut. of X-linked R delayed, toe walking progress. proximal 1/3500 males; 1/3 new mut. Becker’s MD dystrophin inc. CPK weakness DMD: frame shift, <3% dystr. complex calf pseudohypertrophy immobility BMD: in-frame, 3-10% dystr. cardiac/respir. fail gene Xp22 other monogenetic disorders Sickle Cell HbS AR w/ dosage chronic hemolytic anemia failure to thrive African Americans: splenomegaly, infarction recurrent infections 1/12 carrier, 1/625 affected ( 6 glu to val) painful crises cardiomegaly/CHF penicillin prophylaxis stroke risk frequent transfusions shortened lifespan Huntington’s gain of fxn of AD progressive neurodegen. forgetfulness 1/10,000 huntingtin pro. personality change more rpts. = earlier onset, abnormal movements worse degeneration 37-120 CAG rpts death 15y after sx haldol, psychotropics as part on Ch 4p of supportive care Leber’s mitochondrial maternal acute loss of central vision cardiac conduction 1/30,000 males earlier, worse hereditary missense mut. (mitochondrial) 50% bilateral at onset ataxia environmental role optic 50% other eye in 6 mon. sensory neuropathy other genes: G3460A neuropathy 95% G11778A MS-like T14484C (mildest) Genetic diseases: defects in DNA repair disorder abnormality risks/inherit. features med. problems other xeroderma defect in AR hyper & hypopigmentation 1000X incid. skin 1st hit: 1 or more of 8 poss. pigmentosum excision extreme photosensitivity cancers mut. repair corneal clouding 10X internal 2nd hit: pyr dimer in p53 genes for XPA- out-turned eyelid cancers XPG + variant neurologic defects? Cockayne defect in AR photosensitivity neurologic defects extremely rare syndrome transcription- arrested growth, progeria syndrome subset of excision repair (CS) coupled repair development dental defects process- long arms, legs cataracts only affects exons genes: CSA or MR death by 12yrs B XP/CS both defects AR both those above XPB and D part of TFII above, genes: transcription complex XPB, D, or G trichothio- defect in AR brittle hair ichthyosis (scaling) brittle hair b/c sulfur deficient dystrophy excision short stature some pts temperature sensitive, repair subset are UV sensitive i.e. sx only during fever genes: MR XPB, D or TTDA HNPCC defect in AD young age of cancer multiple colon 1st hit: 1 inactivated Mut allele mismatch repair (colon) tumors 2nd hit: 2nd allele inactivated genes: risk of other tumors, incl. in proximal distrib. high microsatellite instability MutS or MutL endometrial, gastric, & urinary, spontaneous mutation ovarian MutS variants: hMSH2, 3, or 6 MutL variants: hMLH1, hPMS1 or 2
Genetic Disorders: Chromosomal Abnormalities
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Recommended publications