CHANGE OVER TIME THEME COMPARISON BY REGION: GENDER STRUCTURES
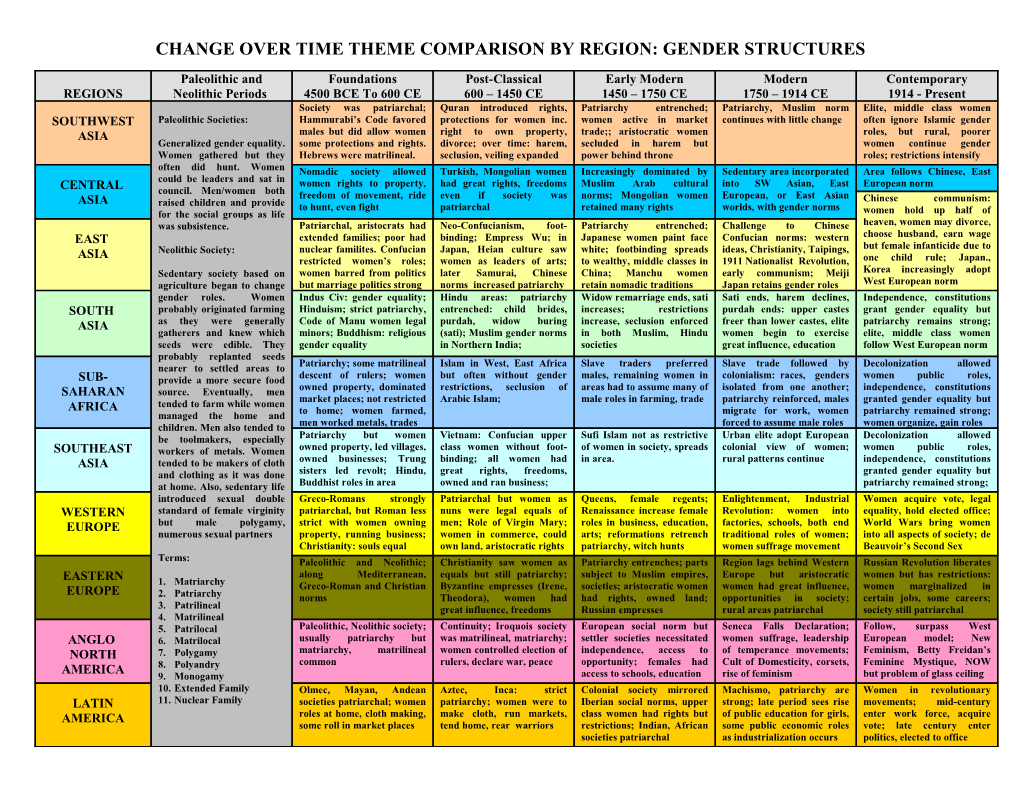
Paleolithic and Foundations Post-Classical Early Modern Modern Contemporary REGIONS Neolithic Periods 4500 BCE To 600 CE 600 – 1450 CE 1450 – 1750 CE 1750 – 1914 CE 1914 - Present Society was patriarchal; Quran introduced rights, Patriarchy entrenched; Patriarchy, Muslim norm Elite, middle class women SOUTHWEST Paleolithic Societies: Hammurabi’s Code favored protections for women inc. women active in market continues with little change often ignore Islamic gender ASIA males but did allow women right to own property, trade;; aristocratic women roles, but rural, poorer Generalized gender equality. some protections and rights. divorce; over time: harem, secluded in harem but women continue gender Women gathered but they Hebrews were matrilineal. seclusion, veiling expanded power behind throne roles; restrictions intensify often did hunt. Women Nomadic society allowed Turkish, Mongolian women Increasingly dominated by Sedentary area incorporated Area follows Chinese, East could be leaders and sat in women rights to property, had great rights, freedoms Muslim Arab cultural into SW Asian, East European norm CENTRAL council. Men/women both ASIA freedom of movement, ride even if society was norms; Mongolian women European, or East Asian Chinese communism: raised children and provide to hunt, even fight patriarchal retained many rights worlds, with gender norms for the social groups as life women hold up half of was subsistence. Patriarchal, aristocrats had Neo-Confucianism, foot- Patriarchy entrenched; Challenge to Chinese heaven, women may divorce, extended families; poor had binding; Empress Wu; in Japanese women paint face Confucian norms: western choose husband, earn wage EAST but female infanticide due to ASIA Neolithic Society: nuclear familites. Confucian Japan, Heian culture saw white; footbinding spreads ideas, Christianity, Taipings, restricted women’s roles; women as leaders of arts; to wealthy, middle classes in 1911 Nationalist Revolution, one child rule; Japan., Sedentary society based on women barred from politics later Samurai, Chinese China; Manchu women early communism; Meiji Korea increasingly adopt agriculture began to change but marriage politics strong norms increased patriarchy retain nomadic traditions Japan retains gender roles West European norm gender roles. Women Indus Civ: gender equality; Hindu areas: patriarchy Widow remarriage ends, sati Sati ends, harem declines, Independence, constitutions SOUTH probably originated farming Hinduism; strict patriarchy, entrenched: child brides, increases; restrictions purdah ends: upper castes grant gender equality but ASIA as they were generally Code of Manu women legal purdah, widow buring increase, seclusion enforced freer than lower castes, elite patriarchy remains strong; gatherers and knew which minors; Buddhism: religious (sati); Muslim gender norms in both Muslim, Hindu women begin to exercise elite, middle class women seeds were edible. They gender equality in Northern India; societies great influence, education follow West European norm probably replanted seeds nearer to settled areas to Patriarchy; some matrilineal Islam in West, East Africa Slave traders preferred Slave trade followed by Decolonization allowed SUB- provide a more secure food descent of rulers; women but often without gender males, remaining women in colonialism: races, genders women public roles, SAHARAN source. Eventually, men owned property, dominated restrictions, seclusion of areas had to assume many of isolated from one another; independence, constitutions market places; not restricted Arabic Islam; male roles in farming, trade patriarchy reinforced, males granted gender equality but AFRICA tended to farm while women managed the home and to home; women farmed, migrate for work, women patriarchy remained strong; children. Men also tended to men worked metals, trades forced to assume male roles women organize, gain roles be toolmakers, especially Patriarchy but women Vietnam: Confucian upper Sufi Islam not as restrictive Urban elite adopt European Decolonization allowed SOUTHEAST workers of metals. Women owned property, led villages, class women without foot- of women in society, spreads colonial view of women; women public roles, ASIA tended to be makers of cloth owned businesses; Trung binding; all women had in area. rural patterns continue independence, constitutions and clothing as it was done sisters led revolt; Hindu, great rights, freedoms, granted gender equality but at home. Also, sedentary life Buddhist roles in area owned and ran business; patriarchy remained strong; introduced sexual double Greco-Romans strongly Patriarchal but women as Queens, female regents; Enlightenment, Industrial Women acquire vote, legal WESTERN standard of female virginity patriarchal, but Roman less nuns were legal equals of Renaissance increase female Revolution: women into equality, hold elected office; EUROPE but male polygamy, strict with women owning men; Role of Virgin Mary; roles in business, education, factories, schools, both end World Wars bring women numerous sexual partners property, running business; women in commerce, could arts; reformations retrench traditional roles of women; into all aspects of society; de Christianity: souls equal own land, aristocratic rights patriarchy, witch hunts women suffrage movement Beauvoir’s Second Sex Terms: Paleolithic and Neolithic; Christianity saw women as Patriarchy entrenches; parts Region lags behind Western Russian Revolution liberates along Mediterranean, equals but still patriarchy; subject to Muslim empires, Europe but aristocratic women but has restrictions: EASTERN 1. Matriarchy EUROPE Greco-Roman and Christian Byzantine empresses (Irene, societies; aristocratic women women had great influence, women marginalized in 2. Patriarchy norms Theodora), women had had rights, owned land; opportunities in society; certain jobs, some careers; 3. Patrilineal great influence, freedoms Russian empresses rural areas patriarchal society still patriarchal 4. Matrilineal 5. Patrilocal Paleolithic, Neolithic society; Continuity; Iroquois society European social norm but Seneca Falls Declaration; Follow, surpass West ANGLO 6. Matrilocal usually patriarchy but was matrilineal, matriarchy; settler societies necessitated women suffrage, leadership European model; New NORTH 7. Polygamy matriarchy, matrilineal women controlled election of independence, access to of temperance movements; Feminism, Betty Freidan’s common rulers, declare war, peace opportunity; females had Cult of Domesticity, corsets, Feminine Mystique, NOW AMERICA 8. Polyandry 9. Monogamy access to schools, education rise of feminism but problem of glass ceiling 10. Extended Family Olmec, Mayan, Andean Aztec, Inca: strict Colonial society mirrored Machismo, patriarchy are Women in revolutionary LATIN 11. Nuclear Family societies patriarchal; women patriarchy; women were to Iberian social norms, upper strong; late period sees rise movements; mid-century AMERICA roles at home, cloth making, make cloth, run markets, class women had rights but of public education for girls, enter work force, acquire some roll in market places tend home, rear warriors restrictions; Indian, African some public economic roles vote; late century enter societies patriarchal as industrialization occurs politics, elected to office Famous Women and Identifications
Ancient Period Classical Post-Classical Early Modern Modern Contemporary REGIONS to 1200 BCE 1200 BCE To 600 CE 600 – 1450 CE 1450 – 1750 CE 1750 – 1914 CE 1914 - Present Goddess Ishtar Mary, Mother of Jesus Khadija Hurem Sultan Roxolana Bahitat al-Badiya SOUTHWEST ASIA Semiramis Zenobia of Palmyra Chabi Golda Meir Nomadic women “Jezebel” Shagrat al-Durr Zainab al-Ghazali CENTRAL ASIA Esther Jinnah Sadat Ruth
Isis Hatshepshut Queen Nzinga Wangari Maathai NORTH AFRICA Queen Nefertiti Winnie Mandela Cleopatra SUB-SAHARAN Queen Amanitere AFRICA Mwana Mkisi
Ban Zhao Empress Wu Dowager Empress Cixi Soong Sisters EAST Amaterasu Lady Murasaki Yoshiya Nobuko Matrieya Buddha Sei Shonagon Jiang Qing ASIA Queen Sondok Yang Guifei Xue Xinran
Mother Goddess Sita, Parvati, Kali, Dhruga Mira Bai Pandita Ramabai Indira Gandhi SOUTH Buddhist nuns Nur Jahan Benazir al Bhutto Mother Theresa ASIA
Trung Sisters Pwa Saw Raden Adjeng Kartini Corazon Aquino SOUTHEAST Aung San Suu Kyi Megawati Sukarnoputri ASIA
Mother Goddess St. Monica Virgin Mary Margaret of Navarre Madame de Stael Margaret Thatcher WESTERN Venus figures St. Helena Eleanor of Aquitaine Queen Elizabeth Queen Victoria Simone de Beauvoir Catholic nuns & abbesses Hildegaard von Bingen Isabella of Spain Emily Pankhurst EUROPE Heloise St. Theresa of Avila Marie Curie St. Catherine of Siena Artemisia Gentileschi Florence Nightingale Christine of Pisan Olympe do Gouges Mother Goddess Athena Empress Theodora Regent Sophie Empress Maria Theresa Alexadnra Kollontai EASTERN Antigone Empress Irene Empress Elizabeth Catherine the Great Nadezhda Krupskaya MEDITERRANEAN Pythia of Delphi Empress Zoe Hypatia of Alexandria Anna Comnena EASTERN EUROPE Olga of Kiev
Iroquois women Harriet Tubman Amelia Earhart ANGLO Frontier, settler women Harriet Beecher Stowe Eleanor Roosevelt Dolly Madison Betty Freidan NORTH AMERICA Clara Barton Oprah Winfrey Susan B. Anthony “Rosie the Rivieter” Margaret Mead Sor Juana Ines de la Cruz Princesa Isabel of Brazil Frida Kahlo LATIN Eva Peron AMERICA Isabel Peron Violeta Chamorro Rigoberta Menchu